56 Predictive Factors Correlating With Pathologic Complete Response Rates in Racially Diverse, Minority Populations Receiving Neoadjuvant Therapy for HR+/HER2– Breast Cancer
Background
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and neoadjuvant endocrine therapy (NET) have become mainstays in the treatment of estrogen receptor–positive (ER+)/HER2-negative (HER2-) breast cancer, though most trials have lacked sufficient representation of minority populations. We sought to evaluate predictive factors that correlate with achieving breast and nodal pathologic complete response (pCR) in node-positive, ER+/HER2- breast cancer within a diverse, multiracial patient population.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective chart review on patients with ER+/HER2-, node-positive breast cancer receiving NAC and surgery at a single institution in the Bronx, a highly diverse county (56% Hispanic, 30% Black, 10% White, 4% Other). We did a comprehensive chart review on patients who were diagnosed between July 2016 and May 2022 to assess variables that may correlate with patient outcomes (eg, age, menopausal status, race).
Results
Chemotherapy Type and Patient Disposition Relating to Outcomes
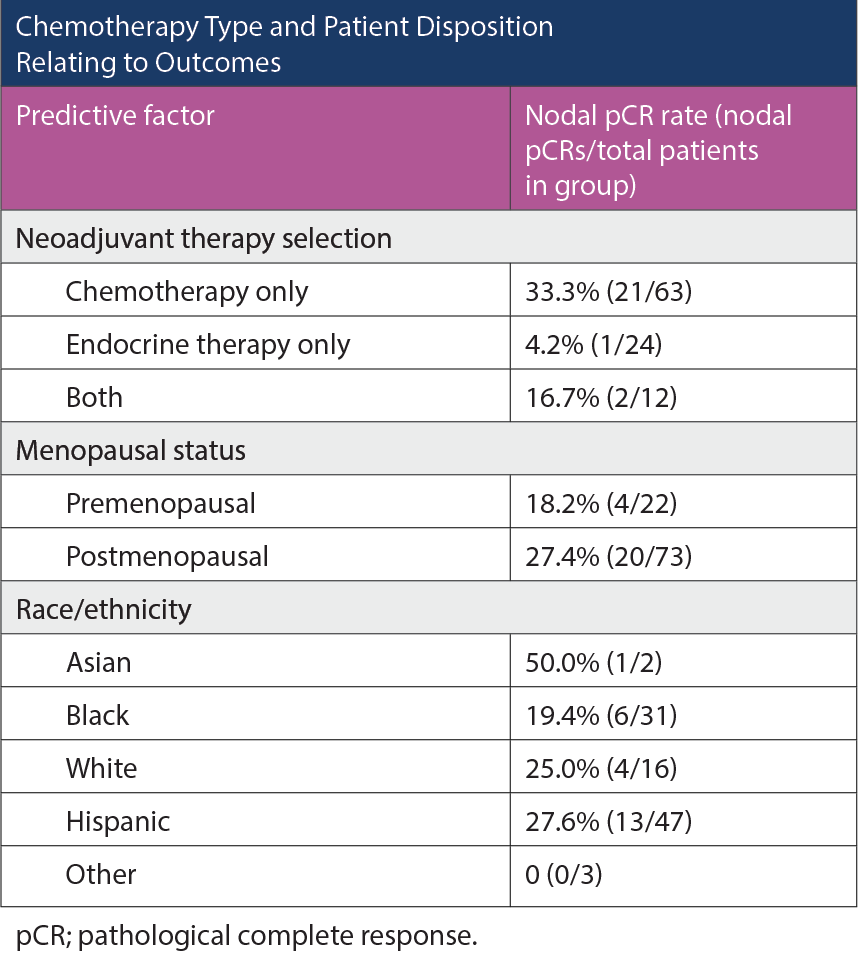
There were 99 patients in this retrospective cohort, with a median age at diagnosis of 59.5 years. There were 22 premenopausal patients, 73 postmenopausal patients, and 4 male patients. Forty-seven (47.5%) patients were Hispanic, 31 (31.3%) Black, 16 (16.2%) White, 2 (2.0%) Asian, and 3 (3.0%) other. Sixty-three patients received NAC, 24 had NET, and 12 had both. Limited testing for proliferative parameters was observed in this population, with oncotype and Ki-67 only available for 9 (9.1%) and 21 (21.2%) of the patients, respectively. Twenty-four (24.2%) patients achieved a nodal pCR and 8 (8.1%) patients achieved a breast pCR. There were no statistically significant differences between nodal pCR rates when patients were stratified by race: 27.6% of Hispanic, 19.4% of Black, 25.0% of White, and 50% of Asian patients achieved a nodal pCR. NAC was superior to NET in achieving nodal pCRs (P = .002) across patient subgroups, including postmenopausal women (P = .006).
Conclusions
In this diverse cohort, nodal pCRs were achieved equally among races, with NAC more effective than NET regardless of menopausal status. Larger studies assessing the predictiveness of proliferative parameters such as Ki-67 and oncotype in minority groups are needed.

Advancing Thoracic Surgery With Robotics and Video-Assisted Strategies
June 13th 2024"Anything that you can do to leverage technology to minimize the variability in surgery eliminates the skill gap so that novice surgeons may become as technically gifted as the intermediate surgeon or the master surgeon."