
CancerNetwork® spoke with Albert H. Kim, MD, PhD, about a new Brain Tumor Center at Siteman, for which he is the inaugural director.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


CancerNetwork® spoke with Albert H. Kim, MD, PhD, about a new Brain Tumor Center at Siteman, for which he is the inaugural director.

A durable clinical benefit was seen from the dual inhibition of the MAPK pathway using BRAF and MEK inhibitors dabrafenib and trametinib, respectively, to treat patients with BRAF V600E mutant low- and high-grade glioma.

Germline variants in cancer predisposition genes were associated with worse event-free and overall survival in patients with neuroblastoma.

ERC-USA announced that the FDA recommended the early termination of a phase 2 clinical trial of ERC1671 to treat patients with recurrent or progressive glioblastoma and pursue a randomized confirmatory phase 3 trial.
The FDA granted fast track designation to paxalisib for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with unmethylated O6-Methylguaninemethyltransferase promoter status who have completed initial radiation with concomitant temozolomide.
Though the combination of bevacizumab and trebananib was found to be well tolerated, it did not significantly improve survival outcomes for patients with recurrent glioblastoma over bevacizumab alone.

A population-based analysis found that racial and ethnic disparities in childhood central nervous system tumor survival seem to have their roots at least partially in post-diagnosis factors, possibly due to the lack of access to high quality care, leading to poorer overall outcomes.

The biologics license application was supported by findings from a global, randomized, controlled phase III clinical trial, evaluating the efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of MYL-1402O versus bevacizumab.
The key to predicting when liquid biopsy would produce clinically actionable information is the ability to image the blood brain barrier and macrophages, according to researchers.

The results presented in this study indicated that neurosurgeons may need to change how they approach tumor removal and, when safe, include non-contrast-enhancing tumor during resection to achieve maximal resection.

These results could present an opportunity to broaden inclusion criteria on clinical trials and intensify chemoradiotherapy treatments.
A perioperative study confirmed brain penetrance and robust biomarker suppression in patients with low-grade glioma with an IDH1 mutation.
Using RNA sequencing for individual pediatric cancer cases could more effectively target gene expression in tumors.
Researchers recently looked at differences in survival time between patients with grade II and grade III spinal meningioma.
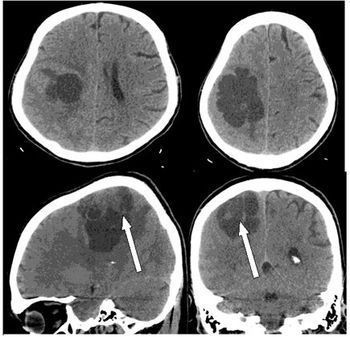
There could be a new way to diagnose brain tumors earlier.
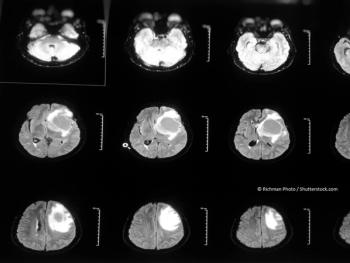
Investigators assessed effects of TIB on cell number, migration, invasion, estrogen, and progesterone receptor activity and content.
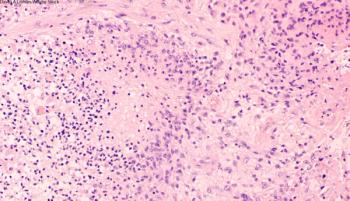
A new study offers hope in predicting glioblastoma responses to chemotherapy, radiation, and combination therapy.

Cancer Network spoke with Rimas V. Lukas, MD, of Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, about the combination of controlled interleukin-12 with a PD-1 inhibitor in recurrent glioblastoma.

Cancer Network spoke with Dr. Shulin Li about his team’s research on the role of the FGL2 protein in glioblastoma immune evasion and tumor progression.
This review focuses on clinical developments and management of newly diagnosed glioblastoma, and includes a discussion about the incorporation of molecular features into the classification of this disease.

Dr. James Perry speaks with Cancer Network about glioma therapy options and the future of brain cancer treatment.
New research published in Neuro-Oncology examines the controversial link between intracranial volume and high-grade glioma.

MRI-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy appears to be safe and effective for glioblastomas and may add an average of 2 months to life expectancy.
Researchers report that the same driving force that makes Zika so detrimental to unborn babies gives it promise as a cancer treatment.
A noncontrolled phase I study in recurrent metastatic glioblastoma showed 3-year survival was five times higher in patients treated with intratumoral PVSRIPO.