
More than one-third of patients with metastatic uveal melanoma had objective tumor regression when treated with adoptive transfer of autologous tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


More than one-third of patients with metastatic uveal melanoma had objective tumor regression when treated with adoptive transfer of autologous tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.

Researchers in Seattle are now reporting success with a biopolymer synthetic scaffold loaded with cancer-fighting T cells and a mix of nutrients to potentially combat solid tumors.

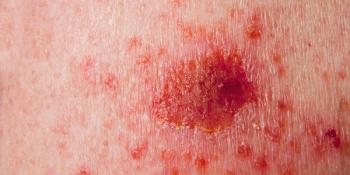
A study has identified several characteristics that can help detect seborrheic keratosis–like melanomas using dermoscopy, which can help to diagnose melanoma.

A nivolumab/ipilimumab combination significantly improved overall survival for advanced melanoma patients.

This video examines phase II results of a single-arm trial that tested checkpoint inhibition plus the IDO–pathway inhibitor indoximod in patients with melanoma.

The combination of an intratumoral injection of CVA21 and ipilimumab has demonstrated durable response with minimal toxicity in patients with advanced melanoma.

The FDA on March 23, 2017, granted accelerated approval to avelumab (Bavencio) for the treatment of adults and pediatric patients 12 years and older with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma.

Penn State College of Medicine researchers have discovered a new class of drugs that may keep a deadly form of skin cancer from becoming resistant to treatment.

The MEK inhibitor binimetinib improved progression-free survival compared with dacarbazine in patients with NRAS-mutant melanoma, according to the results of the NEMO trial.

Although long-term melanoma survivors were more likely to report healthier levels of ultraviolet radiation exposure and sun protection behaviors than controls, some still reported indoor tanning or intentionally seeking sun to tan.
Treatment of keratinocyte carcinomas such as basal cell carcinoma and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma with PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors and targeted agents warrant further investigation, according to recently published studies.

Investigators at the University of California, Irvine report that they have uncovered a specific mutation in the ATR gene that allows melanoma tumor cells to remain undetected by the immune system.

The identification of ugly duckling nevi using a whole-body skin examination for intrapatient comparative analysis improves accuracy of melanoma detection.

The immunotherapy pembrolizumab was active in patients with advanced mucosal melanoma enrolled in a series of the KEYNOTE clinical trials, according to data presented at the European Cancer Congress 2017.

Dietary fat intake might promote the growth of melanoma tumors harboring BRAF V600E mutations, and lipid-lowering drugs can slow that growth, according to a mouse study.

A multicenter study showed that an occurrence of posttransplant skin cancer was common among a group of organ transplant recipients.

Participation in a training program increased levels of self-confidence for both patients and their partners in performing skin self-examinations to detect melanoma.

There is a lot of interest in a new treatment that kills approximately 90% of melanoma cancer cells, an astounding accomplishment for Richard Neubig, MD, PhD, who serves as chairperson of pharmacology toxicology at Michigan State University.

Canadian researchers might have discovered why melanoma is more aggressive in men than women: decreased expression of a melanoma tumor suppressor gene on the sex chromosomes.
Effective systemic therapy for the treatment of stage III melanoma has emerged. Whether this influences treatment choice in stage III melanoma patients with in-transit metastases is the subject of this review.

In the recent era of effective systemic therapies for melanoma, the provocative question of whether isolated limb perfusion still plays a role in the treatment of patients with in-transit melanoma metastases is timely and relevant.

Scientists have found a way to detect earlier if Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is recurring in patients. They have published a paper in the journal Cancer demonstrating how an immune system marker may be able to outperform and supplement imaging studies for recurrence of MCC.

Reducing the use of indoor tanning by enforcing an age restriction could potentially reduce melanoma incidence, mortality, and the costs associated with treating the disease, according to results of an economic analysis.

Researchers have identified characteristics associated with improved outcomes when treating BRAF-mutated advanced melanoma with the combination of dabrafenib and trametinib.

An individual’s clinical risk factors could help guide skin cancer screening and identify those at high risk for melanoma who could benefit from increased surveillance.