
Inflammatory arthritis and sicca syndrome appear to be immune-related adverse events among some patients undergoing cancer treatment with the immune checkpoint inhibitors nivolumab and ipilimumab.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Inflammatory arthritis and sicca syndrome appear to be immune-related adverse events among some patients undergoing cancer treatment with the immune checkpoint inhibitors nivolumab and ipilimumab.

In this video we discuss 3-year overall survival data from the KEYNOTE-001 trial, which studied the anti��–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab in patients with advanced melanoma.

The MEK inhibitor binimetinib resulted in improved progression-free survival and response rates vs dacarbazine in patients with NRAS-mutated metastatic melanoma.
A combination of the checkpoint inhibitors nivolumab and ipilimumab continues to demonstrate superior clinical activity vs ipilimumab monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with advanced melanoma.

Trametinib, which is approved by the FDA for melanoma and other cancers, may block viral infection by stopping Merkel cell polyomavirus transcription and replication.

Details of a first-in-human case report showed that a patient with melanoma was able to achieve a durable complete response with the combination of two types of immunotherapy.

The UV radiation resistance-associated tumor suppressor gene coordinates DNA repair and might predict skin cancer risk, according to research published in the journal Molecular Cell.

It now turns out that Bim, a downstream signaling molecule of the PD-1 pathway, may hold the clue to which patients may be successful on immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma.

Adding total body irradiation to chemotherapy prior to the adoptive cell transfer of TILs had no effect on tumor regression in patients with metastatic melanoma.

Treatment with the anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab yielded good long-term survival outcomes in a phase Ib trial of patients with advanced melanoma.

Through the emergence of new immunotherapies, treatment of melanoma is undergoing a long-awaited revolution. Ongoing research will clarify the outlines of the place that intralesional therapies will occupy in the therapeutic armamentarium in the years ahead.

Perhaps the greatest attraction and chief benefit of intratumoral therapies is their ability to synergize with systemic checkpoint therapies and accelerate the development of a lymphoid infiltrate and perhaps secondary lymphoid structures in vivo, which in turn can result in systemic mobilization of a T-cell response: the local injection–global effect model.

Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) may provide an unlimited number of phenotypically defined, functional and expandable autologous antigen-specific T cells with the characteristics needed to combat cancer.

A recent trial found no survival difference in patients with melanoma with a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy who underwent complete lymph node dissection compared with those who did not undergo dissection. However, the trial failed to achieve the required number of events and is, therefore, underpowered.
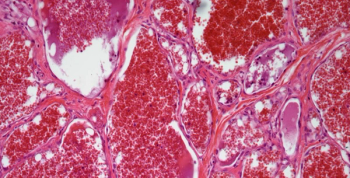
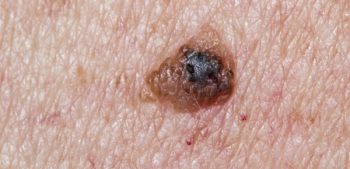
A 37-year old man presents with a bluish lesion in the right arm. After further assessment, a biopsy is performed. What is your diagnosis?

Patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma treated with pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck) as a first-line therapy had durable responses in a phase II clinical trial.

More than one-third of patients with advanced melanoma were still alive 5 years after starting treatment with the anti-PD-1 immunotherapy nivolumab, according to long-term phase I data.

A new study has shown that algorithms of dermoscopic criteria used to detect melanoma had only modest levels of accuracy and lacked interobserver agreement among a group of regular dermoscopy users.

Researchers at the University of Colorado Cancer have created a new tool that will help oncologists match the right therapy to cancer type based on the patient's genetic data.

People who are carriers of two variants of MC1R, a gene that regulates pigmentation, were at increased risk for melanoma regardless of previous UV radiation exposure.

In patients with melanoma, lower vitamin D levels were associated with poorer survival outcomes, according to a prospective study, independent of C-reactive protein levels.
The number of moles, or nevi, a patient had was not related to the likelihood that they had melanoma, according to the results of a new study.
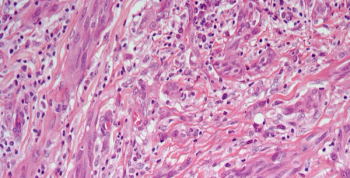
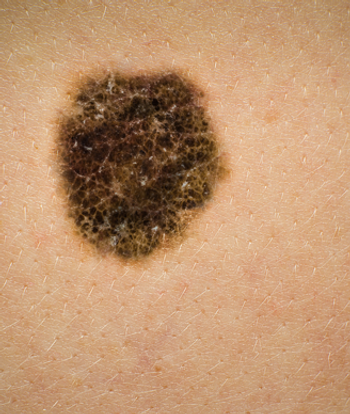
A 90-year-old woman presents with a lesion in the right forearm. After further assessment, a biopsy is performed. What is your diagnosis?

The combination of TriMixDC-MEL and ipilimumab produced durable tumor responses in patients with pretreated advanced melanoma, according to a phase II study.

In light of the recent announcement by Vice President Joe Biden to infuse the US cancer research program with $1 billion, a so-called “Moon Shot” program, we are speaking today with Giulio Draetta, a clinician and cancer researcher at MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas in Houston, who leads that center’s Moon Shots program.