53 The Utility of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in High-Grade Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Background
The upstage rate of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) to invasive carcinoma on final pathology is variable, with rates up to 43.6%. Current guidelines recommend sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) in patients with DCIS with factors for infiltration and in patients undergoing mastectomy. This study aims to assess the utility of SLNB in high-grade DCIS by examining the rate of tumor upstaging, SLNB, and positive lymph nodes.
Methods
A retrospective review was performed of patients at our institution who were diagnosed with high-grade DCIS between 2001 and 2023 and who underwent surgical intervention. Data collected for each patient included demographic factors, clinical factors, biopsy pathology, clinical stage, surgical operation, surgical pathology, pathologic stage, and complications including recurrence and lymphedema. Primary end points were the rate of upstaging to invasive carcinoma, rate of performing SLNB, and rate of sentinel lymph node positivity. Patient characteristics were summarized by mean and standard deviation for continuous variables and by frequency and percentages for categorical variables. Differences between characteristics were assessed by Student t test for continuous variables and Fisher exact tests for categorical variables. Statistical tests were 2-sided with a significance level set at P < .05.
Results
Upstaging, SLNB, and Positive Lymph Node in Patients With High-Grade DCIS (n = 217)
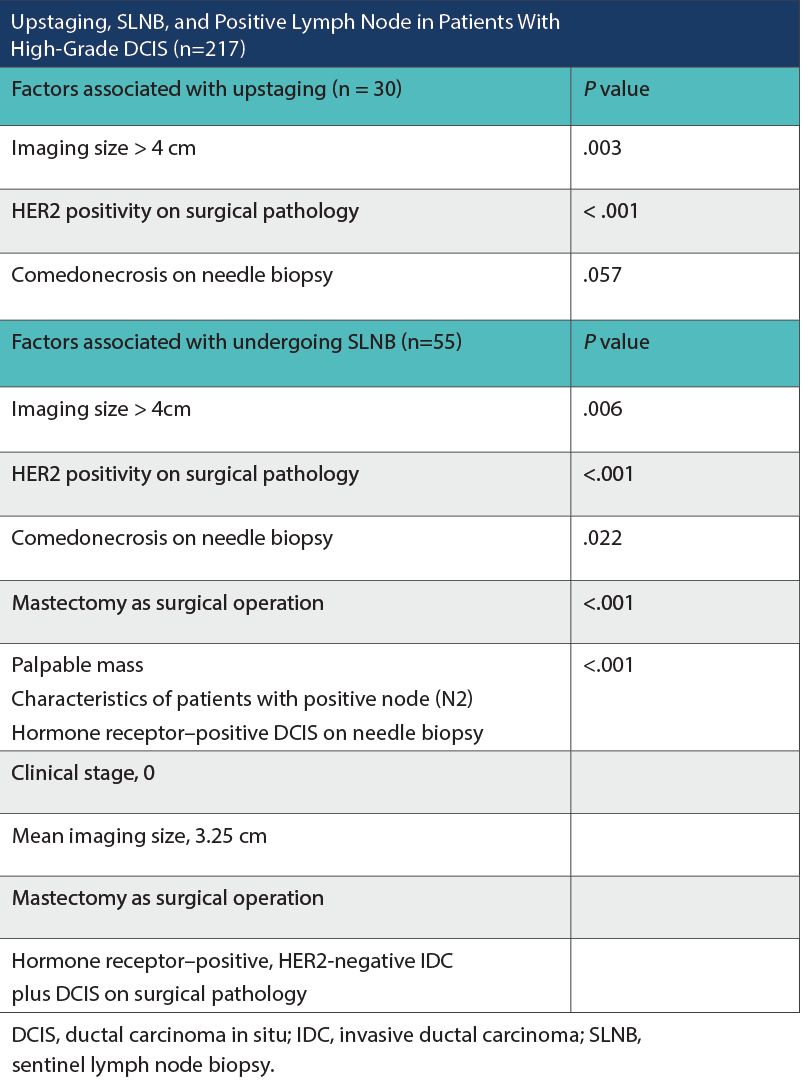
Two hundred and seventeen patients were analyzed. Thirty patients (13.8%) upstaged on final pathologic assessment. Twenty-seven patients upstaged to pathologic stage IA and 3 patients to stage IIA. Factors associated with upstaging included imaging size greater than 4 cm (P = .003) and surgical pathology indicating HER2 positivity (P < .001). Comedonecrosis on needle biopsy, as a predictor of upstaging, approached but did not meet statistical significance (P = .057). Fifty-five patients (25.3%) underwent SLNB. Notable factors associated with undergoing SLNB included comedonecrosis on needle biopsy (P = .022), palpable mass (P < .001), imaging size greater than 4 cm (P = .006), surgical pathology indicating HER2 positivity (P <.001), and mastectomy as the surgical operation (P < .001). Two patients (3.6%) who underwent SLNB had a positive lymph node. Both of these patients’ core needle biopsies demonstrated estrogen and progesterone receptor–positive DCIS, clinical stage 0, with a mean imaging size of 3.25 cm. Neither had a palpable mass. Both patients underwent mastectomy with final pathology showing hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative invasive ductal carcinoma along with DCIS. Of the 24 patients with core needle biopsies demonstrating microinvasive disease, none had positive sentinel lymph nodes. No axillary recurrences or lymphedema were observed.
Conclusions
The overall rate of upstaging in this study was relatively low at 13.8%. Of the 55 patients who underwent SLNB, 2 patients (3.6%) had a positive lymph node. In both patients with a positive node, the SLNB was performed in the setting of mastectomy. While the vast majority of lumpectomy patients completed a radiation therapy protocol, no axillary recurrences were observed. Given these findings, surgeons should consider the value of the SLNB in patients with high-grade DCIS undergoing lumpectomy and counsel patients as to the risks vs benefits. Assessing clinicopathologic factors may assist surgeons in counseling patients regarding the risk of upstaging and the necessity of up-front SLNB.

Newsletter
Stay up to date on recent advances in the multidisciplinary approach to cancer.