54 The Evaluation of Expression Levels of CXCR4, CXCL12, and LASP1 Genes in Peripheral Blood Samples of Breast Cancer Patients
Background
In 2018, more than 22,000 new cases of breast cancer were reported in Turkey. Breast cancer, like many other cancer types, is associated with the activation and overexpression of CXCR4. This overexpression is linked to factors such as tumor growth, the angiogenesis process, increased metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. It has been noted that CXCL12, a specific ligand for CXCR4, plays a significant role in tumorigenesis processes, including survival, migration, and microenvironmental interactions. Similarly, the increased expression of LASP1, an adaptor protein binding to CXCR4, is associated with various tumor types and correlated with factors such as proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. In recent years, the CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling pathway has been discovered to have a significant impact on the development and progression of breast cancer. This signaling pathway regulates numerous events in cancer cells, such as proliferation, motility, and metastasis. Additionally, the CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway contributes to creating a favorable microenvironment for tumors by affecting immune and stromal cells. Therefore, molecules within the CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling pathway hold the potential to determine the prognosis of breast cancer, monitor treatment, and serve as therapeutic agents in breast cancer treatment.
Methods
The research at the Istanbul University Institute of Oncology obtained ethical approval from the Istanbul Faculty of Medicine Ethics Committee on March 26, 2023. Genetic materials from
300 patients with breast cancer and 150 control subjects underwent standard testing and were matched based on crucial parameters. Lymphocyte RNA was isolated after obtaining consent, utilizing Ficoll density gradient centrifugation. Total RNA extraction was performed using the Quick-RNA™ MiniPrep Kit, followed by cDNA synthesis using RevertAid Reverse Transcriptase. Real-time PCR was carried out using the Mic qPCR Cycler and statistically analyzed using GraphPad’s Prism (P < .05). Categorical variables in the study are presented in numbers and percentages for descriptive statistics, while quantitative variables are expressed as mean, standard deviation, median, minimum, and maximum values. The normal distribution of quantitative variables was assessed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The comparison of means between 2 independent groups was conducted using the Mann-Whitney U test. For comparisons involving more than 2 independent groups, the Kruskal-Wallis test was used, followed by post hoc pairwise comparisons employing the Dunn test. Calculations were performed using the IBM (Version 26.0, Armonk, NY: IBM Corp) software package, with a significance level set at 0.05.
Results
Comparative Analysis of Gene Expression Levels: LASP1, CXC12, and CXCR4 Statistics
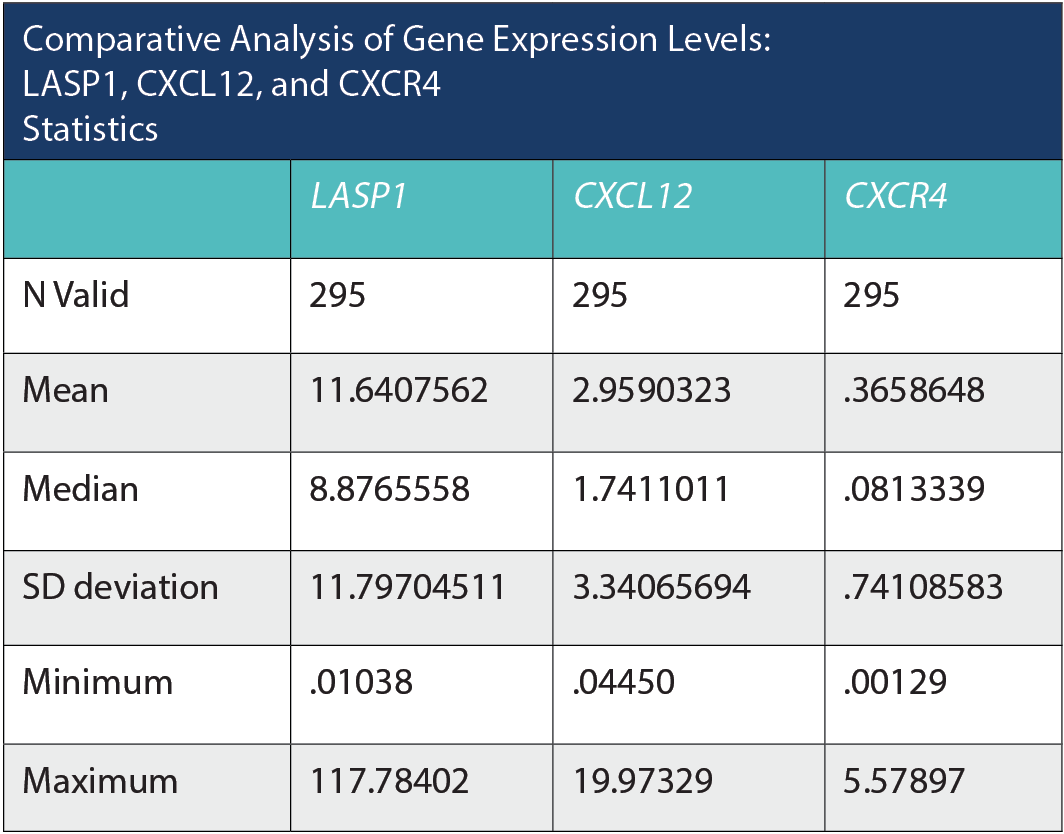
Based on the provided statistics, we can observe variations in the mean, median, and standard deviation among the 3 genes: LASP1, CXCL12, and CXCR4. LASP1 exhibits the highest mean expression level at 11.64, with a relatively large standard deviation of 11.80, suggesting a considerable spread in the data. The median value for LASP1 is 8.88, indicating that there might be some extreme values on the higher end of the distribution. The range for LASP1 is substantial, with a minimum value of 0.01 and a maximum of 117.78. In contrast, CXCL12 has a much lower mean expression level at 2.96 and a lower standard deviation of 3.34, indicating a tighter clustering of data around the mean. The median value for CXCL12 is 1.74, and the range spans from a minimum of 0.04 to a maximum of 19.97. Finally, CXCR4 exhibits the lowest mean expression level at 0.37, with a standard deviation of 0.74. The median value for CXCR4 is 0.08, and the range extends from a minimum of 0.001 to a maximum of 5.58. These statistics suggest that LASP1 has a wider range and higher variability in its expression levels compared to CXCL12 and CXCR4, which display lower means and tighter distributions. The differences in gene expression levels could have significant implications in the context of the study or analysis being conducted.
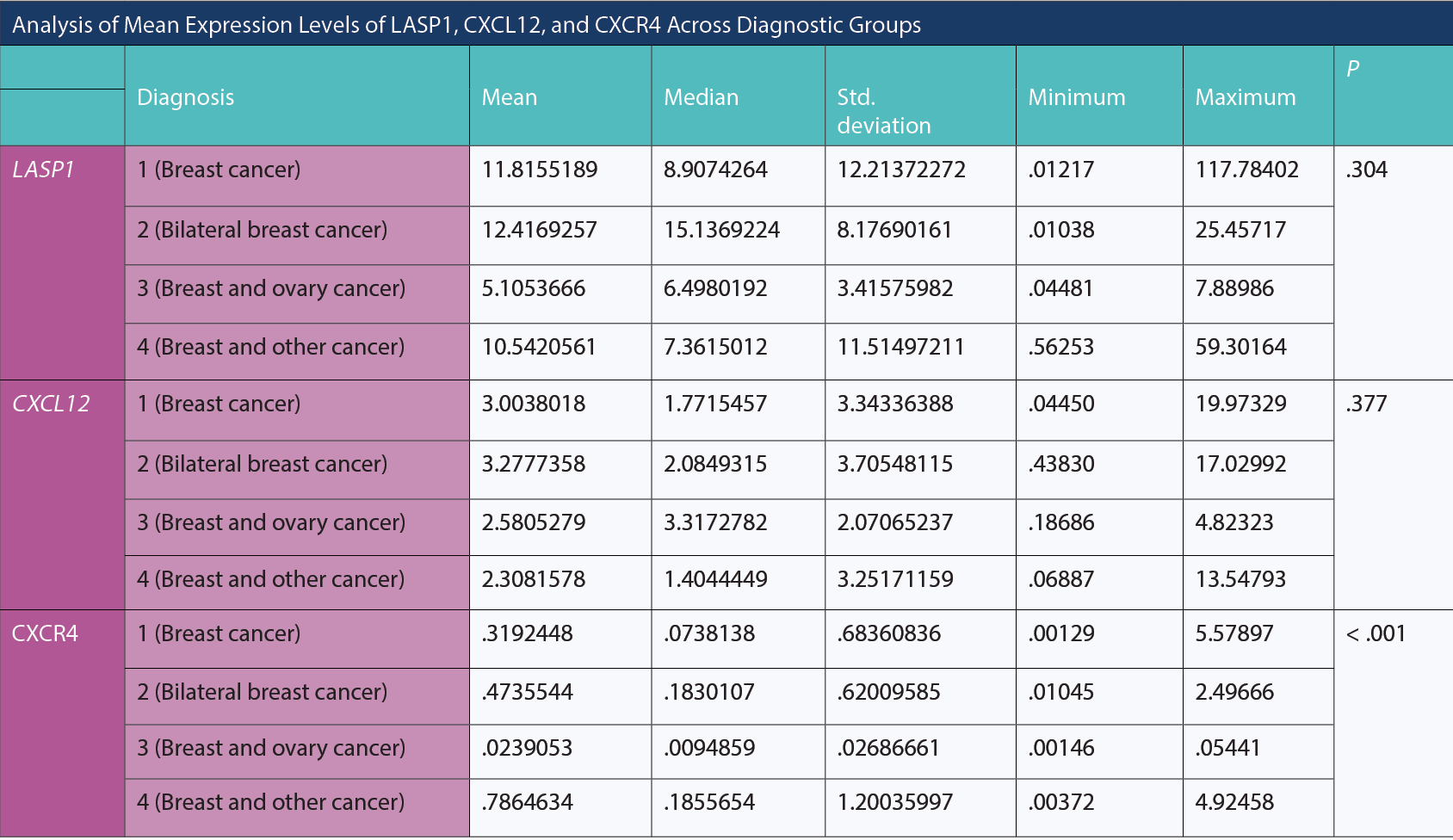
The table below examines whether there are significant differences in the means of LASP1, CXCL12, and CXCR4 among diagnosis groups, providing descriptive statistics and P values. Upon reviewing the table, no significant differences were observed among diagnosis groups in terms of mean LASP1 and CXCL12 (P = .304; P = .377, respectively). However, there was a statistically significant difference among diagnosis groups in terms of mean CXCR4 (P < .001). Upon detailed analysis of the differences, for CXCR4, the mean of diagnosis group 3 was significantly lower than groups 1, 2, and 4 (P = .046; P = .005; P = .002, respectively). The mean of group 1 for CXCR4 was significantly lower than groups 2 and 4 (P = .026; P = .002, respectively). There was no statistically significant difference between diagnosis groups 2 and 4 in terms of mean CXCR4 (P = .565).
Analysis of Mean Expression Levels of LASP1, CXC12, and CXCR4 Across Diagnostic Groups
Conclusions
The analysis of gene expression levels across diagnostic groups—LASP1, CXCL12, and CXCR4—reveals noteworthy findings. While no significant differences were observed in the mean expression levels of LASP1 and CXCL12 among the diagnostic groups, a statistically significant variance was evident in the mean expression of CXCR4. Specifically, the CXCR4 mean expression in diagnostic group 3 was significantly lower compared to groups 1, 2, and 4. Furthermore, group 1 exhibited significantly lower CXCR4 mean expression levels in contrast to groups 2 and 4. Notably, the comparison between diagnostic groups 2 and 4 showed no statistically significant difference in CXCR4 mean expression. These findings suggest a differential expression pattern in CXCR4 across distinct diagnostic groups, implying potential relevance in diagnostic categorization and underlying molecular pathways in the context of the studied condition. Understanding the disparities in CXCR4 expression among these diagnostic groups could be critical in unraveling the molecular intricacies influencing disease progression and treatment responses.

Newsletter
Stay up to date on recent advances in the multidisciplinary approach to cancer.
The Proper Ways to Identify and Use ADCs in Breast Cancer Subtypes
June 29th 2025Deciding when to use immunotherapy and how to utilize antibody-drug conjugates are complicated processes that require multidisciplinary collaboration to ensure that all patients with breast cancer receive appropriate and efficient care.
Cardio-Oncology Considerations for Breast Cancer: Risk Stratification, Monitoring, and Treatment
June 26th 2025Survivors of breast cancer face increased cardiovascular risks due to treatment-related cardiotoxicity, and understanding these risks is crucial for effective management and prevention.