- ONCOLOGY Vol 23 No 10
- Volume 23
- Issue 10
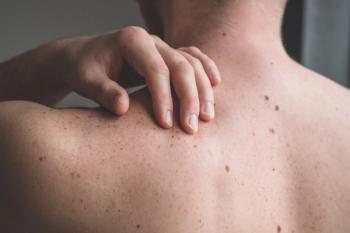
Study Links Virus to Some Cases of Common Skin Cancer
A virus discovered last year in a rare form of skin cancer has also been found in people with the second most common form of skin cancer among Americans, according to researchers at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center–James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute. Their findings were published online June 25, 2009, by the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
A virus discovered last year in a rare form of skin cancer has also been found in people with the second most common form of skin cancer among Americans, according to researchers at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center–James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute. Their findings were published online June 25, 2009, by the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
The researchers examined tissue samples from 58 people with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), a highly curable form of skin cancer that is expected to affect more than 200,000 Americans this year.
They identified the virus in more than one-third of the patients and in 15% of the tumors tested. In addition, all of the virus found in tumor cells had a mutation that could enable the viral DNA to integrate into the DNA of the host cell.
“This is indirect evidence that the virus might play a role in causing some cases of squamous cell carcinoma,” says principal investigator Amanda E. Toland, PhD, assistant professor of molecular virology, immunology and medical genetics and a researcher with the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center–James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute.
The virus was first discovered in patients with Merkel cell carcinoma, a rare, aggressive skin cancer that occurs mainly in the elderly and people with a suppressed immune system. The people in the new study all had a healthy immune system.
“Originally it was thought that this virus caused only this rare skin cancer, but our findings indicate that it is a lot more prevalent than we initially thought,” said Dr. Toland.
More Than One-Third Tested Positive
The investigators detected the virus in 26 of 177 SCC samples, 11 of 63 adjacent-skin samples, and 1 sample from a mouthwash. They found no viral DNA in any of the blood samples from 57 patients. In all, 21 of 58 SCC patients, or 36%, tested positive for the virus.
By sequencing the viral DNA from 31 normal and tumor samples, the researchers showed that the same mutation was present in all the viruses tested from tumors, and in 60% of the viruses tested from adjacent healthy-looking tissue.
“That suggests that the virus may develop a mutation that causes it to integrate into host-cell DNA, and, therefore, may play a role in causing the cancer,” said Dr. Toland.
Articles in this issue
over 16 years ago
Radical Prostatectomy Reigns Supremeover 16 years ago
Gingerover 16 years ago
More Questions About Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Lung Cancerover 16 years ago
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Resectable Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancerover 16 years ago
FDA Approves First Maintenance Drug Therapy for Advanced Lung Cancerover 16 years ago
Accelerated Approval Granted for Bevacizumab in Glioblastomaover 16 years ago
New Opioid Pain Reliever Approved With Required Risk-Reduction Planover 16 years ago
FDA Extends Review of OfatumumabNewsletter
Stay up to date on recent advances in the multidisciplinary approach to cancer.