Articles by Philip J. Bierman, MD
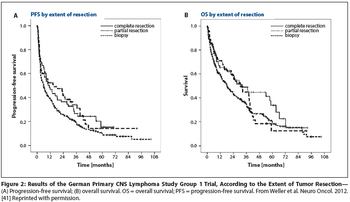
Relatively few patients with primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (PCNSL) will have tumors that are amenable to resection. In the absence of the highest quality data, at least it is good to know that in the modern era, patients with PCNSL are probably not harmed by judicious tumor resection.

Radiation therapy has an essential role for certain patients with DLBCL. It is hoped that ongoing and future trials will identify the patients who will benefit from this treatment and those for whom it is unnecessary.

Drs. Hernandez-Ilizaliturri and Czuczman should be complimented on their comprehensive review of management options for patients with relapsed and refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).

Adult Burkitt Lymphoma: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment
ByIbrahim T. Aldoss, MD,Dennis D. Weisenburger, MD,Kai Fu, MD, PhD,Wing C. Chan, MD,Julie M. Vose, MD, MBA,Philip J. Bierman, MD,R. Gregory Bociek, MD, MSc,James O. Armitage, MD Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is a unique B-cell lymphoma characterized by a high proliferation rate and cytogenetic changes related to c-myc proto-oncogene overexpression. Burkitt lymphoma is a highly aggressive B-cell lymphoma that is most frequently seen in children and young adults in endemic areas.

The past 20 years have brought significant advances in our ability to manage patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. More precise classification systems, improvements in diagnosis and staging, and effective new treatments have improved outcomes and made cure a reasonable goal for many patients with these disorders.

Follicular Lymphoma: Expanding Therapeutic Options
ByApar Kishor Ganti, MD, MS,R. Gregory Bociek, MD, MSc,Philip J. Bierman, MD,Charles A. Enke, MD,Julie M. Vose, MD, MBA,James O. Armitage, MD The most common indolent lymphoma, follicular lymphoma comprises 35% of adult non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) in the United States and 22% worldwide. Features associated with adverse outcome include age, male gender, disease stage, and performance status, with the International Prognostic Index being the most widely used risk classification system. Long-term disease-free survival is possible in select patient subgroups after treatment, but very late relapses suggest that quiescent lymphoma cells might be harbored for long periods of time. Radiation therapy is the mainstay of treatment for limited-stage follicular lymphoma, but there is some experience with chemotherapy and combined chemoradiation. When to initiate treatment in patients with advanced disease is controversial, but options include various combined chemotherapy regimens, monoclonal antibodies, radiolabeled antibodies, and bone marrow or stem cell transplantation. Future directions in the treatment of follicular lymphoma include vaccines, antisense therapy, and proteasome inhibitors.

The analysis, “Graft Purging inAutologous Bone MarrowTransplantation: A Promise NotQuite Fulfilled,” by Drs. Joseph Alvarnasand Stephen Forman, is verytimely. The authors’ conclusion is succinctlypresented in their title.

Records from 653 patients treated between 1991 and 1998 in the Oncology Practice Patterns Study (OPPS) were analyzed to determine contemporary chemotherapy delivery patterns in patients with intermediate-grade non-

Randomized trials are defining the role of autologous stem-cell transplantation in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL), but there is less experience with this treatment in follicular lymphomas. Approximately 40% to 50% of patients with follicular NHL are in remission 4 to 5 years following autologous stem-cell transplantation. Results from phase II studies and retrospective analyses are remarkably similar, despite differences in patient populations, preparative regimens, use of purging, and source of stem cells. Nevertheless, there is little evidence of a plateau in disease-free survival curves, and we do not know whether patients are cured or overall survival is prolonged. Relapses 9 years following transplantation have been described.[1]

Autologous hematopoietic stem- cell transplantation has become an accepted therapy for some patients with Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Convincing evidence for a graft-vs-lymphoma effect has led to increasing use of allogeneic transplantation in these patients. Dr. Winter has written an excellent overview of transplantation in the lymphomas. She has focused on several areas of controversy and described results of randomized trials.



