|Slideshows|February 25, 2015
Slide Show: Renal Cell Carcinoma
Author(s)OncoTherapy Network Staff
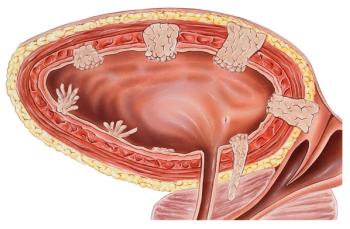
This slide show features various images of papillary, clear cell, chromophobe, and tubulocystic renal cell carcinoma.
Advertisement
Newsletter
Stay up to date on recent advances in the multidisciplinary approach to cancer.
Advertisement
Latest CME
Advertisement
Advertisement
Trending on CancerNetwork
1
Modifiable Risk Factors Suggest Potential for Improving Cancer Prevention
2
2026 Tandem Meetings: What’s the Latest Research in Multiple Myeloma?
3
Dato-DXd Receives Priority Review in Unresectable/Metastatic TNBC
4
Barriers to CAR T-Cell Referral and Center Access in Multiple Myeloma
5