ABSTRACT
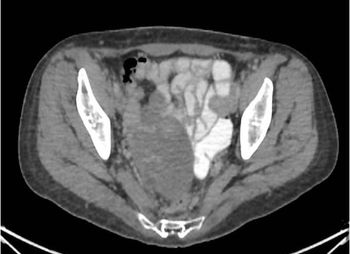
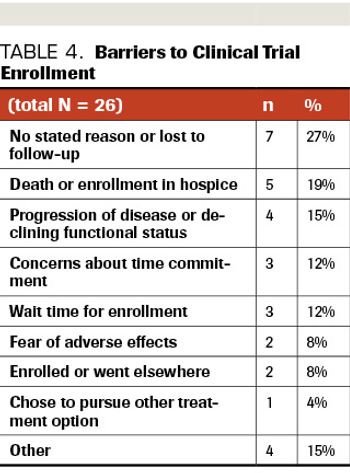
Worldwide incidence and mortality due to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is greatest in the United States, with the initial epicenter in New York. In Nassau County, New York, where we practice, our institution has had more than 2500 cases and has discharged from the hospital more than 1000 patients. As many academic and private institutions have swiftly shifted their clinical and research priorities to address the pandemic, data are emerging regarding both the impact of malignancy on COVID-19 outcomes as well as the challenges faced in assuring that cancer care remains unimpeded. Of concern, recent studies of cancer patients primarily in China and Italy have suggested that advanced malignancy is associated with increased susceptibility to severe COVID-19 infection. At present, more than 500 clinical trials are underway investigating the pathogenesis and treatment of COVID-19, including expanded use of oncology drugs, such as small molecular inhibitors of cytokine pathways. Here, we begin by reviewing the latest understanding of COVID-19 pathophysiology and then focus our attention on the impact of this virus on hematologic and oncologic practice. Finally, we highlight ongoing investigational treatment approaches that are so relevant to the care of oncology patients during this extraordinary pandemic.