43 Impact of Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventing Healing Approach (LYMPHA) on Postoperative Complication Rates in Mastectomy With Immediate Prosthetic-Based Breast Reconstruction
Background
The Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventing Healing Approach (LYMPHA) is a prophylactic microsurgical technique performed at the time of axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) that reduces the rate of developing lymphedema (LE). It is often performed together with immediate implant-based breast reconstruction (IBBR) in patients undergoing mastectomy with ALND. This study aimed to determine whether the additional LYMPHA procedure impacts the surgical outcomes of mastectomy with IBBR.
Methods
Patient Characteristics Across Various Subgroups
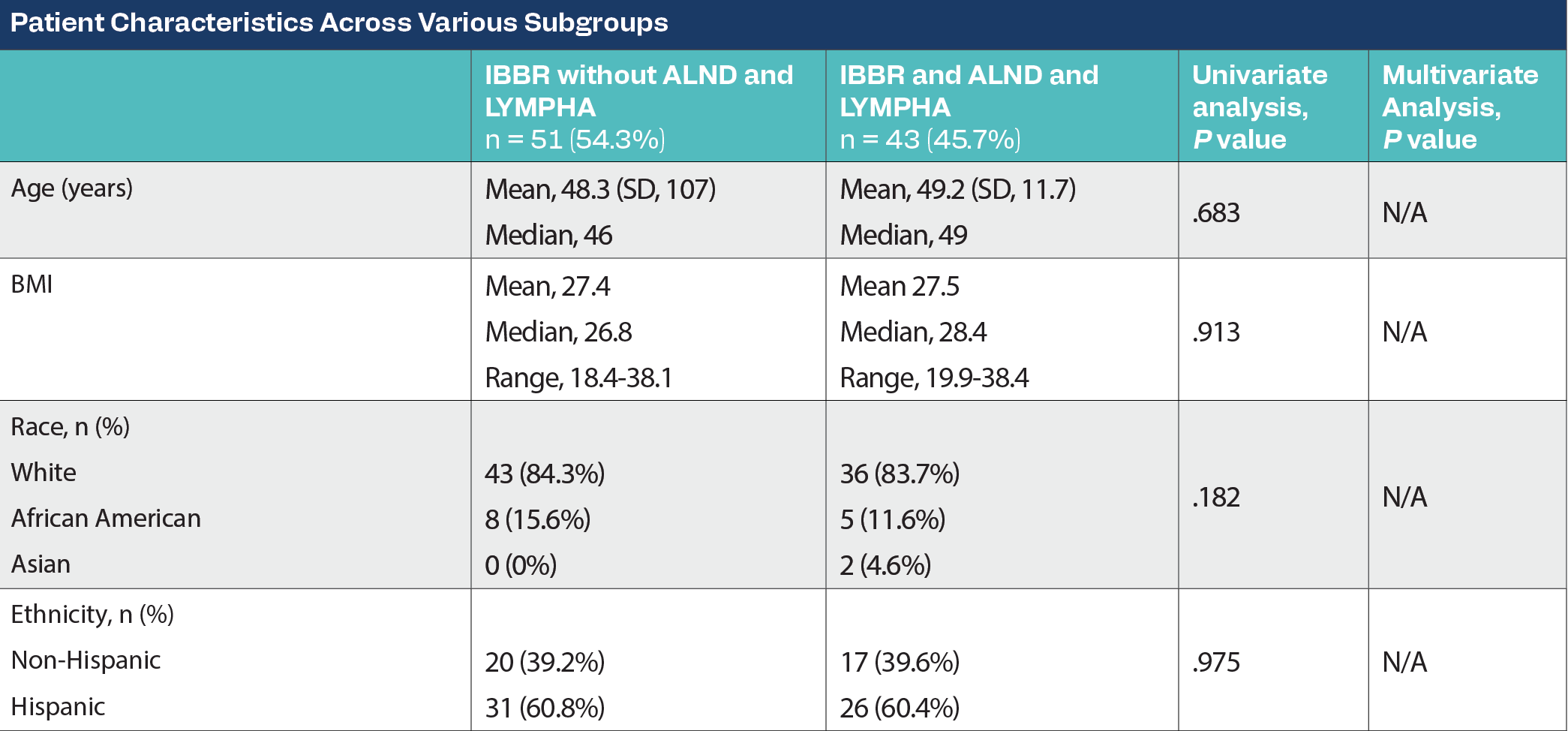
A retrospective cohort study included patients with breast cancer undergoing mastectomy with IBBR (tissue expander [TE] or implant) with and without ALND with LYMPHA between April 2021 and August 2023 at a single institution. Patient demographics, treatment characteristics, and complication rates were collected. The complications evaluated included hematoma, seroma, minor infection (resolved with oral antibiotics), major infection (need for intravenous antibiotics), wound dehiscence, mastectomy flap necrosis, implant/AlloDerm exposure, and readmission within 90 days of surgery. The primary outcome was a comparison of the rate of complications within 90 days of surgery in patients with and without ALND and LYMPHA.
Results
Patient Characteristics Across Various Subgroups (cont.)
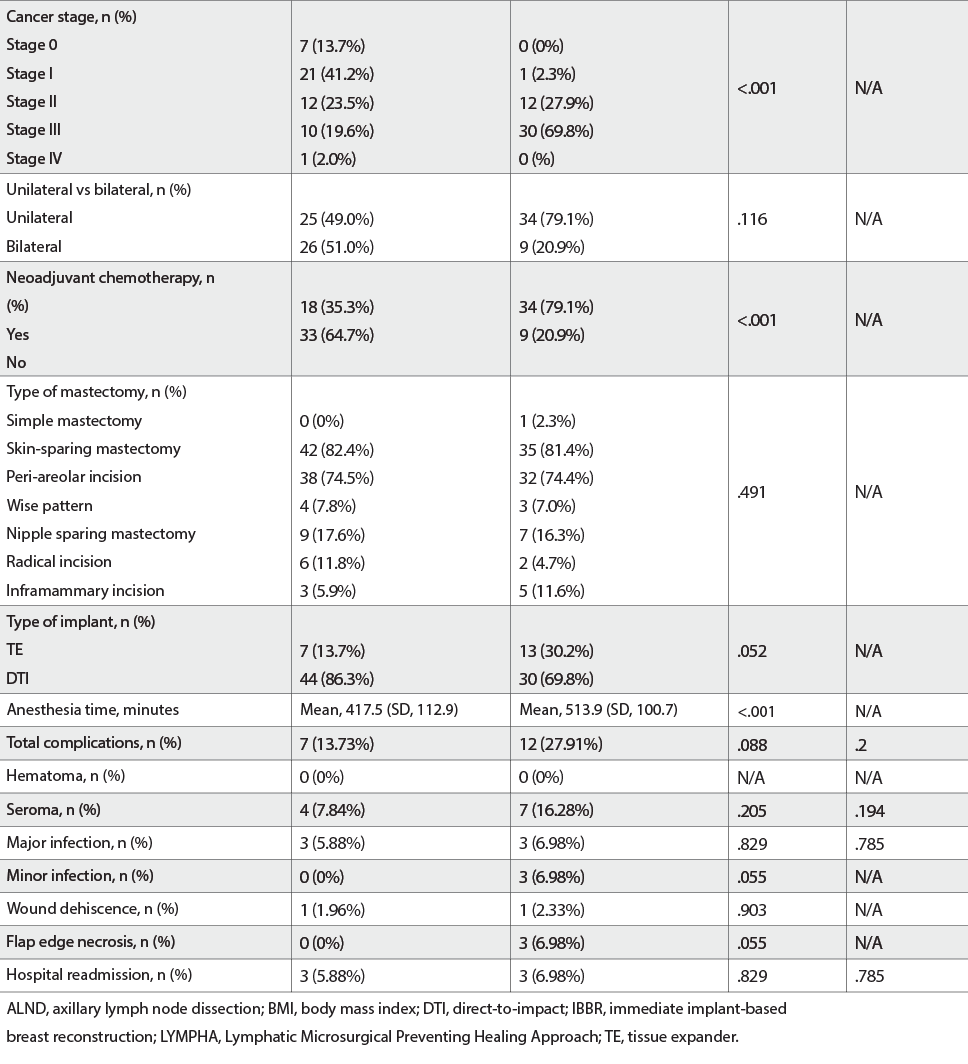
Of 94 patients with mastectomy followed by IBBR, 54.3% (n = 51) had no ALND and LYMPHA, and 45.7% (n = 43) had an ALND and LYMPHA. All baseline demographic features were evenly distributed between both cohorts. Patients with a higher-stage breast cancer requiring neoadjuvant chemotherapy were more likely to be present in the ALND with LYMPHA cohort (P < .001). Mastectomy types, implant types, and laterality of surgery were evenly distributed. ALND with LYMPHA had a longer anesthesia time (417.5 vs 513.9 minutes; P < .001). There was no hematoma in either cohort. Seroma occurred in 7.84% of patients of the non-LYMPHA cohort and 16.28% of those who underwent IBBR with LYMPHA (P = .205). Major infection rates were 5.88% in patients without LYMPHA and 6.98% in those with LYMPHA (P = .829). Minor infections were seen in none without LYMPHA and 6.98% of patients with LYMPHA (P = .05). Wound dehiscence occurred in 1.96% without LYMPHA and 2.33% with LYMPHA (P = .9). Mastectomy flap edge necrosis occurred in no patients without LYMPHA and 6.98% with LYMPHA (P = .05). One patient had implant removal because of AlloDerm exposure in the LYMPHA cohort. In all, 5.88% and 6.98% had complication-related hospital readmission within 90 days of surgery in the non-LYMPHA and LYMPHA cohorts, respectively (P = .829). There were no statistically significant differences in the individual complication rates with multivariate analysis, as well as on controlling for body mass index, cancer stage, chemotherapy, and anesthesia time. Overall complication rates had no statistically significant difference (13.73% vs 27.91%; P = .09).
Conclusions
ALND with LYMPHA had no statistically significant differences in complication rates as compared to no ALND and LYMPHA. LYMPHA should be performed with ALND to reduce LE, as it does not increase the risk of postoperative complications.
