96 Elacestrant Real-World Progression-Free Survival of Adult Patients With ER+/HER2–, Advanced Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis Using Insurance Claims in the United States
96 Elacestrant Real-World Progression-Free Survival of Adult Patients With ER+/HER2–, Advanced Breast Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis Using Insurance Claims in the United States

Background
Endocrine therapy (ET) plus CDK4/6 inhibitor (CDK4/6i) is the standard-of-care (SOC) for first-line estrogen receptor–positive/HER2-negative (ER+/HER2–) advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Sequential ET monotherapy or combinations are used second line post-ET plus CDK4/6i. Combination regimens in second-line or late metastatic breast cancer can be associated with significant toxicities and high discontinuation rates. ESR1 mutations, a type of acquired resistance, eventually emerge in up to 50% of patients after first-line treatment for ER+/HER2– metastatic breast cancer. In the phase 3 EMERALD trial (NCT03778931), patients with ESR1-mutated tumors had a 45% reduction in risk of progression or death with elacestrant vs SOC ET (median progression-free survival [PFS] 3.8 months vs 1.9 months; HR, 0.55; 95% CI, 0.39-0.77; P = .0005). In patients with 12 months or more prior ET plus CDK4/6i, the median PFS with elacestrant was 8.6 months vs 1.9 months with SOC ET (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.26-0.63). Elacestrant was FDA-approved in January 2023 for the treatment of postmenopausal ER+/HER2– ESR1-mutated metastatic breast cancer with progression after at least one line of ET. Sufficient time has passed since approval to characterize the real-world use of elacestrant in the current treatment landscape. This study aims to describe the real-world PFS of elacestrant overall and in patients with no prior exposure to fulvestrant, only 1 to 2 lines of ET, 3 or more lines of ET, and/or visceral metastases.
Materials and Methods
Adults with diagnosed ER+/HER2– metastatic breast cancer who initiated elacestrant in a real-world setting between January 2023 and May 2024 were identified in the Komodo Research Database. Demographic information described at index date (time of first administration of elacestrant) included metastatic sites identified during the 6-month baseline period prior to index date and prior metastatic breast cancer treatments. Real-world PFS was defined as time from index date until earliest outcome (start of next line of metastatic breast cancer therapy to progression or death). Patients were censored at first occurrence of end of data availability or end of health plan enrollment.
Results
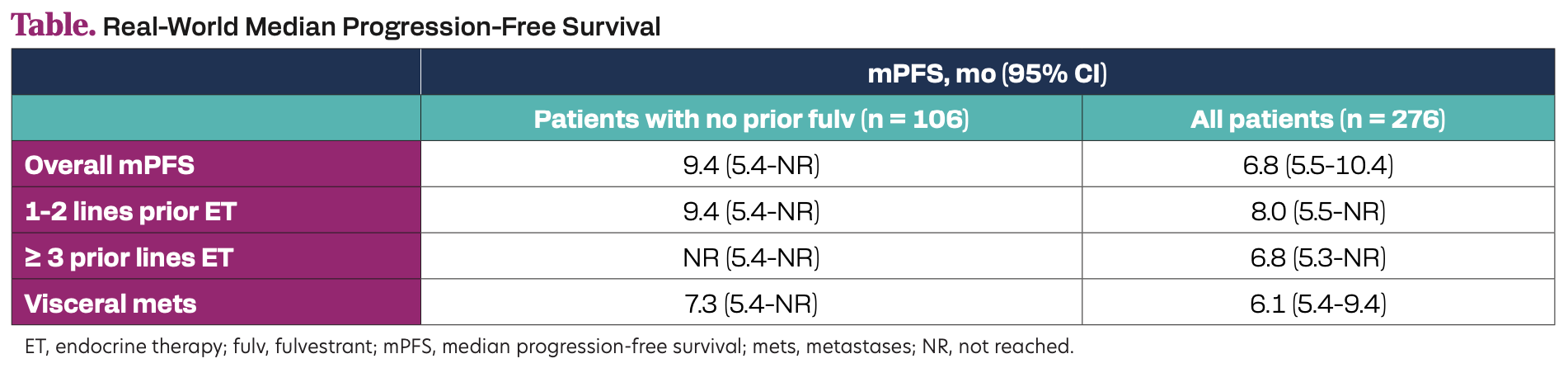
A total of 276 patients treated were evaluated (median age 63 years, 86% visceral metastases, 90% prior CDK4/6i, 61% prior fulvestrant). Real-world PFS was prolonged with elacestrant in patients with prior fulvestrant and in the overall population in all subgroups (Table).
Table. Real-World Median Progression-Free Survival
Conclusion
In a real-world setting, elacestrant showed a consistent real-world PFS benefit among all patients with ER+/HER2– metastatic breast cancer and across clinically relevant subgroups. The real-world PFS with elacestrant exceeded the overall median PFS in EMERALD and is longer when patients are treated in earlier lines.

Newsletter
Stay up to date on recent advances in the multidisciplinary approach to cancer.