
Dose optimization of nilotinib is feasible and may help patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia achieve molecular responses, according to results of a new study.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Dose optimization of nilotinib is feasible and may help patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia achieve molecular responses, according to results of a new study.

A phase III trial failed to demonstrate superiority of eribulin over treatment of physician’s choice in patients with heavily pretreated non–small-cell lung cancer.

An immediate instillation of chemotherapy with mitomycin C following transurethral resection of a bladder tumor reduced the risk of recurrence of non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).

Treatment with imatinib results in good overall survival in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia, approaching a normal life expectancy, according to the CML-IV study.

The FDA has granted priority review status for two new indications of dasatinib (Sprycel), according to the drug’s developer.

The FDA has approved neratinib (Nerlynx) for use as extended adjuvant treatment in adult patients with early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer.

The use of bisphosphonates was not associated with a decrease in the incidence of breast cancer in postmenopausal women, contrary to hypothesis.

Once-daily RT given concurrently with chemotherapy showed no difference in survival compared with the twice-daily standard in small-cell lung cancer.

Taller men are at increased risk for high-grade prostate cancer and prostate cancer death, according to a large registry study. Greater adiposity is also associated with higher-grade tumors and mortality.

T-DM1 administered for 12 weeks with or without endocrine therapy yields good rates of pathologic complete response in women with HER2-positive/hormone receptor–positive breast cancer, according to a new randomized trial.

Long-term follow-up found no significant differences in all-cause or disease-related mortality in men with early prostate cancer randomized to either radical prostatectomy or to observation. Surgery led to more adverse events, but less treatment for disease progression.
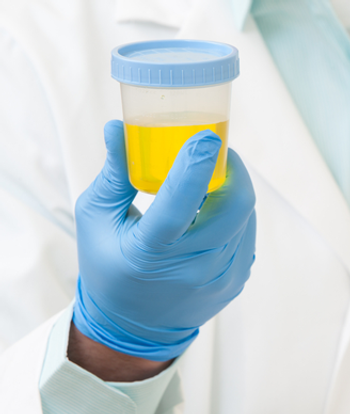
A urine test of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) was found to be a reliable predictor of recurrence in non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer, according to a new study.

Adherence to a Mediterranean diet is negatively associated with advanced colorectal polyps, and the specific portions of the diet that appear to have the most influence include high intake of fish and fruit and low intake of soft drinks.

Patients with colorectal cancer that has metastasized to the liver derive a significant benefit from selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) combined with chemotherapy if their primary tumor is a right-sided tumor, but not if it is a left-sided primary tumor.

A 70-gene expression score can identify women with indolent breast cancer at “ultralow” risk, according to a new study. Women with such a score have extremely low risk of disease-specific mortality over 20 years without systemic therapy.

Proton-beam therapy was found to be safe for patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer in the first prospective registry study of the therapy, with only a small number of high-grade toxicities.

Approximately half of patients with chronic-phase CML who achieved a sustained deep molecular response with nilotinib were able to discontinue therapy and remain in treatment-free remission through 96 weeks.

A combination of netupitant and palonosetron was non-inferior to aprepitant plus granisetron in preventing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.

Women who undergo HPV testing following a test showing abnormal cytology have earlier detection of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, compared to those who do not undergo HPV testing.

Three-weekly cisplatin is superior to a weekly dose in preventing locoregional relapse when combined with radiotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.

Nivolumab did not extend progression-free survival over chemotherapy in the first-line setting in patients with PD-L1–positive advanced non–small-cell lung cancer, according to results of an open-label phase III trial.

Replacing a cyclophosphamide-based regimen with oral capecitabine does not sacrifice efficacy in adjuvant therapy for early breast cancer, and improves quality of life, according to a new study.

Almost one quarter of long-term cervical cancer survivors reported experiencing chronic fatigue, according to a study conducted in Norway.

The addition of two cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy to concurrent chemoradiotherapy improved tumor control in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.

A biosimilar to trastuzumab known as CT-P6 showed equivalent efficacy and similar toxicity to the original agent in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.

Adding the novel CD20 inhibitor ublituximab to ibrutinib offered improved response rates and greater depth of response over ibrutinib alone in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

Adding midostaurin to chemotherapy prolonged survival in younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia and a FLT3 mutation, according to a randomized trial.

After extended follow-up, the KEYNOTE-052 study has shown that first-line pembrolizumab offers durable responses and no new safety signals in patients with cisplatin-ineligible advanced urothelial cancer.

The combination of pembrolizumab and the IDO1 inhibitor epacadostat was active and generally well tolerated in patients with urothelial carcinoma.

The PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab showed substantial responses as a single-agent treatment in patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer with confirmed PD-L1 expression.