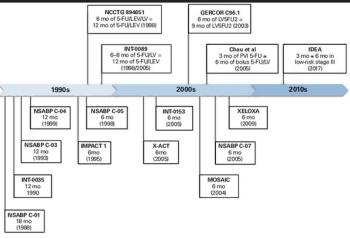
In this article, we review the findings of the IDEA study and discuss the optimal duration of oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy using patient-based risk factors.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


In this article, we review the findings of the IDEA study and discuss the optimal duration of oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy using patient-based risk factors.

This article reviews the critical issues of quality control and standardization of PHY906 and other herbal medicines, and highlights the importance of high-quality material for the conduct of preclinical and clinical studies, for cancer patients.

The issue of tumor heterogeneity is real, and it is present on several different levels. Without question, the presence of tumor heterogeneity has important clinical implications, and at this time, it represents a significant challenge to the success of cancer therapy.

It was originally hoped that the presence of mutations in KRAS and other related genes would provide an easy answer as to whether to administer anti-EGFR antibody therapy to a given metastatic colorectal cancer patient. However, in nature nothing is simple, and there are a number of issues that practicing clinicians should be made aware of.

Over the past few years, significant efforts have focused on developing and validating molecular biomarkers to better define the subset of patients with stage II disease who might derive benefit from adjuvant therapy.

This article reviews the main issues that must be considered in metastatic colorectal cancer from the surgical oncology and medical oncology perspectives, respectively.

In this issue of ONCOLOGY, Golan and Javle present a timely review of the current status of the insulin growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) signaling pathway as a therapeutic target, with a specific focus on gastrointestinal (GI) cancers.

About the ActivityThis activity is based on a brief article developed as part of the E-Update Series and posted on the Web. It was developed from an identified educational need for information about practical management issues in the practice of medical, surgical, and radiation oncology. This activity has been developed and approved under the direction of CME LLC.

Since the early 1990s, postoperative adjuvant chemoradiotherapy was widely viewed as the main approach to treat patients with stage II and III rectal cancer. Over the past few years, significant efforts have shifted towards developing neoadjuvant approaches, which combine chemotherapy with radiotherapy prior to surgical resection.

Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in United States. For nearly 50 years, fluorouracil has been the only anticancer drug proven to benefit patients with metastatic CRC (mCRC), and it continues to be the backbone on which most treatment regimens are built. In the past 10 years, development of the topoisomerase I inhibitor irinotecan (Camptosar), the third-generation platinum analog oxaliplatin (Eloxatin), and the oral fluoropyrimidine capecitabine (Xeloda) advanced mCRC treatment and opened up an era of combination chemotherapy. More recently, monoclonal antibodies such as bevacizumab (Avastin), cetuximab (Erbitux), and panitumumab (Vectibix) have become available for use in mCRC treatment in combination with cytotoxic agents and as monotherapies. The addition of these targeted agents to the mCRC treatment armamentarium has resulted in more therapeutic options and improved treatment outcomes for the patients. The prospect of mCRC treatment is ever promising as more targeted agents such as vatalanib are being introduced and as intelligent combination regimens are being designed based upon a better understanding of pharmacokinetics. In this article we review various treatment options, including cytotoxic and targeted agents, currently available for patients with mCRC.

Anti-EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) therapies, including tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and monoclonal antibodies, demonstrate activity in a variety of tumor types. While both inhibit the EGFR pathway, they act via different mechanisms.

Colorectal cancer is a worldwide public health problem, with nearly 800,000new cases diagnosed each year resulting in approximately 500,000deaths. In the United States, it is the second leading cause of cancer mortality,and nearly 60,000 deaths will be attributed to this disease in 2005. Whendiagnosed as advanced, metastatic disease, colorectal cancer is traditionally associatedwith a poor prognosis, with 5-year survival rates in the range of 5% to 8%. Thissurvival rate has remained unchanged over the past 35 to 40 years. However, duringthe past 5 years, significant advances have been made in treatment options so thatimprovements in 2-year survival are now being reported, with median survival ratesin the 21- to 24-month range in patients with metastatic disease.

Significant advances have been made in the treatment of advancedcolorectal cancer over the past 5 years, namely due to the introductionof three novel cytotoxic agents-capecitabine (Xeloda), irinotecan(Camptosar), and oxaliplatin (Eloxatin)-and the recent approval oftwo biologic agents-bevacizumab (Avastin) and cetuximab (Erbitux).During this time period, the median survival of patients with advanced,metastatic disease has gone from 10 to 12 months to nearly 24 months.Intense efforts have focused on identifying novel targeted therapies thattarget specific growth factor receptors, critical signal transduction pathways,and/or key pathways that mediate the process of angiogenesis.Recent clinical trial results suggest that the anti-VEGF antibodybevacizumab can be safely and effectively used in combination witheach of the active anticancer agents used in colorectal cancer. Despitethe development of active combination regimens, significant improvementsin the actual cure rate have not yet been achieved. Combinationregimens with activity in advanced disease are being evaluated in theadjuvant and neoadjuvant settings. The goal is to integrate these targetedstrategies into standard chemotherapy regimens so as to advancethe therapeutic options for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer.Finally, intense efforts are attempting to identify the critical molecularbiomarkers that can be used to predict for either clinicalresponse to chemotherapy and/or targeted therapies and/or the drugspecificside effects. The goal of such studies is to facilitate the evolutionof empiric chemotherapy to individually tailored treatments forpatients with colorectal cancer.

Published: August 16th 2009 | Updated:

Published: May 1st 2009 | Updated:

Published: May 17th 2011 | Updated:

Published: August 15th 2013 | Updated:

Published: December 24th 2006 | Updated:

Published: March 15th 2012 | Updated: