A new study published in the� Journal of Clinical Oncology reported on the clinical implications of gDDR genes.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A new study published in the� Journal of Clinical Oncology reported on the clinical implications of gDDR genes.
Investigators evaluated whether AZD3463 can induce apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner in a subset of AML patients.
Researchers evaluated the primary mechanisms governing drug resistance and relapse in patients treated with crenolanib, an FLT3 inhibitor.
Researchers conducted the first population-based study of an unselected MTC cohort compared with the general population.
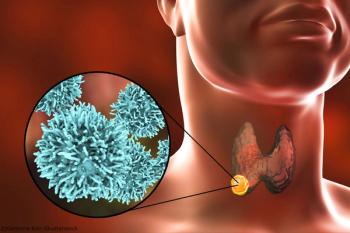
Clinicians may be able to utilize this information as an effective preoperative tool to stratify risk and determine an initial surgical approach for patients with PTC.

Guidelines for cancer screening in survivors of childhood HL may be refined based on the results of this extended follow-up study, say the researchers.
A new study published in Cancer compared ELN-2017 to ELN-2010 in terms of distinguishing prognosis in younger patients with newly diagosed AML.
Researchers reported on the impact of adding the Hedgehog pathway inhibitor glasdegib to low-dose cytarabine.
Researchers investigated whether first-line chemotherapy improved overall survival in NSCLC patients with severe to very severe COPD.
The US Food and Drug Administration recently approved a new agent for treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia.
Clinicians now have a new treatment to offer elderly patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia who have comorbidities that preclude the use of intensive chemotherapy.
Researchers evaluated the survival benefit of adding pembrolizumab to chemotherapy with carboplatin plus paclitaxel or nab–paclitaxel compared with chemotherapy alone.

A recent study in JAMA Oncology compared survival for various multi-modality approaches for treating aggressive prostate cancer.
Researchers examined whether a higher Gleason score impacts the efficacy of androgen deprivation therapy.
A study in Thyroid evaluated the safety and efficacy of concurrent intensity-modulated radiation therapy and doxorubicin in thyroid cancer.
Investigators shared results of an interim analysis evaluating antitumor activity and safety in patients with mMCC receiving avelumab monotherapy.
Interim results are in from a study evaluating whether adding selumetinib to RAI improves complete response, irrespective of MAPK pathway alterations.
The findings of this study, recently published in JAMA Oncology, directly contradict previously conducted research on the same topic.
Oncologists now have some clarification on the use of moderate hypofractionation and ultrahypofractionation from ASTRO, ASCO, and the AUA.
A new study adds to evidence examining whether neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery improves survival vs surgery alone in locally advanced ESCC.
A new study evaluated whether busulfan and melphalan improve EFS and OS when given after vincristine, ifosfamide, doxorubicin, and etoposide induction.
While previous research has proven the role of MHC-I molecules, a new study in Cell suggests that MHC-II may also serve as a target in immunotherapy.
A study in JAMA Oncology found that a wide range of fatal toxic events can occur with immune checkpoint inhibitors, and the type of event varies by agent.
New research in Lancet Oncology confirms previous studies in this population on the addition of apalutamide to androgen deprivation therapy.
A study in Cancer found a lower risk of prostate cancer–specific death and improved overall survival when patients were treated with this combination.

By elevating the expression of ANO7, a potential prostate cancer susceptibility gene, it may be possible to predict disease severity and outcome.
Individuals who develop frequent basal cell carcinomas may have an increased prevalence of germline mutations in DNA repair genes and an increased malignancy risk.

Although the study found lurbinectedin isn't promising, the presence of a chromosomal 11q21-23 abnormality may open doors in treating the disease.
A particular gatekeeper-the nuclear pore protein called POM121-traffics molecules that increase tumor aggressiveness in prostate cancer.

Taking corticosteroids at the time of treatment initiation with PD-L1 inhibitors may lead to inferior outcomes in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer.