For the first time, researchers have isolated a subtype of gamma-delta T-cells that offers protection in women with triple-negative breast cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


For the first time, researchers have isolated a subtype of gamma-delta T-cells that offers protection in women with triple-negative breast cancer.
A new combination may help with overall and progression-free survival in liver cancer.

A recent report highlighted the progress made globally in preventing cancer. However, improvements are still needed.
The combined use of a CDK4/6 inhibitor with endocrine therapy yielded a 9.4-month median OS benefit among patients.

The agency is set to make a decision on the investigational antibody drug conjugate by the first quarter of 2020.
There could be a new way to diagnose brain tumors earlier.

Serena Nik-Zainal, MD, discusses study findings that could change the way treatment strategies for subgroups of patients with triple-negative breast cancer are evaluated.
The agent has a high affinity and specificity for interleukin-1 beta.

The results showed that even patients with disease that has spread to the brain should be considered for immunotherapy.
TAS-102 improved overall survival, compared with placebo, in patients with metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer.
NLR appeared to be a significant predictor of overall survival, and also showed a trend in favor of progression-free survival, among patients with stage III locally-advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
Sequential afatinib and osimertinib improved median overall survival by almost 3.5 years in patients with EGFR T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer, with an even greater benefit seen in those with Del19-positive disease.
Metformin appeared to increase glucose uptake in lung cancer cells, according to results from a phase II trial.
Treatment with 9-ING-41 significantly increased pancreatic tumor cell killing when combined with chemotherapy in pre-clinical trials.
Over that time, the number of active drugs in development has grown by more than 90%.
The neoantigens found in the patients’ tumors (non-small-cell lung cancer) which were highly dissimilar were enriched for hydrophobic sequences, and correlated with survival rates after the PD-1 checkpoint therapy.
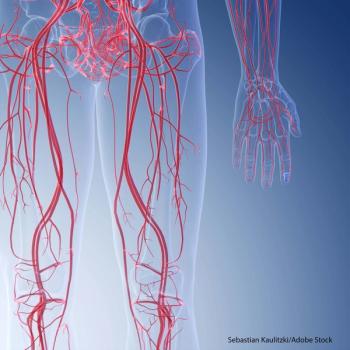
Following administration of checkpoint inhibitor therapy, 2.6% of patients experienced an acute vascular event within 6 months of starting treatment.
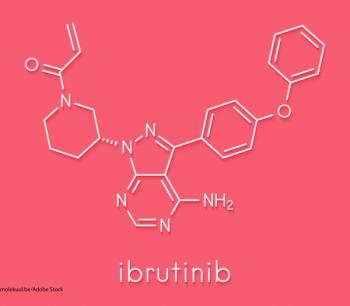
A study found an association between treatment with ibrutinib and an increased risk for death from toxicities.

Three scientists were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology of Medicine for their discovery of the mechanism of how cells regulate oxygen.

Half of the cancer drug trials that led to approvals by the European Medicines Agency may have been associated with a high risk for bias.
Remarkable gains have been made in breast cancer outcomes; however, racial disparities have contributed to breast cancer incidence.

The agency granted breakthrough therapy designation to niraparib for the treatment of men with BRCA1/2-mutant positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
The methotrexate-based regimen proved to lengthen survival and improve quality of life among patients with platinum-resistant oral cancer.
The results of the first therapy to use a PARP inhibitor with chemotherapy for patients with ovarian cancer were presented at ESMO Congress 2019.
A new study looked at trametinib's effect on survival and response rates in ovarian cancer.

A recent study found that women with early-stage breast cancer experienced atrial fibrillation in the first and fifth years following diagnosis.

The combination use of Darzalex with bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone was approved for transplant-eligible patients with multiple myeloma.
A phase III study found that adding 2 years of ovarian function suppression to tamoxifen extended disease-free survival in certain patients with hormone receptor–positive breast cancer.
Administration of antibiotics prior to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy may reduce response to treatment and worsen survival outcomes in patients with cancer.
Immunotherapy could replace chemotherapy in some patients with recurrent/metastatic cervical and vaginal or vulvar cancers.