
Gynecologic Cancers
Latest News
Latest Videos

More News

The panel explains how low-grade serous ovarian cancer differs from high-grade, and if an immunotherapy approach is appropriate for treatment.

Robert Coleman, MD, FACOG, FACS, reviews data from a study investigating combination letrozole plus ribociclib in patients with low-grade serous ovarian cancer.
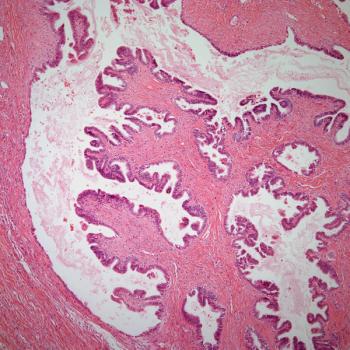
Avutometinib plus defactinib produces no new safety signals among those with low-grade serous ovarian cancer in the phase 2 RAMP 201 trial.
Niraparib Maintenance Improves Survival in Recurrent Ovarian Cancer
Maintenance with niraparib also produces benefits in chemotherapy-free interval and time to first and second therapy among those with BRCA wild-type recurrent ovarian cancer in the phase 3 NOVA study.
Health-related quality of life data support dostarlimab plus chemotherapy as a standard of care in primary advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer, according to an expert from Copenhagen University Hospital in Denmark.
Bevacizumab Regimen Yields Meaningful PFS Benefit in Ovarian Cancer
Maintenance bevacizumab plus durvalumab and olaparib appears to produce a progression-free survival benefit among those with HRD-negative advanced ovarian cancer in the phase 3 DUO-O trial.
Simple hysterectomy may become the new standard of care for patients with low-risk, early-stage cervical cancer, according to an expert from Université Laval in Quebec City, Canada.

Drs Eskander and Lewin discuss the sequencing immune checkpoint inhibitors for women with recurrent endometrial cancer.

Sharyn Lewin, MD, FACS, shares how she discusses side effects with patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer.
Data from the phase 3 DUO-E trial indicate that the safety of durvalumab/chemotherapy with or without olaparib/durvalumab or durvalumab monotherapy maintenance in recurrent endometrial cancer was consistent with previous reports of each agent.

Experts explain what they are looking forward to in the future of treatment for patients with ER/PR+ and P53 wild-type or mutated advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer.

The panel discusses their opinions on the use of immunotherapy in different populations of women with advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer.
Updates in the Treatment of Advanced/Recurrent Endometrial Cancer: Data from the NRG-GY018 Study
Ramez Eskander, MD, presents data from the GY018 study investigating pembrolizumab versus placebo in addition to carboplatin/paclitaxel in patients with advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer.

Updates in the Treatment of Advanced/Recurrent Endometrial Cancer: Data from the RUBY Trial
Dr Robert Coleman details data from the RUBY trial investing the role of checkpoint inhibitor dostarlimab in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer.
Prexasertib is currently under investigation as part of a phase 2 trial as a treatment for patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, endometrial adenocarcinoma, and urothelial cancers.

Standards for Molecular Testing in Endometrial Cancer
Drs Sharyn Lewin and Ramez Eskander share their thoughts on comprehensive molecular testing for all women with endometrial cancer.

Next-Generation Sequencing for Recurrent Endometrial Cancer
Robert Coleman, MD, FACOG, FACS, reviews data from a study investigation the frequency of molecular testing in patients with endometrial cancer.

Multidisciplinary Efforts are 'Essential' to Manage Gynecologic Cancer Symptoms
A recovery tracker and other digital tools may be useful in helping to manage patient symptoms following debulking surgery for gynecologic cancer, according to an expert from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.

Common symptoms following debulking surgery for gynecologic cancer appear to include pain, diarrhea, and nausea, according to an expert from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
Based on findings from the phase 3 MIRASOL trial, investigators plan to submit a supplemental biologics license application for mirvetuximab soravtansine in folate receptor α–positive platinum-resistant ovarian cancer.

“Even in well-resourced countries, there are disparities in exposure to treatments; some of these are rooted deeply in social determinants of health and represent a very complex problem of providing equal access.”

Patients who use a recovery tracker tool appear to experience lower hospital readmission rates following gynecologic cancer debulking surgery compared with those who did not.

Medical oncologists and gynecologic oncologists alike have a shared responsibility to help treat symptoms of neuropathy in patients undergoing chemotherapy for gynecologic cancer, according to an expert from Duke University Medical Center.

Experts from UCLA Health discuss key data presented at The Society of Gynecologic Oncology 2023 Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer and how they may apply to clinical practice.

Future research assessing cryocompression for those with gynecologic cancers will make use of different products to make the intervention easier and more accessible for patients.
















































