A phase III study looks at the efficacy and safety of rituximab biosimilar CT-P10 in patients with follicular lymphoma.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A phase III study looks at the efficacy and safety of rituximab biosimilar CT-P10 in patients with follicular lymphoma.
Researchers discovered clinical and experimental evidence that calls into question the widely held notion that LSCs preferentially outlive chemotherapy.

Stephanie Jackson, MSN, RN speaks with Cancer Network about the role oncology nurses play in managing patients with hematologic malignancies who are undergoing CAR T-cell therapy.
The ground-breaking study, led by the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, is evaluating several novel targeted therapies for acute myeloid leukemia.
In this article, we describe the considerations for the use of BTK inhibitors in lymphoid malignancies from the perspective of an oncology pharmacist.

Does patient race play a role in the efficacy of monoclonal antibodies in multiple myeloma?

The ELOQUENT-3 trial looks at how the of addition of elotuzumab to pomalidomide and dexamethasone impacts patient outcomes in multiple myeloma.
Cancer patients in England will receive a new game-changing therapy treatment under the first negotiated deal of its kind struck in Europe.
An inflammation marker was associated with several unfavorable characteristics in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.

New research evaluated whether symptomatic indolent follicular lymphoma requires new long-term therapy after first-line rituximab without chemotherapy.
A study shows that lower doses of ibrutinib after a full-dose cycle may be enough for continued biological activity.
Long-term data from the phase III HELIOS trial indicates ibrutinib plus bendamustine and rituximab improve survival outcomes in CLL patients.

Evaluating the prognostic value of PET-CT responses after first-line immunochemotherapy in follicular lymphoma.

Dr. Ian Flinn spoke with Cancer Network about incorporating the newest approved therapies for the management of CLL.
FDA approves once-weekly carfilzomib/dexamethasone combo for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.
A study shows thalidomide-based treatment carries risk, but could be an option for certain multiple myeloma patients.
The research, published in JAMA Oncology, evaluates survival outcomes of a second allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant vs donor lymphocyte infusion.
A study in The Lancet Haematology suggests this combination could become first-line for elderly or unhealthy patients with newly diagnosed AML.

Minimal residual disease negativity measured by next-generation sequencing was a valuable prognostic biomarker for multiple myeloma.
A study shows stress may affect certain cellular, cytokine, and chemokine markers in the body of patients with CLL.
A study shows treatment with ibrutinib is superior to chemoimmunotherapy for patients with chronic treatment-naive CLL.
CX-01, a low-anticoagulant heparin derivative, has demonstrated good rates of complete remission, rapid platelet recovery, and no serious adverse events.
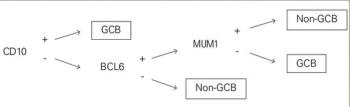
In this article, we review the methods of determining cell of origin (COO); use of COO in clinical practice; clinical trials in DLBCL according to COO; and future directions of tailoring treatment, including alternate categorization of genetic subtypes or clusters in DLBCL.

A study shows expanding access to care through insurance has the potential to improve outcomes in adults with follicular lymphoma.
Although the study found lurbinectedin isn't promising, the presence of a chromosomal 11q21-23 abnormality may open doors in treating the disease.