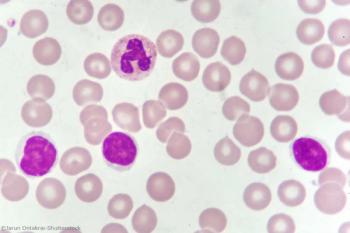
A study shows bendamustine followed by venetoclax and obinutuzumab was active in treatment-naive or relapsed/refractory CLL.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A study shows bendamustine followed by venetoclax and obinutuzumab was active in treatment-naive or relapsed/refractory CLL.
Using mediation analysis, researchers were able to identify three gene expression markers that help explain the observed prognostic difference between certain AML patients.
Investigations into the CSF3R gene may help lead to better classification and precise treatment of AML.
In Part 2 of this two-part series, this review covers extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma, indolent T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma, and hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma.

Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma patients experience high response rates, overall survival with bortezomib-based therapy.

A high level of resilience was associated with a better mental and physical health-related quality of life among patients with multiple myeloma.
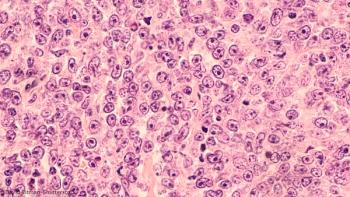
New data support PFS as a surrogate endpoint for OS in future trials evaluating chemoimmunotherapy in DLBCL.
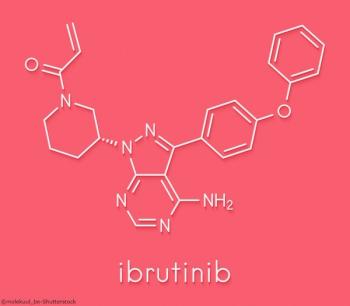
In the DBL3001 trial, the combination of ibrutinib and R-CHOP was not superior to treatment with R-CHOP alone.
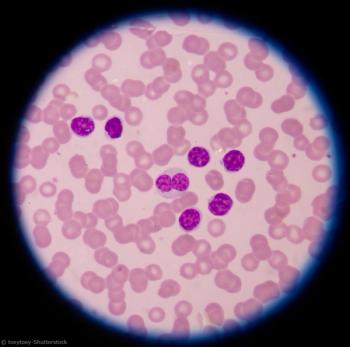
Chemoimmunotherapy followed by lenalidomide consolidation is tolerated and extends PFS and OS in CLL patients.
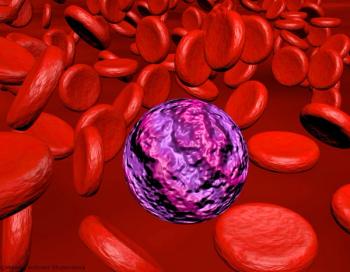
Strong efficacy and safety outcomes with this agent, which targets the molecular driver of an AML subset, have led to its approval in IDH1-mutated R/R disease.

In the emerging era of personalized treatment, it may be time to rethink which surrogate markers are used in AML clinical trials.
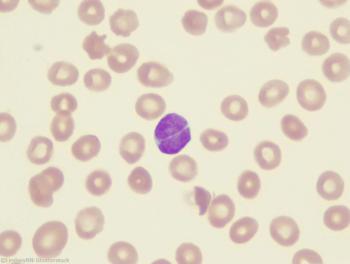
In addition to significant improvements in 5-year OS and PFS with maintenance rituximab, there was a trend toward an association between maintenance and reduced transformation risk.
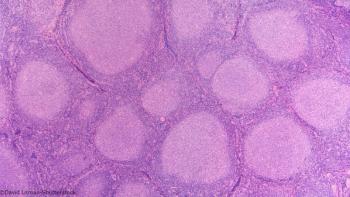
TROG 99.03 constitutes “the only high level evidence currently available to guide decision making for this group of patients,” says investigator Michael MacManus.
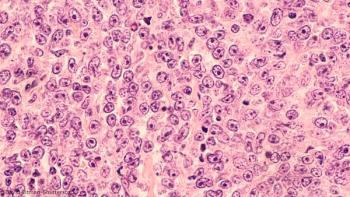
This two-part series highlights the most important aspects of PTCLs and describes current treatment options and investigative opportunities. Part 1 will cover PTCL not otherwise specified, follicular T-cell lymphoma, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma, anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), and breast implant–associated ALCL.
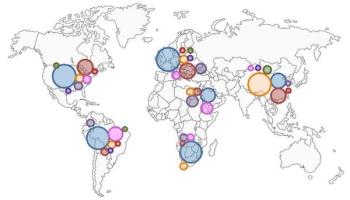
The OS benefit associated with standard treatment diminished in patients older than 80 with high comorbidity scores, but other age groups fared better.

From 1990 to 2016, incident cases of multiple myeloma increased by 126% globally, while deaths increased 94%. The US had the most incident cases and deaths.

Investigators concluded ixazomib “may offer a more convenient, active, and well-tolerated alternative to a parenterally administered PI in this setting.”

This study is the first to show significantly improved OS from single-agent treatment in this particularly difficult to treat population.

De-escalated treatment may be possible in patients with advanced HL who reach a metabolic response after only 2 cycles of escalated BEACOPP.

Overall response was strong even in high-risk patients (over age 65, with 17p deletion, with prior ibrutinib therapy, and mutations of BTK and PLCγ2).

FDA warns, however, about the possibility of TLS due to rapid tumor cell destruction.
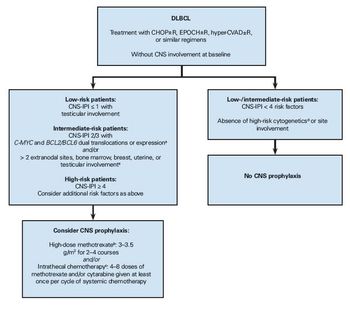
Here we review current prognostic models, risk factors, and prophylaxis methods to provide a practical approach to preventing CNS relapse in patients with DLBCL.

Until the superiority of novel agents is proven for all prognostically relevant subgroups of patients with CLL, we believe chemoimmunotherapy continues to have a role.

Elimination of chemotherapy from our combination regimens should be a shared goal among researchers that will move us a step closer to more patient-friendly and scientifically driven therapies for CLL.

A case series of rare peripheral T-cell lymphoma that is associated with breast implants found that most cases have an indolent clinical course.