
A new collaboration among industry, nonprofit, academia, and the federal government may lead to a change in the treatment paradigm for acute myeloid leukemia.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


A new collaboration among industry, nonprofit, academia, and the federal government may lead to a change in the treatment paradigm for acute myeloid leukemia.

Maintenance therapy with norethandrolone significantly improved survival in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia without increasing toxicity.

An analysis of tyrosine kinase inhibitor initiation and adherence in Medicare beneficiaries with chronic myeloid leukemia suggests that out-of-pocket costs may be a barrier to treatment.

When CML patients develop resistance or intolerance to these drugs, transplant may be the only option.

Frontline intensive therapy with rituximab plus high-dose sequential chemotherapy did not improve outcomes for high-risk patients with DLBCL compared with treatment with R-CHOP-14.
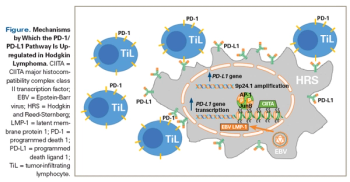
In this article we review the scientific rationale, preclinical evidence, and most recent clinical data for the use of checkpoint inhibitor therapy in patients with relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma.
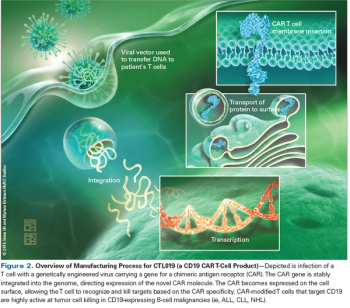
In this review, we will describe the mechanism of action of CAR T cells, discuss outcomes of current clinical trials, and highlight emerging directions for this exciting approach to cancer treatment.
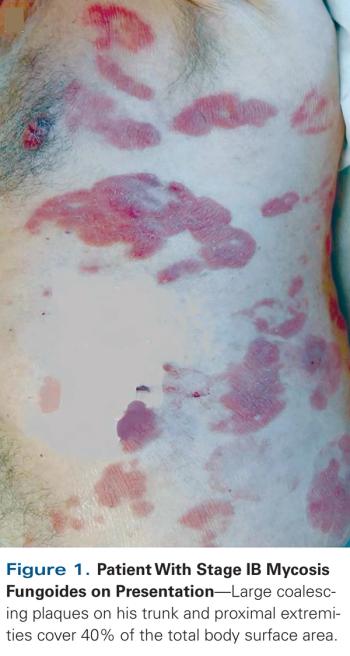
An 80-year-old man presented with a disabling pruritic rash characterized by disseminated and coalescing plaques on the trunk and proximal extremities and covering 40% of his total body surface area, without peripheral lymphadenopathy.

Ultimately, the management goal is not for patients with relapsed/refractory disease to live with chronic Hodgkin lymphoma while receiving immune checkpoint blockade therapy, but rather to cure more patients with first- or second-line therapy.

Identification of effective lymphodepletion strategies, optimization of patient selection, and management of novel toxicities remain challenges in the growing field of cellular immunotherapy.

Longer durations of maintenance therapy with lenalidomide were associated with longer survival among patients who underwent autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant for multiple myeloma.

Patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms revealed discrepancies between patient and physician recollection of management and communication in a research survey.

Several FDA-approved anti-malarial and anti-fungal drugs might be able to overcome a previously unexploited mechanism that allows some leukemia cells to escape programmed cell death.

In leukemias, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) can play a role in cancer cell maturation and can be both pro- and antiapoptotic.

Several anti-malarial and anti-fungal drugs might be able to overcome a previously unexploited mechanism that allows some leukemia cells to escape programmed cell death.

A supplemental New Drug Application has been submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration for marginal zone lymphoma (MZL), and if approved, ibrutinib (Imbruvica) will be the first therapy specifically approved for patients with MZL.

It turns out that CAR T cells can do more than directly attack cancer cells. They can be used as “micro-pharmacies” for precise therapeutic delivery in B-cell lymphomas.

Adding daratumumab to lenalidomide and dexamethasone significantly improved progression-free survival in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.

Development of targeted therapies for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) represents an ongoing challenge for the field. There is substantial promise, however, in several different approaches to targeted AML therapy, including IDH inhibitors, FLT3 inhibitors, and others.

The STIM1 study shows that patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who have undetectable minimal residual disease can safely discontinue imatinib therapy.

Clinicians and patients now have several options for frontline management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia; exactly which option is preferred remains up for debate.

Helping patients through toxicities and discomfort from multiple myeloma and its therapies remains a challenge and must be addressed with supportive care practices.

The 5-year survival rate for relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia has been below 10%. Immunotherapies, however, are starting to challenge that paradigm.

Because of the high cure rate in early-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma, reducing toxicity is a primary concern. One idea for doing so is a subject of ongoing research: is elimination of all radiotherapy in many of these patients a possibility?

As more and more new options come on the market, integrating them into proper management of multiple myeloma has become an important challenge.