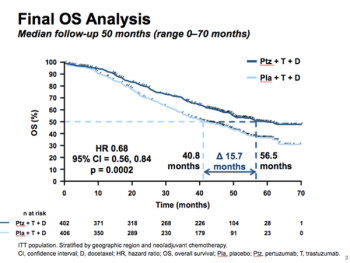
The development of CT lung cancer screening, the publication of results from the NLST in 2011, and the grade-B recommendation for CT lung cancer screening in high-risk smokers by the USPSTF raise a number of interesting national health policy issues.