Preoperative staging of esophageal cancer with PET/MR is approximately as good as with endoscopic ultrasound, and may improve slightly over ultrasound and PET/CT scans, according to a new study.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Preoperative staging of esophageal cancer with PET/MR is approximately as good as with endoscopic ultrasound, and may improve slightly over ultrasound and PET/CT scans, according to a new study.

There is a need to learn more about the effect of hypofractionation on an individual patient’s breast cancer outcomes and tissue toxicities, based on both biologic and technical variables, so that the treatment decision is not primarily a matter of dollars and cents.

Customized more aggressive treatments should be given to patients with the worst prognosis. For most of the other breast patients, shorter and often milder treatment is also a humble victory in our daily struggle against cancer.

Barriers to cost discussions fall into three categories: inaccessible cost data, ethical concerns, and insufficient training.
In this review we discuss the rationale and underlying radiobiologic concepts for hypofractionation, and review the clinical trials and ASTRO guidelines supporting hypofractionated radiation in the treatment of breast cancer.

A pooled analysis of three prospective trials showed that post-induction therapy PET-CT scans are highly predictive of progression-free and overall survival in follicular lymphoma patients.

Words like value, quality, and even cost flowed freely at the ASCO Annual Meeting this year. Along with great excitement about the latest and greatest ways to understand tumor biology and treat cancer patients, there is an increasing recognition that we need to consider whether the things we do are worth it.
Treatment with sorafenib after curative resection or ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma did not improve recurrence-free survival compared with placebo, according to the results of the phase III STORM trial.

The addition of cediranib to treatment with cisplatin/gemcitabine did not improve progression-free survival in patients with advanced biliary tract cancer, according to the results of the phase II ABC-03 trial.

The issue of value in cancer care was a prominent theme at the 2014 ASCO Annual Meeting. A question that inevitably arises in any discussion of value is what the professional and ethical obligations of practicing oncologists are in the current climate of escalating healthcare costs.

Thoracic radiotherapy along with prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) significantly prolonged progression-free and overall survival in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer, according to results of a new study presented at ASCO.

Exposure to a preference-based mail and telephone navigation intervention increased colorectal cancer (CRC) screening adherence compared to a standard mailed intervention among African Americans.

In his address, Dr. Clifford Hudis proposed the following solutions for achieving social justice in cancer care: creating more private and public resources, addressing disparities in cancer risk and in access to high-quality care, defining “value” in cancer care, and harnessing the new power of information technology.

With cancer care costs rising rapidly there is increased pressure to search for value in how we care for our patients.

Advertisements for cancer centers often appeal to consumers’ emotions but rarely provide useful information about the benefits, risks or costs of treatment, a recent analysis concluded.

Medicare’s payment system for cancer care services should be restructured to focus on value over volume and offer incentives for providing high-quality, patient-centered care.

As part of our coverage of ASCO's Annual Meeting, we discuss the role of chemotherapy in prostate cancer, as well as study results on novel targeted approaches and agents in development for prostate cancer that will be presented at the meeting.

Take a minute to recall those patients who showed up in the emergency room without your knowledge, or who died 1 week after starting a new treatment, or whom you neglected to enroll in hospice. In each scenario the cost of their care rose without a corresponding increase in value. I’ve listed some behavioral skills that have a chance to prevent unnecessary expense.

This slide show features 8 ways oncologists can create value in cancer care, from building a great team of staff members to staying on top of the latest developments in your field.

In this interview we discuss outcomes in clinical trials and how to improve trials by redefining clinically meaningful outcomes.

To ultimately find what we are actually looking for, the invasive malignant nodule in a haystack of benign lesions, new strategies and qualitative and quantitative tools are needed to propel noninvasive evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules into the 21st century.

What distinguishes those practices that are successful in their use of the EMR is their commitment to the product and their recognition that it is the central element in the treatment of their patients.

Researchers at the Moffitt Cancer Center have created a computational model to simulate the bone metastasis process and to predict the outcomes of specific prostate cancer therapies.

The number of lesions detected with low-dose CT, only some of which are early cancers, is so great that algorithms are being developed for more efficient evaluation and management of solitary pulmonary nodules. This article will discuss current tools, approaches, and concerns regarding patient care in this setting.
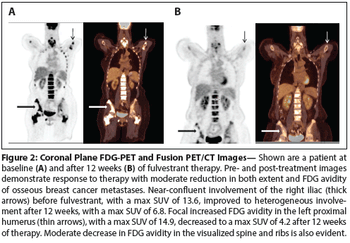
We review how radiolabeled glucose and estrogen analogs can be used in breast cancer patients. We focus this review on the application of positron emission tomography imaging to ER-positive metastatic breast cancer as an example of how imaging can guide breast cancer treatment.

The simple answer, according to some, is that lung cancer screening’s time has come. However, in my opinion, the answer is not that simple.

Implementation of a national lung cancer screening program using low-dose CT will identify almost 55,000 additional lung cancer cases over 5 years, but will add $9.3 billion to Medicare expenditures.

A meta-analysis of over 15,000 patients with liver cirrhosis who were diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma demonstrates the benefit of screening these patients for liver tumors.


With the goal of helping to standardize and optimize care, ASCO has issued two new clinical guidelines on treating patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.