
All News


The mTOR inhibitor everolimus showed clinical efficacy for the initial treatment of advanced papillary renal cell carcinoma, according to the phase II results of the RAPTOR trial.

Asking patients to track their nausea and vomiting after a course of chemotherapy helped the health care team to adjust medications and achieve better control of symptoms, according to the results of a small single center study.

The anti-RANKL antibody denosumab is more effective for preventing bone metastasis in men with high-risk castration-resistant prostate cancer compared with low-risk disease, according to results of a new study.

Why do doctors have such a hard time embracing hospice care and using it to benefit patients, particularly oncology patients? Referring a patient to a hospice program starts a sophisticated plan of care wholly directed at patient comfort, education of the family and grief counseling for the family.

Ten-year follow up two large randomized trials in the UK show that less frequent but higher dose radiotherapy regimen are as safe and effective as the standard regimen of more frequent lower doses for women with early breast cancer post-surgery.

A large study shows a difference in the cancer outcomes of married and unmarried individuals, finding that those who are married are less likely to be diagnosed with metastatic disease and to die of their cancer compared with those who are unmarried.

I am seriously thinking about firing my oncology software. It has been 19 months now since I found myself stuck with this relapse. I don’t dare tell my father anything yet-he’ll start going on about how I should see a human doctor. He has been pushing me to visit a LiveDoc who supposedly is still practicing oncology in midtown. Right-like I’m going to do that.

Researchers have identified a novel pathway that promotes bone metastasis of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). The study is in mice, but points to a potential target that could be exploited to control or prevent metastatic disease.

In order for malignancies to establish in metastatic sites, cancer cells must acquire attributes of those sites; specifically how this occurs in many cancers is relatively unknown, but a new study implicates the stroma of certain breast cancer tumors in the development of bone metastases.

We examine efforts to correct cost inequities of oral anti-cancer agents through legislation, and we look at further efforts to reduce the cost of oral chemotherapy via cycle management and waste reduction.

Expert radiologists were able to screen magnetic resonance images and rule out breast cancer diagnosis with a negative predictive value of about 99% using an abridged breast MRI protocol in a single-center study presented Saturday at the ASCO Breast Cancer Symposium 2013.

How long ago did we learn that smoking caused lung cancer? The USPSTF is poised to recommend annual screening CT scans for the detection of lung cancer in high risk individuals. Are there enough CT scanners to handle the volume? The LLC’s are forming now to put a dedicated lung screening CT machine next to every convenience store. Get your carton and CT in one stop!

Researchers have demonstrated that a two-step screening test can identify ovarian cancer early, before the disease progresses to an advanced, poor prognosis stage.

In this interview we discuss why patient-centered research is important, why this type of information is frequently ignored, and paths toward implementing this information into cancer trials.

Most community cancer centers are only beginning to measure quality of care and are struggling with the challenge of collecting data while adding services and keeping costs in check, concluded a recent survey by the Association of Community Cancer Centers (ACCC).

The first obvious problem with peer review is delay. On other occasions, I observed what appeared to be strong and persistent bias on the part of reviewers that ultimately led to rejection or intrusive revision of the manuscript.
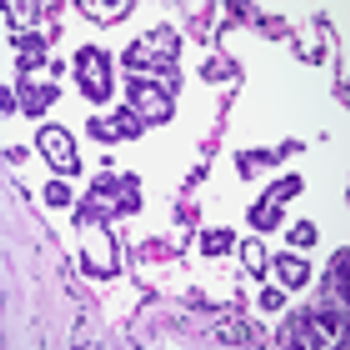
Identification of a significant micropapillary component within lung adenocarcinomas predicts a higher risk of relapse following lung-sparing surgery, according to results of a new study.

Being offered a brief, dedicated discussion of end-of-life decisions relatively early in the trajectory of advanced cancer led to an earlier placement of do-not-resuscitate orders and decreased the likelihood that patients died in a hospital, a new study showed.

The management of patients receiving treatment with oral oncolytics presents challenges such as cost, adherence, monitoring of side effects, and safe handling.

Today, after reviewing a CT scan (and screwing my courage to the sticking-place) I went into an exam room, looked a patient in the eye and said: “The liver lesions have started to grow again. I think we need to change your treatment.”

ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Localized Nodal Indolent Lymphoma
The present guidelines review epidemiology, pathology, presentation, workup, staging, prognostic factors, and treatment options for patients with localized nodal indolent lymphoma, with an emphasis on radiation guidelines, including radiation dose, field design, and radiation techniques.

A new study demonstrates a way to exploit a metabolic vulnerability of senescent cells. The strategy provides evidence for an anticancer approach that targets a cellular process or condition of the cell rather than a distinct molecular pathway.

Based largely on evidence from the NLST, the USPSTF recently issued a draft recommendation for annual lung cancer screening using low-dose CT in high-risk individuals.

A new endoscopy technology called photometric stereo endoscopy, which captures the topography of the colon surface to create a 3D image, could be a more robust way to screen for precancerous lesions of the colon.
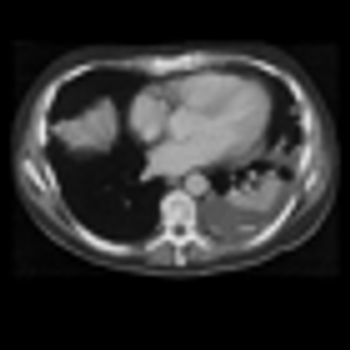
Results from the National Lung Screening Trial showed that screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography yielded the most benefit among individuals who were at highest risk for cancer and less benefit in lower risk people.

Both Internet and print-based decision aids equally helped men make important decisions related to prostate cancer screening, but did not affect actual screening rates.
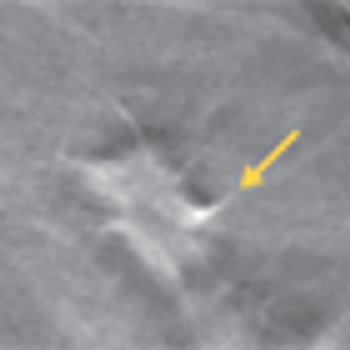
A new study shows that the combination of digital mammography plus tomosynthesis results in fewer false positive results compared with digital mammography alone. Women under the age of 50 and those with dense breasts had the greatest benefit from the combined screening approach.
A meta-analysis by researchers in Australia shows that those infected with the human papillomavirus have a threefold higher risk of developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.

