
Expression of MET as measured by immunohistochemistry was not associated with any difference in the performance of cabozantinib as compared with everolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Expression of MET as measured by immunohistochemistry was not associated with any difference in the performance of cabozantinib as compared with everolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.

The combination of bevacizumab and an investigational nanoparticle-drug conjugate known as CRLX101 failed to improve outcomes in metastatic renal cell carcinoma compared with standard of care.

Active surveillance of small renal masses has been shown in recent years to be a generally safe and reasonable approach, though there are a number of factors for clinicians to keep in mind in taking this path.

Radiotherapy in advanced kidney cancer is generally only used in select metastatic settings, but the use of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy offers promise in a number of indications in this malignancy.

Adding the WEE1 inhibitor AZD1775 to carboplatin offered enhanced response rates in women with TP53-mutated ovarian cancer that was refractory or resistant to first-line platinum-based therapy in a phase II study.

A cognitive rehabilitation program known as Insight resulted in improvements in cognitive symptoms compared to standard care in adult cancer survivors.
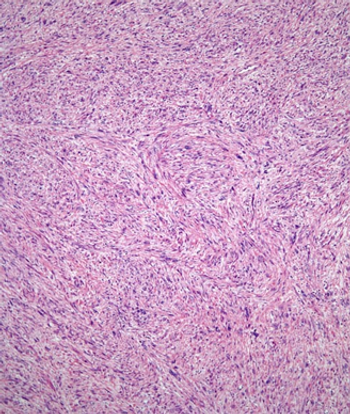
A phase II trial found that the multikinase inhibitor regorafenib has clinical activity and offers improved progression-free survival in certain types of advanced soft-tissue sarcoma.

The initiation of and adherence to tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors (AIs) such as anastrozole is low among older women with estrogen receptor-positive ductal carcinoma in situ.

The combination of cabazitaxel and abiraterone was well tolerated and showed antitumor activity in previously treated patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.

The presence of circulating tumor cells at baseline was associated with decreased overall and disease-free survival in patients with inflammatory breast cancer undergoing treatment with neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with bevacizumab.

A new study showed that a 24-gene signature can predict outcomes following postoperative radiotherapy in patients with prostate adenocarcinoma who underwent radical prostatectomy.

Patients with chronic myeloid leukemia with a history of prior malignancies generally fare as well as those without such a history, according to a new study.

Adding seribantumab to paclitaxel failed to improved progression-free survival in unselected patients with platinum-resistant or -refractory ovarian cancer. Expression of heregulin and HER2, however, could identify a subset of patients that derive benefit from the therapy.

In patients with HER2-positive breast cancer undergoing trastuzumab therapy, elevated troponin I or T before the treatment is associated with an increased risk of trastuzumab-related cardiac dysfunction.

Common breast cancer risk alleles are correlated with both the incidence of breast cancer and mortality, and using these alleles along with other factors could identify women at very low risk of breast cancer who could potentially avoid mammography.

The FDA granted accelerated approval to olaratumab (Lartruvo) in combination with doxorubicin for the treatment of soft-tissue sarcomas that is not amenable to curative treatment with radiotherapy or with surgery and with a histologic subtype treatable with anthracycline-containing regimens.

The addition of selumetinib to docetaxel failed to improve progression-free and overall survival in patients with KRAS-mutated locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC.

Response to the HER2-targeted therapies lapatinib and trastuzumab are correlated with pathway-level genetic alterations, but not specific gene mutations.

An analysis of tyrosine kinase inhibitor initiation and adherence in Medicare beneficiaries with chronic myeloid leukemia suggests that out-of-pocket costs may be a barrier to treatment.

The oral PARP inhibitor rucaparib showed strong activity and an acceptable safety profile in women with high-grade, BRCA-mutated ovarian carcinoma who had previously received at least two lines of chemotherapy.

Venous thromboembolism is significantly more likely over the long term in breast cancer patients than in the general population, according to a study in Sweden.

Microsatellite instability analysis and immunohistochemistry analysis are highly concordant with regard to testing for mismatch repair deficiency in endometrial cancer.

The oral PARP inhibitor niraparib yielded significantly improved progression-free survival for women with platinum-sensitive, recurrent ovarian cancer in a phase III trial.

A study of patients receiving rituximab therapy found that screening for hepatitis B virus infection (HBV) was suboptimal, and some patients who did not receive antiviral treatment experienced HBV reactivation or flare. Screening rates, however, do appear to be improving over time.

A trial of five rare sarcoma subtypes found that though dasatinib failed to achieve progression-free survival goals, more than half of patients with certain subtypes did have reasonably good survival outcomes.

The combination of nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel) and nedaplatin showed promising activity and was relatively well tolerated in a small phase II trial.

Adding ribociclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, to letrozole significantly improved progression-free survival in postmenopausal women with advanced, HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer.

Development of targeted therapies for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) represents an ongoing challenge for the field. There is substantial promise, however, in several different approaches to targeted AML therapy, including IDH inhibitors, FLT3 inhibitors, and others.

The STIM1 study shows that patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who have undetectable minimal residual disease can safely discontinue imatinib therapy.

Patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) and visceral metastases (liver and lung) fare better with the androgen receptor inhibitor enzalutamide than placebo, according to a new analysis from the phase III AFFIRM trial.