
Vietnam War veterans exposed to Agent Orange as part of Operation Ranch Hand were at double the risk for monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, a precursor to multiple myeloma, according to results of a new study.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Vietnam War veterans exposed to Agent Orange as part of Operation Ranch Hand were at double the risk for monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, a precursor to multiple myeloma, according to results of a new study.

Perineural invasion was a significant predictor of increased risk for bone metastases in men with prostate cancer who had suspicion for bone metastases after a whole-body bone scan.
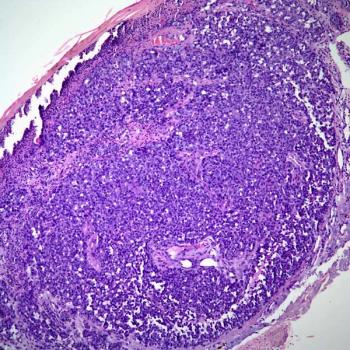
Metastasis to sentinel lymph nodes was significantly lower among patients with melanoma with histologic regression of their disease compared with those without regression.
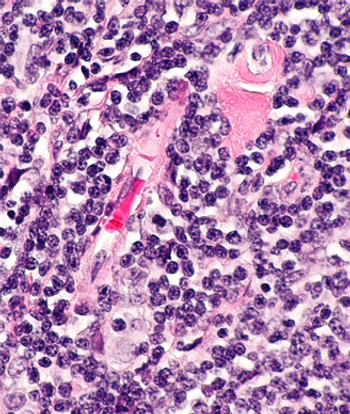
Combined treatment with lenalidomide/rituximab resulted in better clinical response in patients with recurrent follicular lymphoma than did lenalidomide alone.
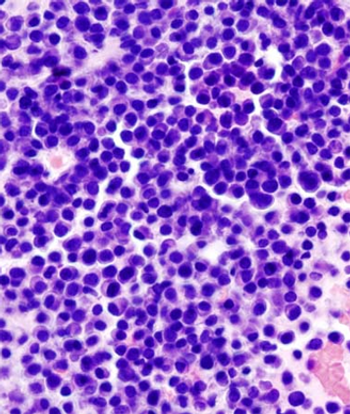
Daratumumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets CD38, was safe and effective in patients with heavily pretreated and refractory multiple myeloma.

Beta-blockers were associated with increased overall survival in women with epithelial ovarian cancer, according to a retrospective study.

Continuous therapy resulted in delays in first and second progression compared with fixed-duration therapy in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.

Treatment with the PARP inhibitor olaparib plus paclitaxel resulted in an overall survival benefit in patients with metastatic gastric cancer.

Researchers combined clinical risk factors with mutation status from seven genes to improve prognostication for patients with follicular lymphoma.

Consumption of four or more cups of coffee a day was associated with a reduced risk for colon cancer recurrence and death in patients with stage III disease.
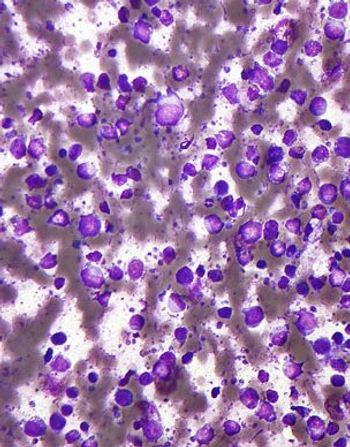
Using a gene expression-based assay on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue, researchers were able to identify groups among DLBCL patients with significantly different outcomes from R-CHOP treatment.

Women younger than 35 with low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary or peritoneum or those who still had persistent disease at the completion of primary therapy were found to have worse disease outcomes.

A study has found that mutations in the genes RAD51C and RAD51D confer risk for epithelial ovarian cancer, causing approximately one in every 90 high-grade and one in every 120 epithelial ovarian cancer occurrences.

Patients who have undergone chemotherapy for nonseminoma testicular cancer are at an increased risk for cardiovascular disease, especially in the first year after treatment.

A new scoring system may help to identify patients at low risk for colorectal cancer who could forego screening with colonoscopy.
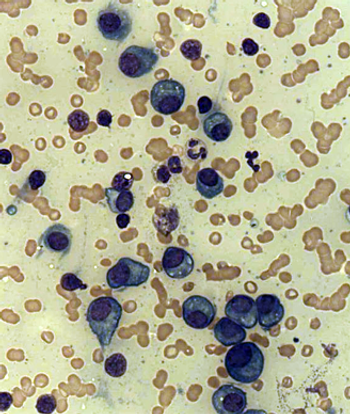
The International Myeloma Working Group has published a revised International Staging System for multiple myeloma that incorporates chromosomal abnormalities.

Long-term results of the CROSS study have confirmed that neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy added to surgery should be the standard of care in esophageal or esophagogastric junction carcinoma.
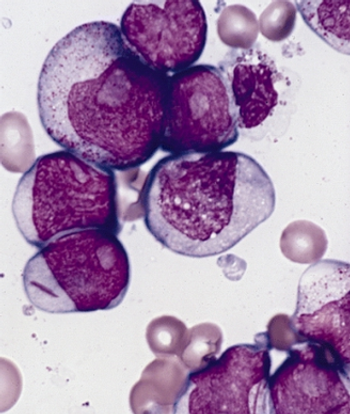
Adding vosaroxin to cytarabine resulted in no significant improvement in overall survival in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia, but the trial did suggest that vosaroxin could be an option for salvage therapy in patients aged 60 and older.
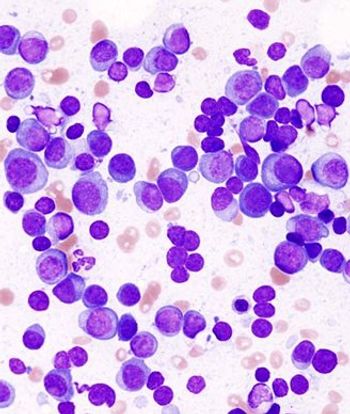
Eighty percent of patients with advanced multiple myeloma had a clinical response to a new T cell–receptor therapy that used T cells to target cells expressing NY-ESO-1.
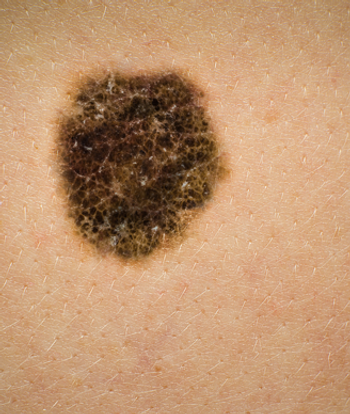
Results of a new study have indicated that the risk of developing melanoma may be almost doubled among certain survivors of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma.

Despite trials showing a benefit when combining IP and IV chemo for ovarian cancer, fewer than 50% of eligible patients are currently receiving this treatment.

By exploring gene expression variables in addition to clinicopathologic variables, researchers were able to better predict which melanoma patients would have sentinel lymph node biopsy positivity.

Lymphoma survivors who underwent autologous HSCT may be at greater long-term risk for heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction than previously thought.

Treatment with carfilzomib plus lenalidomide and dexamethasone resulted in high rates of minimal residual disease negativity in patients with newly diagnosed or smoldering high-risk multiple myeloma.

Advanced Hodgkin lymphoma patients who discontinue their treatment with bleomycin and vincristine as part of a BEACOPP regimen did not experience an effect on survival.

Results of a large trial have indicated that the use of interim PET/CT imaging has limited prognostic value to DLBCL patients being treated with R-CHOP-14.

Treatment with FOLFOX plus cetuximab resulted in improved PFS vs FOLFOX alone in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer with “all-RAS” wild-type tumors.

A subgroup analysis of the phase III RECOURSE trial has shown that TAS-102 is effective at improving survival in patients with both KRAS wild-type or mutant metastatic colorectal cancer.

Two phase III trials have confirmed the benefit of regorafenib, an oral multikinase inhibitor, in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer.

Ovarian cancer progression may be driven by the activation of an endoplasmic reticulum stress response factor that disrupts the function of dendritic cells and, subsequently, antitumor fighting T cells.