Combining rintatolimod with pembrolizumab may confer a synergistic effect in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Combining rintatolimod with pembrolizumab may confer a synergistic effect in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.

Toripalimab plus axitinib is now an approved regimen in China for patients with medium- to high-risk unresectable or metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
Real-world data may serve as a benchmark for future studies in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
Findings from SELECT-AML-1 support the potential benefit of tamibarotene in those with acute myeloid leukemia harboring RARA gene overexpression.

Investigators also look to assess linvoseltamab in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma as part of the phase 3 LINKER-MM3 trial.
In-hospital mortality and complication rates were lower at accredited hospitals vs those not accredited for patients undergoing rectal cancer surgery.
First-in-patient findings support AZD1390 as a potential radiosensitizer during the management of glioblastoma.
The phase 1/2 WU-KONG1 findings support the breakthrough therapy designation for sunvozertinib for those with EGFR-mutated non–small cell lung cancer.
Data from the phase 1/2 KRYSTAL-1 trial may support adagrasib plus cetuximab as a new standard in previously treated metastatic KRAS G12C–mutated CRC.
The pilot trial is planning to enroll 20 patients who are deemed inoperable but do not have metastatic disease.
The liquid biopsy combining miRNA and CA19-9 had the best validation rates for detecting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.

Patients with advanced solid tumors may be able to stay on treatment with saruparib longer compared with other approved PARP inhibitors, thereby improving efficacy.
Patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer who remain molecular residual disease negative following cystectomy may be spared from adjuvant therapy.
Retrospective findings may establish a “framework” for improving the accessibility, timeliness, and appropriateness of surgical cancer care in disadvantaged areas.

Leaders in genitourinary oncology spoke about key research advances as well as personal experiences in navigating the field.

Tailoring neoadjuvant therapy regimens for patients with mismatch repair deficient gastroesophageal cancer represents a future step in terms of research.
The PREEMPT trial analyzed samples from 27,010 average-risk adults to determine the specificity of detecting colorectal cancer.

Not much is currently known about the factors that may predict pathologic responses to neoadjuvant immunotherapy in this population, says Adrienne Bruce Shannon, MD.
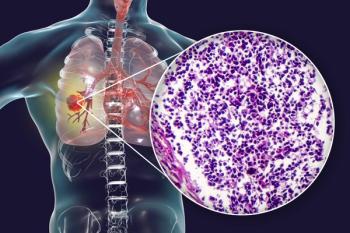
Data from a phase 3b trial support a supplemental new drug application in China for savolitinib in previously treated non–small cell lung cancer with MET exon 14 alterations.

The toxicity profile of tislelizumab also appears to look better compared with chemotherapy in metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.

Results from 3 DESTINY trials led to the accelerated approval of fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki for patients with unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive solid tumors.

Treatment with durvalumab raises no new safety signals among patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer in the phase 3 ADRIATIC trial.
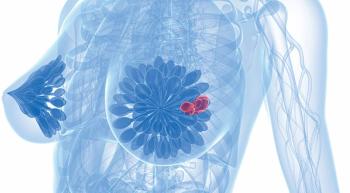
Data from the NATALEE trial show that ribociclib may benefit a broad population of patients with early breast cancer who have an increased risk of recurrent disease.

Results from the phase 3 KarMMa-3 trial of ide-cel vs standard of care in previously treated multiple myeloma led to the FDA approval.

Patients with unresectable or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and higher PD-L1 expression may benefit from treatment with tislelizumab, according to Syma Iqbal, MD.
Quantifying disease volume to help identify potential recurrence following surgery may be a helpful advance, according to Sean Dineen, MD.
Further research may be needed to help determine the underlying mechanisms of polybrominated diphenyl ether exposure contributing to the risk of cancer-related mortality.

MK-1084 previously demonstrated manageable safety and preliminary activity in non–small cell lung cancer harboring KRAS G12C mutations as part of a phase 1 trial.

Sean Dineen, MD, highlights the removal of abdominal wall lesions and other surgical strategies that may help manage symptoms in patients with cancer.

Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab appears to reduce the risk of disease progression or death vs chemotherapy in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma.