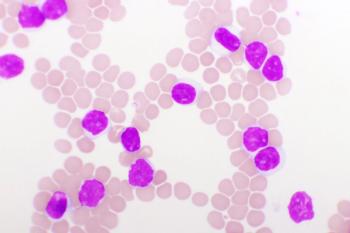
Reducing caloric and nutrient intake for patients who were overweight or obese and undergoing induction for B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia was feasible and improved patient response, according to an early-phase trial.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Reducing caloric and nutrient intake for patients who were overweight or obese and undergoing induction for B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia was feasible and improved patient response, according to an early-phase trial.
During an After Hours segment of Medical World News®, Loren Winters, MSN, ANP-BC, OCN, spoke about her passion for health and wellness, expressed through yoga instruction and Ayurvedic health coaching.

For the detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma and oropharyngeal cancer, a novel technology has been granted breakthrough device designation by the FDA.

The lead author from a study presented at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021 explained the main findings regarding potential differences in tumor mutation burden by race in patients with early-onset colorectal cancer.
CancerNetwork® spoke with Sanju Sinha of the National Cancer Institute about the resulting data from his research into sex differences associated with using tumor mutational burden to predict response to PD-1 inhibition.
The 3-year follow-up analysis of 4 treatment groups who received CNS prophylaxis found a decreased incidence of CNS relapse for patients with high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, although the data were not statistically significant.
Data reported from the phase 3 POSEIDON trial are the first to demonstrate a statically significant overall survival benefit with tremelimumab.
The KATHERINE trial found a clinical benefit without increasing the risk of CNS recurrence for patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer treated with T-DM1.
Nurse Navigator Janeen Bazan, RN, OCN, BSN, talks about the 4R Care Sequence® and its impact on the care of patients with breast cancer at the 2021 Oncology Nursing Society Annual Congress.
An optical coherence tomography–based imaging system was granted breakthrough device designation for detection of residual tissue during certain surgical procedures in patients with breast cancer.

In the advanced treatment setting, an FDA decision has indicated that the combination of pembrolizumab and lenvatinib may soon be available for certain patients with endometrial tumors and renal cell carcinoma.
CancerNetwork® sat down with Hans P.A. Van Dongen, PhD, Shobhan Gaddameedhi, PhD, and Jason McDermott, PhD, to discuss their research into how circadian disruptions may lead to changes in cancer-related genes.

Based on response data from a randomized phase 3 trial, the FDA granted accelerated approval to pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for the treatment of HER2-positive gastric tumors.
Research focusing on first-line single-agent carboplatin was terminated due to an independent data monitoring committee’s recommendation after worse survival outcomes were observed in adult patients with ovarian cancer.
Statistical significance was reached across all end points of the phase 3 GENESIS trial investigating granulocyte colony stimulating factor plus either motixafortide or placebo in patients with multiple myeloma receiving autologous bone marrow transplantation.

Based on results of a phase 3 study, the IDH1-targeted agent ivosidenib will be considered by the FDA as therapy for cholangiocarcinoma following prior treatment.

Holowatyj touched on the need to learn more about the biological factors contributing to disparities in early-onset colorectal cancer and the associated burden of the disease.
CancerNetwork® spoke with Francesco Ravera, MD, PhD, during the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021 to discuss how results of a study aimed at determining pathological complete response in patients with locally advanced breast cancer by cell-free DNA may spare certain patients from needing further biopsies.
A retrospective study evaluating over 3.9 million children found that Down syndrome was a strong risk factor for the development of childhood leukemia and has a stronger association with acute myeloid leukemia than previously recorded.
The NanoTherm therapy system for focal ablation of intermediate-risk prostate cancer continued to show a tolerable safety profile in a recent analysis.
Adding daratumumab led to at least a very good partial responses in all 41 patients receiving weekly carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone, and complete responses in all but 2 patients.

CancerNetwork® shares its latest investigation into novel practices for rendering surgical management of prostate cancer from experts at Vanderbilt Institute for Surgery and Engineering.

Look back at some of the important news and notes from last week in the world of oncology, featuring articles from live events, the latest issue of the Journal ONCOLOGY®, and an episode of “Oncology Peer Review On-The-Go.”
A phase 3 trial found that pembrolizumab for patients with microsatellite instability–high or mismatch repair–deficient metastatic colorectal cancer significantly improved health-related quality of life compared with chemotherapy.
Rolling submission with the FDA for surufatinib treatment in patients with pancreatic and extra-pancreatic neoendocrume tumors was completed and an expanded access program for the drug is currently underway for patients in the United States.
Recent guidelines have advised against routine use of sentinel lymph node biopsy and radiotherapy in patients over age 70 years with breast cancer, but a new study finds most patients still receive the interventions.

CancerNetwork® spoke with Neelam and Sanju Sinha of the National Cancer Institute about their research into sex differences associated with using tumor mutational burden to predict response to PD-1 inhibition.
Data in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that low-intensity chemotherapy without additional intensified pegaspargase cured almost all patients treated on the Children’s Oncology Group AALL0331 trial.

The phase 2 trial showed that tipifarnib was effective for patients with metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma who have limited therapeutic options available.
CancerNetwork® spoke with Francesco Ravera, MD, PhD, during the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021 to discuss results of a study aimed at determining pathological complete response in patients with locally advanced breast cancer by either cell-free DNA assessment or traditional MRI.