Researchers identified the prevalence of germline mutations associated with the early-onset renal cell carcinoma, as well as clinicopathologic factors linked to an increased risk of carrying these mutations.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Researchers identified the prevalence of germline mutations associated with the early-onset renal cell carcinoma, as well as clinicopathologic factors linked to an increased risk of carrying these mutations.
A phase 2 study found that the investigational HIF-2α inhibitor MK-6482 has durable efficacy in patients with Von Hippel-Lindau associated clear cell renal cell carcinoma and non-renal lesions.

Voorhees noted that despite challenges associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, emerging therapies offer hope for patients with multiple myeloma.
Gadzinski spoke about the most exciting aspect of the research coming out of the 21st Annual Meeting of the Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO).
A clear and reliable biomarker to select patients with prostate cancer for active surveillance or focal therapy has not yet been determined but inferring a course of action from existing biomarkers may be possible.

A study presented at the 21st Annual Meeting of the Society of Urologic Oncology found that the implementation of telemedicine was able to significantly reduce or eliminate travel and financial burdens for patients seeking quality urologic cancer care.
The last 5 years in prostate cancer have seen exponential growth for the field of biomarkers. Specifically, not only do guidelines that now incorporate many biomarkers offer guidance on how to treat these patients, but they can also assess the potential for developing prostate cancer.
The procedure provided effective, long-term local control for patients with localized penile cancer, highlighting the need for a multidisciplinary approach to patient care.
Research shows that the PARP inhibitor demonstrated superior PFS and OS for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM alterations.
An update on the PROSPER trial analyzing enzalutamide plus androgen deprivation therapy found a lower risk of death than placebo for patients with non-metastatic CRPC.
“Providers should consider using BLC for surveillance of high-risk NMIBC patients undergoing BCG as it could change clinical management by identifying patients who are BCG unresponsive and eligible for alternative therapy and clinical trials,” said Meera Chappidi, MD.

Deep-learning algorithms could be used to alert pathologists to suspicious areas of cancer burden prior to clinical assessment, according to Nitin K. Yerram, MD.

The novel androgen receptor-signaling inhibitor led to negative repeat biopsies after 90 days of treatment among men with very-low risk to favorable intermediate risk prostate cancer on active surveillance.

A study from the 21st Annual Meeting of the Society of Urologic Oncology concluded that active surveillance is a safe management strategy for patients with small renal masses suspicious for renal cell carcinoma.

The novel first-in-class small molecule inhibitor of HIF-2α, PT2385 demonstrated the ability to stabilize disease with tolerable safety in patients with von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease-associated clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and non-renal tumors, according to results presented in a poster during the 21st Annual Meeting of the Society of Urologic Oncology (SUO).

Enzalutamide improved progression-free survival and increased time to prostate-specific antigen progression, compared with bicalutamide, in patients with nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.

A phase 1 trial showed that treatment with neoadjuvant nivolumab was tolerable in patients with nonmetastatic high-risk clear cell renal cell carcinoma.

The efficacy of the novel intravesical gene-mediated therapy nadofaragene firadenovec was sustained across subgroups of patients with high-grade, BCG-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.

Research presented at the 21st Annual Meeting of the Society of Urologic Oncology found organized telehealth systems effectively lessened the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on appointment cancellations.

Researchers utilized the Seamless MD app to aid in ERAS protocols for patients undergoing radical cystectomy, while mitigating risks from in-person visits during the COVID-19 pandemic.
This study found that radiation therapy may provide some benefit for patients with high-risk non–muscle invasive bladder cancer, though the quality of evidence in this current setting is low.

A telemedicine Multidisciplinary Urologic Cancer Clinic at the University of Washington/Seattle Cancer Care Alliance conducted video visits, inducing high patient satisfaction, sparing substantial travel burden and providing individuals access to multidisciplinary urologic cancer care.
A pooled analysis compared survival among patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with cytoreductive nephrectomy and either targeted therapy or immunotherapy regimens utilizing checkpoint inhibitors.
Research suggested oncologists may recommend specific timeframes in which cystectomy should be performed to avoid unnecessary mortality due to delays.
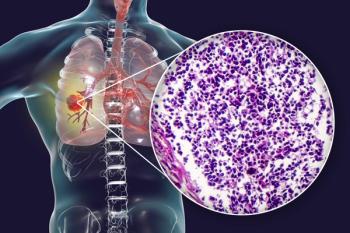
The study evaluated lurbinectedin (Zepzelca) in combination with doxorubicin versus physician's choice of topotecan or cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/vincristine for adult patients with small cell lung cancer whose disease progressed following 1 prior platinum-containing line of therapy.

Researchers sought to better understand the impact of treatment on intimate relationships for patients with bladder cancer.

Janssen submitted a biologics license application to the FDA seeking approval of amivantamab for the treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations whose disease has progressed on or after platinum-based chemotherapy.
The director of the new Women’s Lung Cancer Program at Mount Sinai spoke about the gaps in lung cancer research for women and what she hopes this new program will offer women moving forward.

The guidance is intended to inform gastroenterologists of how to assess lesions for endoscopic features associated with cancer, discuss how these factors guide endoscopic management, and to outline the factors that frame whether to advise surgery after a malignant polyp has been endoscopically resected.

The clinical trial indicated that supplementation with vitamin D reduced the incidence of advanced cancer in the overall study population of adults without a diagnosis of cancer at baseline, with the strongest risk reduction seen in individuals with normal weight.