
Oral agents and “watchful waiting” might make it possible to delay or avoid overtreatment with surgery and radiotherapy for many women diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Oral agents and “watchful waiting” might make it possible to delay or avoid overtreatment with surgery and radiotherapy for many women diagnosed with ductal carcinoma in situ.

Following breast-conserving surgery for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), younger women face a higher risk than older patients for recurrence of both DCIS and invasive carcinomas.

Two leading breast cancer experts debated the proposition that platinum-based or other additional systemic agents should be used in difficult-to-treat cases of high-risk triple-negative breast cancer.
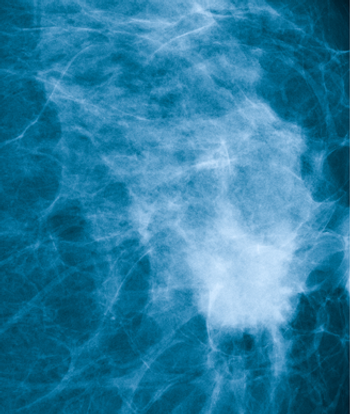
Clear guidelines about the utilization of MRI in breast cancer detection and management are needed, as the modality is being overused in women for whom it offers few benefits (and potential harms), and underused when it might be appropriate.

Breast density legislation is based on a misunderstanding of density’s association with cancer risk, and clinicians should focus not on density per se, but density residuals-the difference between a patient’s predicted and actual breast density.

In a review of axillary management, it was found that regional node irradiation is likely important in reducing distant metastasis in high-risk breast cancer.

With increasing maternal ages worldwide, patients undergoing breast cancer treatment while pregnant is becoming a more common experience in clinical oncology.

Not all DCIS is dangerous, and the prognostic genomic Oncotype DX DCIS Score allows for routine risk stratification of patients to avoid unnecessary treatment.

Targeted axillary dissection improves axillary staging and pathologic evaluation of residual nodal involvement after chemotherapy in node-positive breast cancer.

Innovative “adaptive” clinical trial designs are using molecular tools and biomarkers in ways that will streamline research efforts and bring new treatments more quickly to regulatory approval and clinical use.

Expression of programmed death-1 (PD-1) and programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) is associated with poor glioblastoma outcomes.

Pregnancy might stimulate tumor growth among women diagnosed with gliomas, according to a single-institution retrospective review of cases.

HLA-A2-positive glioblastoma patients experienced more frequent immune responses to the dendritic-cell immunotherapy IDT-107, responses that may be associated with improved survival.

Adding adjuvant gene-mediated cytotoxic immunotherapy using aglatimagene besadenovec and valacyclovir to standard of care improves survival among patients undergoing surgery for newly diagnosed malignant glioma.

Targeted MAPK-pathway inhibitor therapies appear to have reduced tumor sizes in four children’s inoperable astrocytomas-tumors that had progressed despite chemotherapy.

Adding procarbazine, CCNU, and vincristine to radiotherapy offers pronounced survival benefits for patients with low-grade gliomas harboring IDH1 R132H mutations.

Serum matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and HER2 extra-cellular domain (HER2-ECD) might be predictive biomarkers for the metastasis of breast cancer to the brain, according to a case-control study.

Adding rindopepimut to bevacizumab therapy was associated with improved long-term survival in patients with recurrent EGFRvIII-positive glioblastoma.
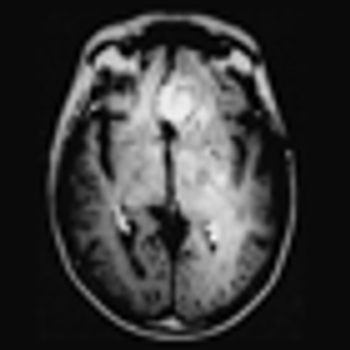
Despite promising progression-free survival results, the combination of bevacizumab and lomustine for the treatment of first recurrence in glioblastoma did not improve overall survival, according to findings from the phase III EORTC-26101 trial.

A Japanese study found that weekly paclitaxel was safe and well-tolerated among patients with anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, a notoriously aggressive malignancy.

Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy is looking increasingly plausible as a potential investigative strategy for treating thyroid cancers.

The coexistence of mutations in telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) and BRAF genes dramatically increases the risk of thyroid cancer aggressiveness, tumor recurrence and thyroid cancer-specific deaths.

Researchers in Germany appear to have identified a gene-expression signature associated with metastasis in sporadic medullary thyroid cancer and prognostic molecular tumor markers of medullary thyroid cancer response to vandetanib therapy.

New ATA Guidelines offer clear and welcome guidance against routine post-thyroidectomy remnant tumor ablation with radioactive iodine, agreed experts at the 85th Annual Meeting of the ATA.
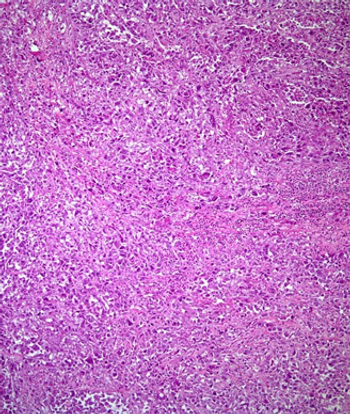
For patients who can tolerate aggressive multimodal therapy for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, survival rates can exceed historical outcomes, according to a retrospective study of patients treated at the Mayo Clinic.

It is too soon to determine the influence of radiation exposure on thyroid cancer risk among children and adolescents exposed to the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant disaster in Japan, according to the lead author of findings presented at the 85th Annual Meeting of the ATA.

Release of newly revised, evidence-based clinical management guidelines for thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancers were announced at the 85th Annual Meeting of the ATA.

Preclinical findings suggest that autophagy inhibition might prove useful in overcoming BRAF-mutant thyroid cancers resistant to vemurafenib.

The FAM83F protein contributes to papillary thyroid cancer cell viability and doxorubicin resistance, according to a study presented at the 85th Annual Meeting of the ATA.

A high number of patient life-years are lost to regulatory delays for drug approvals, according to an analysis presented at the 2015 World Conference on Lung Cancer.