
An early-phase trial tested the combination of pembrolizumab with trastuzumab in patients with PD-L1–positive, trastuzumab-resistant, advanced HER2+ breast cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


An early-phase trial tested the combination of pembrolizumab with trastuzumab in patients with PD-L1–positive, trastuzumab-resistant, advanced HER2+ breast cancer.

Researchers conducted a validation study of four breast cancer risk models currently in use.
The addition of denosumab to adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy offered improved outcomes in women with postmenopausal HR+ early breast cancer.

The researchers looked at cardiac outcomes among a group of HER2+ breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab who had an asymptomatic LVEF decline of < 50%.
The study findings suggest that disease-free survival can continue to be used as a surrogate endpoint in the setting of early HER2+ breast cancer.
Researchers compared hypofractionated radiotherapy vs a conventional regimen to study outcomes and toxicity in breast cancer patients.
Researchers conducted a study to evaluate the short-term clinical outcomes of varying approaches to immediate implant-based breast reconstruction in the UK.

Cancer Network spoke with Dr. Michael Holick about the role of and effectiveness of vitamin D in cancer prevention.

A large study looked at previously confirmed and newly discovered associations between several genes and breast cancer and ovarian cancer risk.
In this review, we focus primarily on describing locoregional and systemic management strategies for isolated locoregional recurrences manifesting as isolated first-failure events following mastectomy or breast-conserving therapy.
An oncology pharmacist discusses how to manage neutropenic toxicity from treatment with CDK4/6 inhibitors for HR-positive breast cancer.

Cancer Network spoke with Dr. Carmen Bergom about advancements in the treatment of DCIS and the importance of using local recurrence patterns to help guide future research.
Researchers tested whether combining trastuzumab/paclitaxel with dasatinib would have a high response rate in patients with metastatic HER2+ breast cancer.
The Opti-HER HEART trial examined whether liposomal formulations of chemotherapy agents may reduce cardiac toxicity in HER2+ breast cancer patients.

Researchers tested whether the GnRH antagonist degarelix was better at achieving and maintaining ovarian function suppression than the commonly used GnRH agonist triptorelin in premenopausal women with breast cancer.

Data from the Women’s Health Initiative showed that higher levels of body fat were associated with an increased risk of invasive breast cancer, calling into question BMI as an adequate marker for increased risk.

Dr. Lewis Cantley discusses targeting the PI3K pathway in breast cancer and the importance of managing ambient insulin levels during therapy.

Dr. Susan Domchek discusses the increased understanding of moderate penetrance genes and the importance of managing patients with these genes on a case-by-case basis.

Dr. Charles Geyer discusses the phase III KATHERINE trial, which compared ado-trastuzumab emtansine vs trastuzumab in HER2-positive early breast cancer.

In this video, Dr. Allison Kurian discusses polygenic risk scores, genetic testing in diverse populations, and more as they relate to breast cancer.

In looking to improve quality of life, researchers studied whether partial breast irradiation was just as effective as whole breast irradiation.
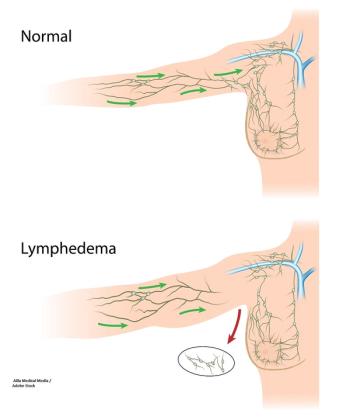
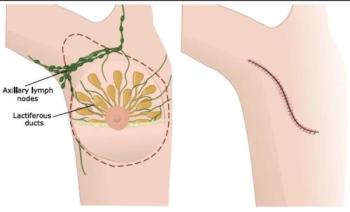
The AMAROS trial tested RT to the axillary lymph node against ALND to see if some of the morbidity associated with surgery for breast cancer could be avoided.
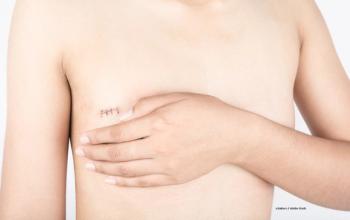
Unilateral or bilateral mastectomy can have a significant effect on quality of life when compared with breast-conserving surgery in young breast cancer survivors.
In patients with HER2-positive breast cancer treated with anthracyclines plus trastuzumab, can adding lisinopril or carvedilol reduce the risk of cardiotoxicity?

A study of a lifestyle intervention looked for improvement in disease-free or overall survival in early breast cancer patients.