Adding the chemotherapy docetaxel to active symptom control in advanced esophagogastric adenocarcinoma improves survival of patients. These are the results of the phase III COUGAR-02 trial.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Adding the chemotherapy docetaxel to active symptom control in advanced esophagogastric adenocarcinoma improves survival of patients. These are the results of the phase III COUGAR-02 trial.
The use of imatinib mesylate preoperatively for a maximum of 12 months resulted in a high rate of complete microscopic resection in a group of patients with marginally resectable gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), according to the results of a phase II trial.

Using a large genome-wide study of more than 28,000 individuals, three new genetic links to colorectal cancer have been identified, holding the potential for new therapeutic targets.

Researchers have developed a relatively simple breath analysis testing volatile organic compounds that may one day be used as a way to screen for colorectal cancer.
A new study shows two chemotherapy drugs prevalent in the clinic-gemcitabine and 5-fluorouracil-may influence the immune response in a way that facilitates tumor growth.

Colon cancer patients whose diet consists more of carbohydrates and foods that cause high blood-sugar levels had an increased risk of cancer recurrence and death, according to a new study.

We describe areas where major inroads were initially achieved by targeting angiogenesis and by unraveling pathways in the heterogeneous tumors of mesenchymal origin-spurred by the identification of c-Kit–activating mutations in GIST and the regressions that ensued when tumors harboring these mutations were exposed to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (Gleevec).
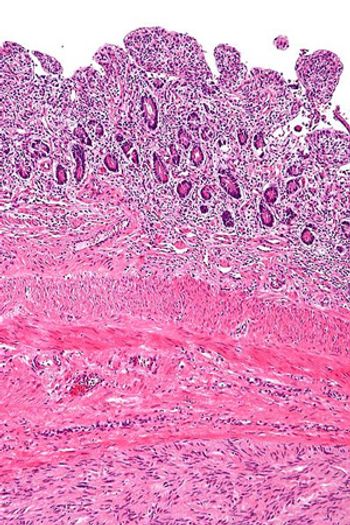
Treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) with regorafenib after prior treatment failure with both imatinib and sunitinib resulted in a PFS survival benefit for patients across all prespecified subgroups.

Maintenance therapy with a new immunomodulator agent called MGN1703 improves progression-free survival over placebo in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, according to a new study presented at the ESMO 2012 Congress.

The FDA has approved the multikinase inhibitor regorafenib (Stivarga) to treat patients with colorectal cancer that has metastasized following previous treatment.
A new oral treatment is showing promise in relapsed, refractory colorectal cancer. Patients given TAS-102, an antitumor agent, showed improved survival and reduced risk of death compared to those given a placebo.
Researchers in Germany have found that longer-term follow-up would still lower risk of colorectal cancer development among patients who had an adenoma detected and removed.

As we look forward, we suggest that the priority should be to further our understanding of the tumor’s interactions with its microenvironment and with the immune system. We think that such an understanding will be critical for advances in locally advanced rectal cancer therapy.

The preferred integrated treatment modality for locally advanced rectal cancer is preoperative radio(chemo)therapy followed by total mesorectal excision, though certain aspects of this standard are still debated.

The FDA has approved aflibercept (Zaltrap) to be used with the chemotherapy regimen FOLFIRI in the treatment of adults with metastatic colorectal cancer.

CancerNetwork discusses the diagnosis and treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer with Dr. Diane Simeone, who is involved in both pancreatic cancer clinical trials as well as research to better characterize important pancreatic cancer pathways and identify biomarkers for the disease.

Schrader and colleagues provide four compelling examples of the power of genetic testing to impact medical management for probands and their family members.

In 2002, the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) established the Cancer Prevention Committee (CAPC), which was formed in the hope of ensuring the integration of cancer prevention into oncology practice and research.[1]

In this article, we use a case-based approach to focus on the hereditary aspects of the most common GI cancers, including pancreatic, gastric, and colon cancer.

Though the calcium-dependent chloride channel DOG1 is strongly expressed in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), a new laboratory study suggests that methods targeting it for therapies in treating these cancers are still a ways off.

Treatment with tremelimumab stabilized patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma due to chronic hepatitis C infection for more than 12 months, according to data from a phase II clinical trial presented at the AACR annual meeting.

Three papers published today show that aspirin, taken daily, may prevent cancer, and could even treat certain cancers.

This article reviews the main issues that must be considered in metastatic colorectal cancer from the surgical oncology and medical oncology perspectives, respectively.

Combined-modality therapy has rendered disease-free an increasing number of patients who were previously considered to be incurable. Still, despite myriad advances in imaging, and in surgical and therapeutic modalities, many patients who undergo resection of limited metastatic disease with curative intent ultimately relapse.

In their article in this issue of ONCOLOGY, authors Bartlett and Chu discuss a very provocative suggestion that the possibility exists to cure patients with advanced colorectal cancer.