
In the VICTOR trial, patients with PI3KCA-positive colorectal cancer who took aspirin had a lower cancer recurrence compared to those with a wild-type PI3KCA gene.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


In the VICTOR trial, patients with PI3KCA-positive colorectal cancer who took aspirin had a lower cancer recurrence compared to those with a wild-type PI3KCA gene.

The use of a centralized nurse-led telephone-based care coordination system failed to improve outcomes including quality of life, unmet supportive needs or visits to the emergency department after surgical resection of colorectal cancer, according to the results of a new study.

Two separate studies have found direct evidence that F. nucleatum, a bacteria found in the mouth and in periodontal plaques, promotes growth of colorectal tumors.

At this juncture, various commercially available assays for colon cancer may be of little added value, and accelerated biomarker development with clinical validation is desperately needed.

In this review, we will discuss adjuvant chemotherapy in non-metastatic colon cancer, the existing prognostic and predictive molecular biomarkers in the field, and how to integrate these molecular biomarkers into the decision about whether to administer adjuvant therapy.

A new endoscopy technology called photometric stereo endoscopy, which captures the topography of the colon surface to create a 3D image, could be a more robust way to screen for precancerous lesions of the colon.
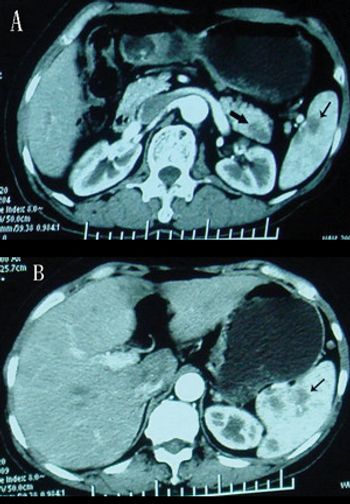
The patient is an otherwise healthy 45-year-old female who presented to her primary care physician with 6 weeks of increasing left upper quadrant abdominal pain with radiation to the back. She underwent an abdominal ultrasound, which revealed a large cystic abdominal mass.

In this interview we discuss the role of aspirin in colorectal cancer prevention and treatment. Various studies have suggested that a daily aspirin pill can help prevent certain types of cancers. Other studies suggest that there may even be a role for aspirin in treating cancer.

A study of colorectal cancer survivors shows those who consume higher amounts of red and processed meats before a colorectal cancer diagnosis are at higher risk of death from any cause compared to those who eat less of both types of meat.

An analysis of two colorectal cancer studies found that patients with BRAF mutations were less sensitive to the effects of aspirin as treatment or prevention.
Results from the German AIO KRK-0306 study, FIRE-3, show that the addition of cetuximab (Erbitux) to chemotherapy rather than bevacizumab (Avastin) increased overall survival by nearly 4 months in patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer.

In this interview we discuss the advances in treatment for colorectal cancer, as well as ongoing developments to find new and better therapies to treat this type of cancer.

A large study shows that middle-age men engaged in lots of cardiovascular exercise have a reduced risk of developing and dying from lung and colorectal cancer.
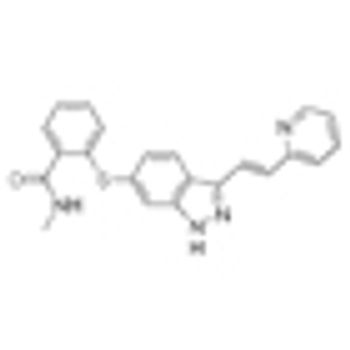
Adding the VEGF inhibitor axitinib to first-line treatment of FOLFOX-6 for metastatic colorectal cancer failed to improve progression-free and overall survival.
Women diagnosed with endometrial cancer at age 50 or younger had a fourfold increased risk for a subsequent colorectal cancer diagnosis, according to a historical cohort study published recently in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
A majority of patients on imatinib for treatment of GIST or CML had low or absent levels of osteocalcin, a bone marker secreted by osteoblasts, and about 50% of patients had a decrease in bone mineral density, signaling that long-term treatment may affect bone health in these patients.

Patients with stage III colon cancer who have a history of smoking are more likely to have worse outcomes, according to a large, randomized phase III trial result.

Limited surgical resection of duodenal gastrointestinal stromal tumors resulted in positive outcomes for both local and systemic disease-free survival, according to the results of a small study.
Using blood samples of pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis patients, researchers in Japan have developed a metabolomics-based test that may be an easy and noninvasive way to detect pancreatic cancer.

This review covers symptoms and complications in patients with late-stage pancreatic cancer, including venous thromboembolism, anorexia-cachexia, pain, and depression.

Optimal supportive care for patients with pancreatic cancer is essential. Putting these interventions into practice requires that oncologists and oncology teams incorporate innovations at both the individual and the system level.

FDA approval of palliative chemotherapy is largely based on disease-free and overall survival, quality of life, and symptom reduction; the latter should be routinely measured by the treating oncologist. Physician assessments of symptoms underreport symptom severity compared to patient-reported symptom assessments.

Colorectal cancer patients testing positive for Lynch Syndrome on MSI and IHC were most likely to seek genetic counseling when contacted by a genetic counselor.

In a new study, researchers found that higher body mass index was associated with a risk of CTNNB1-negative colorectal cancer, while higher physical activity was associated with a lower risk for this type of disease.

The US Food and Drug Administration approved the multi-kinase inhibitor regorafenib (Stivarga) yesterday, for the treatment of patients with unresectable metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) that no longer respond to imatinib and sunitinib.