
Developing a scoring system for staging patients with hepatic colorectal metastases is important for prognosis and for identifying those who will benefit from additional systemic therapy.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Developing a scoring system for staging patients with hepatic colorectal metastases is important for prognosis and for identifying those who will benefit from additional systemic therapy.

Due to advances in chemotherapy, biologic therapy, and the development of liver-oriented treatment options, the survival of patients with metastatic cancer has more than doubled, and increasing numbers of patients have been cured, even among those with advanced disease.
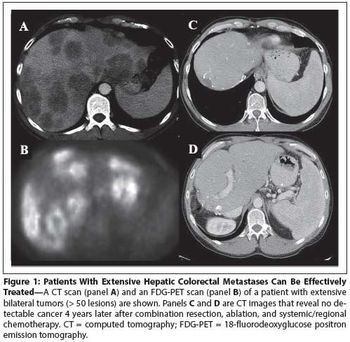
This article will review the current practice of hepatic resection for colorectal liver metastases, including the possibility of combined resection of hepatic metastases at the time of resection of the primary cancer.

Survivors of multiple myeloma and pancreatic cancer may have some of the poorest physical health-related quality of life outcomes, according to a new study.

The FDA approved ramucirumab (Cyramza) in combination with paclitaxel for treating patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.
About 9% of pancreatic cancer cases appear to be familial, and the risk of cancer in relatives of these patients does not appear limited to the pancreas.
People who underwent genetic and environmental risk assessment evaluating their colorectal cancer risk were no more likely to undergo screening for the disease.

Only 14% of newly diagnosed lung or colorectal cancer patients reported discussing clinical trial participation with their physician, and fewer participated.
In 2008, 770,000 out of 989,000 gastric cancer cases worldwide were attributed to H pylori, suggesting eradication could yield drastic reductions in incidence.

Adopting a combination of five healthy behaviors is linked to a reduction in the risk of developing colorectal cancer, according to the results of a study.

The management of rectal cancer in patients with metastatic disease at presentation is highly variable. Although chemoradiation is standard for patients with stage II/III rectal cancer, its role in the metastatic setting is controversial.

The management of colorectal cancer is a complex endeavor that requires treatment individualization founded on molecular characterization of the tumor, an in-depth understanding of the patient, and an appreciation of the interaction between the two.

A 35-year study of males in Sweden found a link between obesity and inflammation during adolescence and a risk for colorectal cancer in adulthood.
In a recent study, researchers found that certain amino acids in the blood were associated with a twofold increased risk of a pancreatic cancer diagnosis.
Two French studies have shown that screening for colorectal cancer with fecal occult blood tests can be very effective, according to results presented at the ESMO 2014 Congress.
Expression of the protein ALDH1A1 is associated with outcomes in gastric cancer, according to a new study, and could be used as a prognostic tool.

In spite of recent encouraging developments in the setting of GI neuroendocrine tumors, many clinical questions remain to be answered and will be highlighted in this commentary.

The relative abundance of new data on the biological underpinnings of neuroendocrine tumors, combined with clinical trial data supporting new treatment options, is a clear sign of progress. Yet, as is so often the case, these recent studies have generated a multitude of new and different questions.
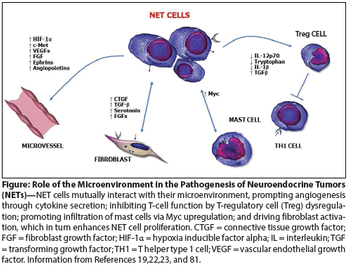
In this review, we summarize biologic, pathologic, and clinical aspects of gastroenteropancreatic-neuroendocrine tumors, focusing on recent advances in their treatment.
In a preliminary study using a mouse model, researchers found that vagal denervation using Botox or other methods could help slow gastric cancer’s growth.
Adding cetuximab (Erbitux) to the standard first-line FOLFIRI chemotherapy regimen results in longer overall survival in metastatic colorectal cancer patients.
A systematic, best-practice approach to colorectal surgery can decrease the risk of surgical site infections, according to a new study.

Measuring expression of several microRNAs were significantly predictive of complete pathologic response to treatment in patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma.
The stage of esophageal adenocarcinomas after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is predictive of outcomes, rather than the stage determined prior to therapy.

This article discusses features that predict local recurrence and distant metastasis in rectal cancer, and how to use MRI to guide treatment decisions.