
Points made in commentaries on “Colorectal Cancer: How Emerging Molecular Understanding Affects Treatment Decisions” are addressed by authors Hubbard and Grothey.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Points made in commentaries on “Colorectal Cancer: How Emerging Molecular Understanding Affects Treatment Decisions” are addressed by authors Hubbard and Grothey.

A new study shows that people with high levels of the 15-PGDH enzyme who used aspirin regularly were half as likely to be diagnosed with colorectal cancer.

The FDA has approved the angiogenesis inhibitor ramucirumab for the treatment of gastric cancer and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.

We have yet to establish a standard practice for maintenance therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Of course, ideally we could find a biomarker of benefit for patients who should be managed this way, but thus far we have had no such luck.

The addition of cetuximab to chemotherapy containing oxaliplatin and fluorouracil resulted in a significantly shorter progression-free survival in patients with operable KRAS exon 2 wild-type colorectal cancer liver metastases, according to results of a recent study.

The greater distance a patient had to travel to reach a diagnosing facility the more likely that patient was to present with a higher stage disease of colon cancer, according to the results of a recent study.

A high body mass index prior to a colorectal cancer diagnosis is linked to a higher risk of death, even when the patient’s tumor type is generally associated with a better prognosis.
Pathologic and molecular features of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) were generally not correlated with outcome in a study involving adjuvant imatinib therapy following resection of the primary tumor.

A new study reports that a multitarget stool DNA test is sensitive and accurate and is an improvement over previous DNA stool-based detection tests.
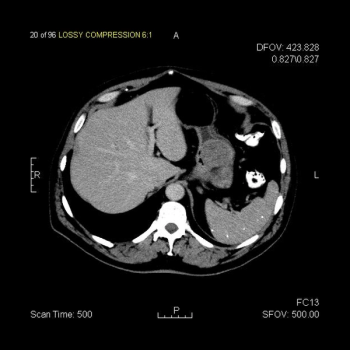
This slide show features a CT image, and pathology images of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) arising in the stomach using H&E, CD34, and c-Kit staining.

The rates of colon cancer in US adults aged 50 and older have decreased by 3% per year over the last 10 years, with the largest decrease seen in those over the age of 65.
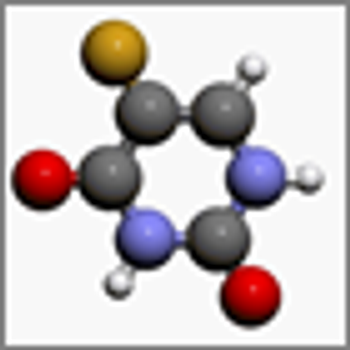
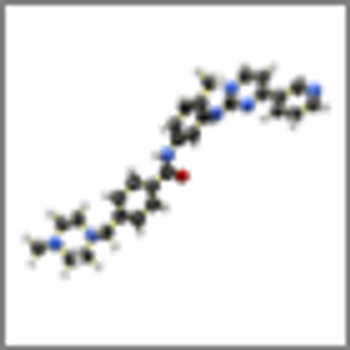
Current evidence suggests that only four DPYD and TYMS variants should make up the panel of genetic biomarkers for testing for toxicity to capecitabine monotherapy, according to the results of a recent study.
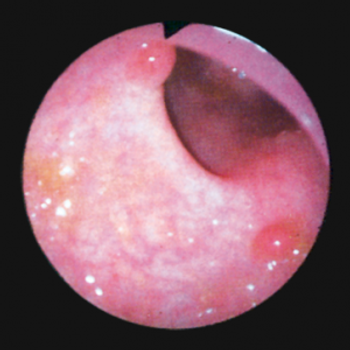
The use of full-spectrum colonoscopy significantly decreased the number of adenomas missed during an examination compared with the use of forward-viewing colonoscopy, according to the results of an international, multicenter study.

A recent exploratory study found that GIST cells showed unexpected sensitivity to certain kinds of chemotherapy drugs not typically associated with the diseases’ treatment.
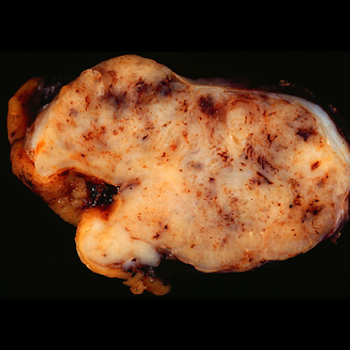
The results of a retrospective study indicated that patients with metastatic GIST who are able to achieve complete macroscopic surgical resection of their disease may be able to achieve long-term survival.

The preoperative diagnosis of combined gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) and gastric cancer is often missed, according to the results of a recent study.

Proteomic cyst fluid mucin profiling may serve as an accurate diagnostic tool for the identification of pancreatic cancer precursor lesions, according to the results of a recently published study.
Using two new diagnostic panels based on microRNA in whole blood, researchers were able to distinguish patients with pancreatic cancer from healthy control patients.

Molecularly profiling colorectal cancer has opened many potential opportunities for the use of this information in therapeutic decision-making. However, at present, only RAS testing in the metastatic setting has a definitive place in the decision-making paradigm.
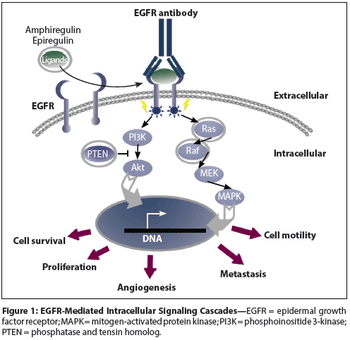
In this review we discuss the current treatment options in metastatic colon cancer, with a special focus on biologic agents and how molecular understanding guides treatment decisions.

It was originally hoped that the presence of mutations in KRAS and other related genes would provide an easy answer as to whether to administer anti-EGFR antibody therapy to a given metastatic colorectal cancer patient. However, in nature nothing is simple, and there are a number of issues that practicing clinicians should be made aware of.

Progress in the area of targeted therapies for colorectal cancer has come slowly and with some difficulty.

In this interview, we discuss the current state of pancreatic cancer management, and look toward trials to further define the best course of treatment for this deadly disease.
Patients with heavily pretreated metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors were able to tolerate combined treatment with the pan-deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat and imatinib, according to the results of a small phase I study.

As part of our coverage of the 2014 ASCO GI Symposium, we highlight some of the most interesting trials presented at this year's meeting.