
Both radiofrequency ablation and stereotactic body radiotherapy are effective in the treatment of inoperable, non-metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Both radiofrequency ablation and stereotactic body radiotherapy are effective in the treatment of inoperable, non-metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma.

A program implemented in New York City successfully increased colorectal cancer screening rates and diminished racial and ethnic disparities in screening.

A retrospective cohort study showed that socioeconomic variables including race, marital status, insurance status, and geography are associated with rates of resection for early-stage pancreatic cancer. Most of these factors, however, were not associated with survival following resection.

A meta-analysis found that a number of dietary factors play a role in the risk of developing gastric cancer, with protective effects seen with fruit and certain vegetables and increased risk seen with high-salt foods and certain forms of alcohol.

Imatinib had no impact on failure-free or overall survival in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor, but it did have an effect on relapse-free survival.

Reaching out to underserved populations about colorectal cancer screening using mailed invitations resulted in significantly improved colorectal cancer screening rates in a recently published study.

Adding the EGFR-targeting drug panitumumab to chemotherapy had no effect on survival in a group of patients with wild-type KRAS status advanced biliary tract cancer.
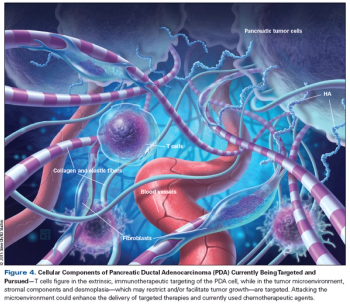
This article reviews the current treatment paradigms for metastatic disease, focusing on ways to ameliorate symptoms and lengthen survival. We then summarize recent advances in our understanding of the molecular and cellular aspects of pancreatic cancer.

The ultimate benefit to patients will come from a demonstration of clinically worthwhile benefits of new drugs that have been tested in well-designed and adequately powered clinical trials performed in an expedited fashion.

Patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and a low BMI were at higher risk for disease progression and death; this risk did not affect those with a high BMI.

The FDA has approved the combination of irinotecan liposome injection plus 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer in patients who previously progressed on gemcitabine-based chemotherapy.

Patients with a prior history of colorectal adenomas saw no reduction in the risk for recurrence with the use of a daily supplement of vitamin D, calcium, or both.

Minimally invasive laparoscopic-assisted surgery did not result in better outcomes compared to open surgery for rectal cancer, according to two clinical trials.

A study showed that tumors of younger patients with early-onset colorectal cancer differ from the tumors of those diagnosed later in life, both genetically and epigenetically.

Blocking the MAPK pathway through treatment with dabrafenib and trametinib resulted in meaningful clinical activity in a subset of patients with BRAF V600-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer.
The USPSTF recently issued a draft recommendation advising the use of aspirin to prevent cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer in certain patients aged 50 to 69 years.
A payment system for colonoscopies offering full insurance coverage at low-priced facilities and cost sharing at high-priced alternatives reduced spending with no increase in complications.

Treatment with the PARP inhibitor olaparib plus paclitaxel resulted in an overall survival benefit in patients with metastatic gastric cancer.

Consumption of four or more cups of coffee a day was associated with a reduced risk for colon cancer recurrence and death in patients with stage III disease.
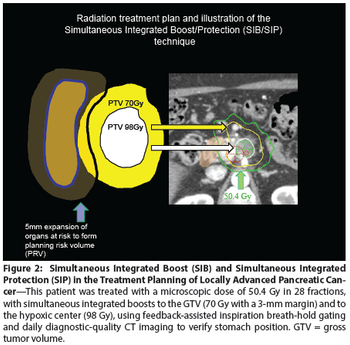
Five randomized trials involving patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer illustrate most clearly the substantial degree to which standard therapies are limited in their effectiveness.

For resectable gastric cancer, perioperative chemotherapy or adjuvant chemoradiation with chemotherapy are standards of care. The decision making for adjuvant therapeutic management can depend on the stage of the cancer, lymph node positivity, and extent of surgical resection.

A new scoring system may help to identify patients at low risk for colorectal cancer who could forego screening with colonoscopy.

Long-term results of the CROSS study have confirmed that neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy added to surgery should be the standard of care in esophageal or esophagogastric junction carcinoma.

Patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer at younger ages are more likely to have an underlying hereditary syndrome than older patients, according to a new study.

The use of BEAMing technology on circulating DNA to identify multiple mutations in real time could help guide treatment in colorectal cancer patients.