
This video covers the latest research in pancreatic cancer, including the possible role of PARP inhibitors, immunotherapy, and the novel drug PEGPH20.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!

Recent improvements in our understanding of the biology of colorectal cancer have led to the identification of several important prognostic and predictive markers of disease-associated risk and treatment response for the individual patient.

This video covers the latest research in pancreatic cancer, including the possible role of PARP inhibitors, immunotherapy, and the novel drug PEGPH20.

Young men who are overweight or obese are at risk of developing severe liver disease or liver cancer in later life, particularly those who have type 2 diabetes mellitus.

In this interview we discuss the role of genetic testing in patients with colon cancer.

A novel calculator can more easily identify which esophageal adenocarcinoma patients derive an overall survival benefit from neoadjuvant chemoradiation to help guide treatment choices.

No difference in time to recurrence, recurrence-free survival, or overall survival were noted for patients with rectal cancer who underwent one of three different preoperative radiotherapy regimens.
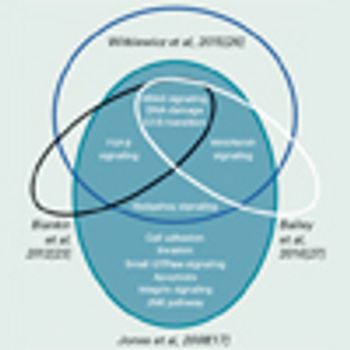
In this article, we review seminal articles that have evaluated the molecular architecture of pancreatic cancer. We compare the methods used and the molecular subtypes defined, and assess the predominant subgroups in order to better understand which therapies may improve patient outcomes.

Completing a course of preoperative radiotherapy prior to undergoing surgical resection for rectal cancer was associated with improved survival compared with patients who had an incomplete course of radiotherapy.

This video examines the promise of recent trials studying single-agent immunotherapy as well as ongoing trials testing combinations of immune-checkpoint inhibition.

This video reviews the standard of care for locally advanced anal carcinoma, examines new trials studying novel agents and immunotherapy in the advanced setting, and highlights the need for HPV vaccination for preventing the disease.

Overweight individuals in early adulthood who gained additional weight to become obese later in life are at an increased risk for esophageal and gastric cardia adenocarcinomas.

This video examines current options for the treatment of midgut neuroendocrine tumors and highlights results of the NETTER-1 trial.

The onset of diabetes or the rapid deterioration of existing diabetes may be an early signal for pancreatic cancer for some patients, according to the results of a study presented at the European Cancer Congress.

This video examines the results of a prospective study that looked at associations between survival outcomes and fish and omega-3 fatty acid intake among colon cancer patients.

Young and middle-aged patients diagnosed with colon cancer were more likely to receive postoperative chemotherapy compared with their older-age counterparts, according to the results from a recent cohort study.

A study found that normal-weight women should be evaluated for metabolic health to reduce their risk for colorectal cancer.

This video examines a population-based study that examined colorectal cancer mortality and gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with long-term use of low-dose aspirin.

This video examines a pair of studies that looked at molecular variances and clinical differences between left-sided colon and rectal cancers.

The immune checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab showed durable responses and disease control in a group of heavily pretreated patients with DNA mismatch repair deficient/microsatellite instability high (MSI-H) metastatic colorectal cancer.

Using immunohistochemistry to measure the expression of certain target enzymes-cox-2 and 15-prostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH)-in premalignant colorectal adenomas, researchers were able to get significant predictive and prognostic information in patients treated with the cox-2 inhibitor celecoxib for prevention of colorectal adenomas.

The addition of the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib to irinotecan and cetuximab prolonged progression-free survival and resulted in a higher disease control rate than treatment with irinotecan and cetuximab alone in patients with BRAF-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer.

Adjuvant chemotherapy for biliary tract cancer using GEMOX (gemcitabine/oxaliplatin) was feasible, but did not result in an improved recurrence-free survival or quality of life compared with surveillance in the phase III PRODIGE 12-ACCORD 18 trial.

This video covers results of the SWOG 1406 study, which tested the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib in combination with irinotecan and cetuximab for patients with metastatic, BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer.

Use of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) was equally effective as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as a method of bridge to transplant among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.

This video examines results of the CHARTA trial, which tested first-line FOLFOX plus bevacizumab with or without irinotecan in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.

This video examines an exploratory analysis of the RESORCE trial, which tested regorafenib vs placebo in hepatocellular carcinoma patients following radiographic progression on sorafenib.