
Regular use of aspirin may reduce the risk of developing cholangiocarcinoma, according to the results of a new study.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!



Regular use of aspirin may reduce the risk of developing cholangiocarcinoma, according to the results of a new study.

Annual screening of people at high risk for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) because of CDKN2A mutations was relatively successful and allowed for the detection of disease in time to perform surgery.

The use of a noninvasive colorectal cancer screening test called a multi-target stool DNA test (mt-sDNA) detected the disease in patients who had previously avoided more invasive screening procedures.

Researchers have identified two species of bacteria linked with periodontal disease in healthy individuals that are associated with a risk of developing pancreatic cancer.

Drinking coffee resulted in a more than 25% decreased risk for developing colorectal cancer, according to the results of a new study.

Researchers from the National Cancer Institute are predicting that the rate of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the United States will likely decrease by the year 2030.

Higher preoperative levels of serum albumin were significantly associated with greater overall survival among patients undergoing resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
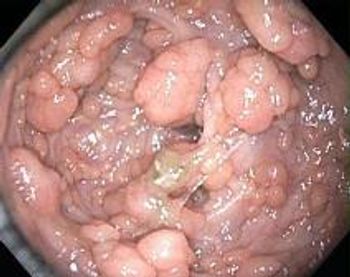
The combination use of sulindac and erlotinib significantly reduced the number of small intestine, or duodenal, polyps present in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis.
Results of a new Swedish study have shown that a surgeon needed to perform at least 15 esophagectomies in cancer patients in order to achieve stable survival results in the first months after the operation.

An integrated genomic analysis has found that pancreatic cancer can be divided into four specific subtypes based on molecular characteristics. This division could help guide treatment decisions and future research avenues into this difficult malignancy.

US-born Hispanics are more likely to get hepatocellular carcinoma and to die from chronic liver disease compared with their foreign-born counterparts.
Regular use of aspirin has been linked with a small but significant reduction in the risk for overall cancer, and especially gastrointestinal cancers.

The addition of selective internal radiation therapy with yttrium-90 resin microspheres to standard FOLFOX chemotherapy did not improve progression-free survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, but it did significantly delay disease progression in the liver.

High expression levels of EGFR ligands epiregulin and amphiregulin are associated with increased benefit from panitumumab in patients with RAS wildtype advanced colorectal cancer.

A combination of four biomarkers may be able to help clinicians identify patients who have a high-risk type of colorectal cancer.

Pancreatic cancer patients who received adjuvant therapy at a high-volume center had superior overall survival vs patients who were treated in a community setting.

Nanoliposomal irinotecan combined with fluorouracil/leucovorin improved overall survival in metastatic pancreatic cancer patients who have already been treated with gemcitabine.

A short-course of preoperative radiation therapy plus consolidated chemotherapy was shown to be as effective as standard preoperative chemoradiation in the treatment of locally advanced rectal cancer.

Everolimus improved progression-free survival by 6 to 8 months compared with placebo in patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract.

A novel drug, 177Lutetium-DOTATATE (Lutathera), significantly lowered the risk for disease progression or death among patients with previously treated, advanced midgut neuroendocrine tumors.

Here, we review the studies that have explored different treatment regimens, therapeutic sequencing, and biologic inclusions for the treatment of these patients, with neoadjuvant intent. We also describe how we have established our own treatment paradigm for the management of potentially curable metastatic colorectal cancer.

Although immunotherapy is not yet approved for the treatment of gastrointestinal cancers, it is already clear that many gastrointestinal cancers can be sensitive to it. We will review recent clinical trial results demonstrating this, and offer our perspective on the role that immunotherapy might play in the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal malignancies in the years ahead.

Advanced gastrointestinal malignancies are a major oncologic challenge for which successful durable personalized therapies are currently lacking.

It remains difficult to decipher which patients are appropriate candidates for conversion therapy vs upfront surgery. Therefore, in predicting potential outcomes, several factors should be considered. Here, we will attempt to address such factors and provide insights.

In all other settings, giving chemotherapy just to make us feel better emotionally in exchange for potential harm to the patient is not the right strategy. We need to find better treatments for this new clinical indication.