Pembrolizumab also demonstrated a disease-free survival benefit vs placebo for patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Pembrolizumab also demonstrated a disease-free survival benefit vs placebo for patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.
Phase 2 findings support nana-val as a promising treatment option for those with EBV-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma.

“If you were to ask me what the 1 magic thing would be, it would be that we would adopt a concept of 1 team, one fight nationally, and that we would be able to have our structures and our coordination of care.”

Results from the INSITE trial support the utility of pegulicianine fluorescence-guided surgery during breast cancer surgery.
Patients who are African American appeared to have worse clinical stages of colon and rectal cancer during surgery in 2020.
TLX101 is currently under assessment as a treatment for glioma in the IPAX-2 and IPAX-Linz studies.

The recent Hot Topics section focuses on survival rates for patients with cholangiocarcinoma.
Molecular profiling is a tool that can best determine first-line therapy options for patients with advanced RCC.
An increased TIL count in the breast tissue was associated with improved distant recurrence-free survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer.
Patients who are predisposed to medullary thyroid cancer should be advised against the use of GLP1 agents.
The phase 3 TOPAZ-1 trial of durvalumab plus chemotherapy showed a significant benefit vs chemotherapy alone for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer.

Clinicians are learning how to identify adverse effects relating to either immunotherapy or tyrosine kinase inhibitors for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.
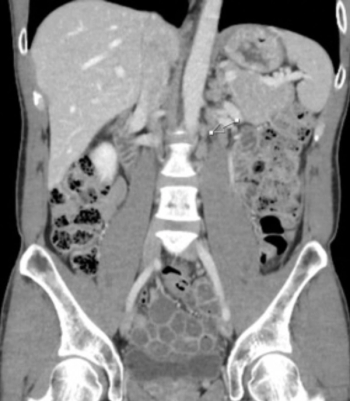
The clinical quandary by Langer et al discusses a contralateral late relapse of the original right nonseminomatous germ cell tumors.

Moshe Ornstein, MD, discusses the heterogeneous population that comprise patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Several presentations from the 41st Annual Miami Breast Cancer Conference focused on new and evolving data in the space, according to Neil M. Iyengar, MD.
Additional data and results from the phase 3 STARGLO trial of glofitamab for patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma will be presented at an upcoming medical meeting.
Sacituzumab tirumotecan elicited responses prominently in the second- and third-line and beyond setting and in those with high TROP2 expression.

Experts discuss findings related to gastrointestinal cancer outcomes as well as treatment inequalities presented at the 2024 SSO Annual Meeting.

HR001 was found to have an efficacious response for patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma.

A proteogenomic analysis found savolitinib plus osimertinib elicited a response in patients with EGFR-mutated, MET-amplified advanced NSCLC.

Pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma were less likely to have severe COVID-19 infection.

Minimal residual disease can now be considered an end point in trials leading to accelerated approvals by the FDA for multiple myeloma.

LYT-200 is currently being investigated for those with solid tumors and hematologic malignancies.
Phase 2 findings support olutasidenib as a potentially “valuable” treatment option in IDH1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia.
Microwave ablation may be a go-to treatment option instead of surgery for patients with multifocal T1N0M0 papillary thyroid cancer.
Oncologic outcomes from a real-world analysis appear to be comparable with those observed in the sentinel lymph node biopsy arm of the SOUND trial.
The National Accreditation Program for Breast Centers looked at time intervals to see where delays occurred throughout the process for those with breast cancer.
Young patients with breast cancer were more likely to be the reason for diagnostic delays vs system delays, partly due to less concern for their symptoms.