Patients with nonmetastatic esophageal cancer who received FLOT chemotherapy achieved a 3-year OS rate of 61.1% in an analysis of the phase 3 ESOPEC trial.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Patients with nonmetastatic esophageal cancer who received FLOT chemotherapy achieved a 3-year OS rate of 61.1% in an analysis of the phase 3 ESOPEC trial.
Researchers developed a CAR T-cell therapy to target CAIX/CD70 overexpression for patients with clear cell RCC.
A new biomarker, KIM-1, has the potential to show outcomes and response for patients with renal cell carcinoma.
Patients with RCC who received 100 mg once daily casdatifan had an ORR of 33%, and those who received casdatifan plus cabozantinib had an ORR of 46%.

Results from a Q-TWiST analysis of the LITESPARK-005 trial showed a trend favoring belzutifan over everolimus for patients with clear cell RCC.
Data from the KEYNOTE-B61 trial demonstrate antitumor activity across histologic subtypes, including those with papillary and chromophobe disease.
The regulatory decision is based on data from the phase 3 DESTINY-Breast09 results presented at the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting.
Stereotactic body radiotherapy is less expensive and has demonstrated an improved safety profile vs immunotherapy and tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Data from a Q-TWiST analysis of the LITESPARK-005 trial provide additional evidence for the use of belzutifan in those with advanced renal cell carcinoma.
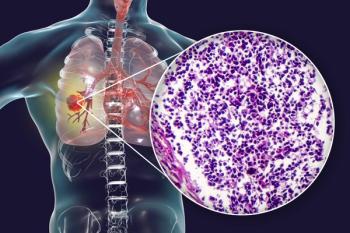
The investigational agent showed particularly strong efficacy in an ES-SCLC subgroup, with a chemotherapy-free interval of 90 or more days.

With the recent approvals of T-DXd and Dato-DXd, the care for breast cancer continues to evolve and expand.

ODAC voted against the favorability of the agent in combination with dexamethasone and pomalidomide or bortezomib in multiple myeloma.
Phase 2b SunRISe-1 trial findings supported the FDA to grant priority review to TAR-200 in BCG-unresponsive high-risk NMIBC with carcinoma in situ.
Particularly strong efficacy signals were observed in patients with non-squamous non–small cell lung cancer previously treated with PD-1 inhibition.

Paolo Tarantino, MD, PhD, discusses sequencing ADCs, managing cross-resistance, and understanding ADC composition for patients with breast cancer.

Erika Hamilton, MD, gave an overview of evolving therapies and recent trial updates for patients across breast cancer subtypes.

Combining ADCs has shown a potential improvement in survival, but it may also come with increased toxicities.

No dose-limiting toxicities or unexpected adverse effects occurred with carotuximab/apalutamide in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
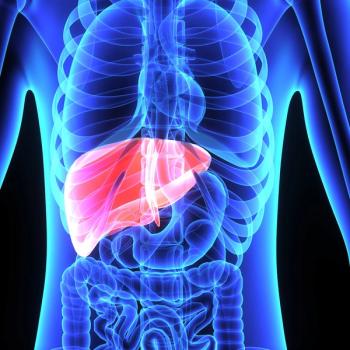
Transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib did not significantly improve overall survival in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma vs sorafenib alone.
The FDA has asked tambiciclib’s developer to start a trial investigating the combination in front-line acute myeloid leukemia.
Investigators are evaluating ZEN-3694 in combination with abemaciclib or cisplatin/etoposide across 2 clinical trials in NUT carcinoma.

Cross-resistance makes it important to determine sequencing options across antibody-drug conjugates for patients with breast cancer.

Patients with node-negative disease who are older and have comorbidities may not be suitable to receive CDK4/6 inhibitors.

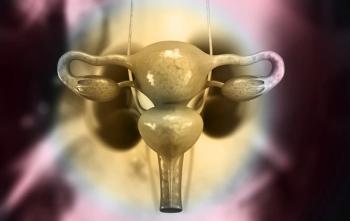
Relacorilant plus nab-paclitaxel led to a median PFS and OS of 6.54 months and 15.97 months, respectively, in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer.
The confirmed objective response rate among 56 patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer was 87.5%, all of whom experienced partial responses.
The FDA lifted a clinical hold on a new drug application for tabelecleucel as a treatment for EBV-positive lymphoproliferative disease in May 2025.

Heather McArthur, MD, focused on current and future strategies for treating early-stage breast cancer.

An observed carryover effect with CDK4/6 inhibitors may reduce the risk of recurrence years after a patient stops treatment.