
Prostate tumors may not readily evolve from low to high grade, according to a new study. The results have important clinical implications for patients and clinicians when choosing active surveillance or treatment.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Prostate tumors may not readily evolve from low to high grade, according to a new study. The results have important clinical implications for patients and clinicians when choosing active surveillance or treatment.

Researchers have demonstrated that a two-step screening test can identify ovarian cancer early, before the disease progresses to an advanced, poor prognosis stage.

Two separate studies have found direct evidence that F. nucleatum, a bacteria found in the mouth and in periodontal plaques, promotes growth of colorectal tumors.

The long-term follow-up of the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial confirms that finasteride reduces the risk of low-grade prostate cancer by one-third, but there were no significant survival differences between the two study arms.
Use of calcium-channel blockers for treatment of high blood pressure for more than 10 years can increase the risk of breast cancer for women after menopause, a new study shows.

A new study demonstrates a way to exploit a metabolic vulnerability of senescent cells. The strategy provides evidence for an anticancer approach that targets a cellular process or condition of the cell rather than a distinct molecular pathway.

A new endoscopy technology called photometric stereo endoscopy, which captures the topography of the colon surface to create a 3D image, could be a more robust way to screen for precancerous lesions of the colon.

Both Internet and print-based decision aids equally helped men make important decisions related to prostate cancer screening, but did not affect actual screening rates.
A new study shows that the combination of digital mammography plus tomosynthesis results in fewer false positive results compared with digital mammography alone. Women under the age of 50 and those with dense breasts had the greatest benefit from the combined screening approach.
A meta-analysis by researchers in Australia shows that those infected with the human papillomavirus have a threefold higher risk of developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.

Using easy-to-obtain risk factors for breast, ovarian, and endometrial cancers, researchers have come up with models that can predict an individual woman’s absolute risk for developing each type of cancer.

The combination of the chemotherapy capecitabine with external beam radiation was found to be both safe and effective in treating pain from bone metastases in patients with advanced breast cancer.

A study published today has linked higher stature in women after menopause with a higher risk of developing any of 19 cancer types.

Researchers have identified pathways that are important for prostate cancer growth after the tumor becomes resistant to androgen therapies.

A large and prospective study shows that a high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids is linked to a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer.

The FDA approved afatinib (Gilotrif) as a first-line therapy for patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer whose tumors harbor certain mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor gene.
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) has updated its guidelines on treating women at high risk of developing breast cancer with pharmacologic drugs.
A pair of studies from the ASCO annual meeting examined bone metastases from lung cancer, with one study finding that survival in patients was poorer in patients with bone metastases, and another study finding that the development of bone metastases could predict subsequent development of metastasis in the brain.

The expression levels of two genes could indicate whether a woman with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer is at risk for recurrence after 5 years of tamoxifen therapy and should receive subsequent therapy.

A study of colorectal cancer survivors shows those who consume higher amounts of red and processed meats before a colorectal cancer diagnosis are at higher risk of death from any cause compared to those who eat less of both types of meat.

From 2004 to 2009, use of advanced treatment technologies increased among prostate cancer patients with low-risk disease and high risk of noncancer mortality.

An analysis of two colorectal cancer studies found that patients with BRAF mutations were less sensitive to the effects of aspirin as treatment or prevention.
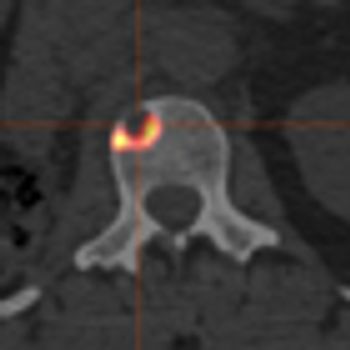
Bone metastases result in poorer outcomes for those patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), who were treated with a molecularly targeted therapy. The results were presented in two separate analyses at the annual ASCO meeting.
Researchers found that the more cost-effective option (surgery vs SBRT) in stage I lung cancer depends on whether the disease is clearly or marginally operable.
A new imaging approach, combining PET with magnetic resonance (MR), was shown to be more sensitive in detecting recurrent prostate cancer compared with PET/CT.
Phase II trial results of the targeted agent ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma show that the drug led to promising and durable responses.

In a new study presented at the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting, researchers using animal models show that early BPA exposure increases prostate cancer risk.

The first treatment for a rare tumor called giant-cell tumor of the bone has been approved by FDA. The approval of denosumab (Xgeva) was based on a priority FDA review.
Researchers from the Mayo Clinic have identified variants in two genes that result in a higher chance that tamoxifen or raloxifene will actually prevent breast cancer. More studies are needed, but if confirmed, women with these variants may be more likely to undergo the 5-year preventive regimen.
Recent studies suggest patients with bladder cancer are not receiving optimal care or the follow-up surveillance as recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN).