
The FDA approved the combination of nivolumab plus ipilimumab as a first-line treatment for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors express PD-L1 (≥1%), as determined by an FDA-approved test.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


The FDA approved the combination of nivolumab plus ipilimumab as a first-line treatment for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors express PD-L1 (≥1%), as determined by an FDA-approved test.

The FDA approved rucaparib for the treatment of adult patients with a deleterious BRCA mutation-associated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Results from this study demonstrated that patients with cancer had a significantly lower detection rate of SARS-COV2 antibodies 15 days or later after COVID-19 symptoms and RT-PCR-positive test than healthcare workers.

This study found that fine particulate matter pollution was associated with mortality in pediatric, adolescent, and young adult patients with specific cancers, suggesting a need to enforce air quality policies.

Pomalidomide was approved for patients with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma whose disease has become resistant to highly active antiretroviral therapy, or in patients with Kaposi sarcoma who are HIV-negative.
Researchers suggested that treatment-free remission may be successfully obtained with an effector-suppressor score which is calculated using absolute natural killer cells, FoxP3+ regulatory T cells, and monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells.
A phase II study presented at AACR found that the combination of atezolizumab plus cobimetinib improved cancer control in some patients with biliary tract cancer.
The phase II study found that nivolumab was well tolerated and demonstrated moderate efficacy with durable response in patients with refractory biliary tract cancer.
Researchers found that a high dose of CAR T-19 may be more effective than a low dose at inducing a complete response without excessive toxicity.
The oncology hematologist spoke about the guidelines she and her colleagues outlined regarding treating patients with hematologic malignancies during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The combination of tavo and pembrolizumab was associated with a higher than anticipated response rate in patients with advanced melanoma with low frequencies of checkpoint positive cytotoxic lymphocytes.
Researchers found that 2 studied strategies, which combined nivolumab and doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine, are feasible, highly effective, and result in excellent 12-month progression-free survival.
SGX301 is being evaluated for the treatment of patients with early-stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in the pivotal phase III FLASH study, which demonstrated that continued treatment twice weekly for 12 weeks increased the positive response rate.
The study, titled OLYMPUS, suggested that primary chemoablation of low-grade upper tract urothelial cancer with intracavitary UGN-101 resulted in clinically significant disease eradication.
Researchers indicated that targeted approaches to improving time from diagnosis to definitive surgery for black patients are essential in reducing racial disparities in melanoma outcomes.
The medical oncologist discussed reported outcomes of larotrectinib in patients with TRK fusion cancer by the number of lines of priory therapy or baseline status.

The FDA expanded the indication of olaparib to include a combination regimen with bevacizumab for the first-line maintenance treatment of adult patients with advanced epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer.
In this study, the feasibility and safety of DETECT-A coupled with PET-CT imaging to detect cancer was evaluated using a prospective, interventional study of 10,006 women not previously known to have cancer.

This study found that the consumption of antioxidants through dietary intake was correlated with reduced rates of infection or mucositis, with no increased risk of relapse or reduced survival.

Given these findings, researchers suggested that a better understanding of the quality of survivorship care that patients with suboptimal insurance receive could help determine how external factors may impact outcomes for these patients.
These findings suggest that patients with COVID-19 who do not require intensive care unit admission with total T-cell counts lower than 800/μL may still require urgent intervention.

The FDA granted accelerated approval to capmatinib for adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer.
The phase III UNITY-CLL trial evaluating the combination of umbralisib plus ublituximab met its primary endpoint at a prespecified interim analysis and will be stopped early for superior efficacy.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services issued a second interim final rule, which established new regulatory waivers and rule changes to increase flexibility for healthcare providers during the COVID-19 pandemic.
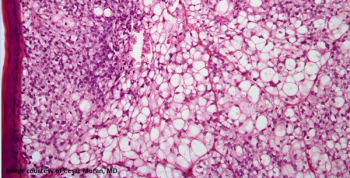
Cemiplimab showed clinically meaningful and durable responses in this group of patients for whom there are no currently approved treatments.

Baum spoke about the transition to telemedicine as a result of COVID-19 and the best practices for using the platform moving forward.
The first-in-human clinical trial for TruUCAR GC027 in relapsed or refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia was announced by Gracell Biotechnologies.
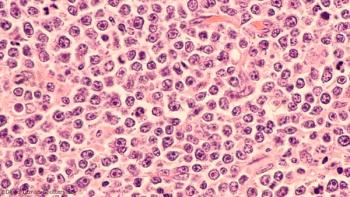
Hypercalcemia at diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma was found to be strongly correlated with adverse prognostic factors and a short diagnosis-to-treatment interval.

The FDA granted orphan drug designation to Ascentage Pharma’s HQP1351 for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia.

This study suggested that identifying which lung cancer screening options are generally more attractive to patients may increase screening.