Researchers in New York City reported a significant increase in case fatality in patients with cancer and COVID-19 compared with patients with COVID-19 who did not have cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Researchers in New York City reported a significant increase in case fatality in patients with cancer and COVID-19 compared with patients with COVID-19 who did not have cancer.

In this systematic review, researchers highlighted the strengths and weaknesses of existing decision aids for women with an average risk of breast cancer who are eligible for mammographic screening.
According to researchers, these observations suggest a potential need to modify the current framework for clinical risk disclosure.
Olaparib was found to be associated with longer progression-free survival and improved measures of response and patient-reported end points than either enzalutamide or abiraterone in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
The results from this random-effects meta-analysis suggested that dietary fiber intake may decrease the risk of breast cancer, including both premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancers.
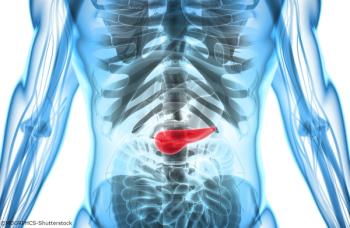
Researchers demonstrated that risk models that include established clinical, genetic, and circulating factors are better able to identify people at significantly higher than normal risk of pancreatic cancer over those using clinical factors alone.
In a webinar, a multidisciplinary team from Duke Cancer Center came together to discuss the differences in treating patients with genitourinary cancer as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.

The FDA approved the use of daratumumab and hyaluronidase-fihj (Darzalex Faspro) in adult patients with newly diagnosed or relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma.

The FDA granted priority review to a new drug application for CC-486 for the maintenance treatment of adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia based on efficacy and safety results from the pivotal phase III QUAZAR AML-001 study.
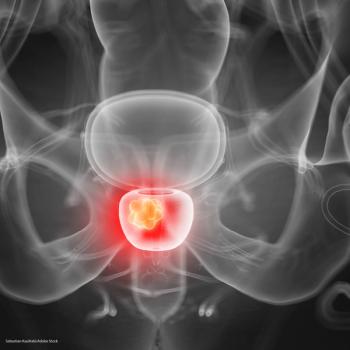
The model was able to use data from each treatment cycle to estimate intratumor subpopulations and accurately predict the outcomes in each subsequent cycle.
The study was presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Virtual Meeting 2020 and demonstrated encouraging preliminary antitumor activity with objective responses as a monotherapy and in combination with nivolumab.
These findings suggest that there are significant outcome inequalities for patients with small cell lung cancer which are relevant to the policy debate on Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act.
Given that thrombotic risk is significantly affected by race, researchers suggested that these findings may indicate that pulmonary vasculopathy may contribute to the unexplained differences in racial susceptibility to COVID-19 mortality.

This data analysis suggested that larotrectinib is highly effective in patients with NTRK gene fusions, however offered minimal benefit in patients with other non-fusion NTRK alterations.

The FDA approved niraparib for the maintenance treatment of adult patients with advanced epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who are in a complete or partial response to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy.
The multi-center trial is comprised of 2 phases, with phase I determining the maximum tolerated dose of palbociclib and phase II determining the clinical benefit rate of treatment with anastrozole, palbociclib, trastuzumab, and pertuzumab.
Interim data from cohort B of KEYNOTE-555, a phase I trial evaluating a 400 mg every 6-week dosing regimen of pembrolizumab in patients with metastatic melanoma, demonstrated a consistent benefit-risk profile.
Researchers analyzed pooled data from 159 patients enrolled in 3 larotrectinib trials to assess outcomes stratified by prior lines of therapy and ECOG performance status.
The breast cancer expert discussed the implications of this approval, as well as the data that led to the approval of sacituzumab govitecan-hziy.

The American Society of Clinical Oncology and its affiliate organization the Association for Clinical Oncology announced the results of a survey that focused on the changes in cancer care due to COVID-19.
The ongoing trial is treating patients with relapsed or refractory CLL/SLL or NHL who failed or were intolerant to 2 or more lines of established therapy, or for whom no other treatment options are available.
Updated interim results from the phase Ib/II CLASSICAL-Lung study showed promise for pepinemab in combination with avelumab in patients with advanced stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Encouraging interim data were reported from the ongoing phase I clinical trial of STRO-002 regarding safety and anti-tumor activity results in heavily pre-treated patients with ovarian cancer.
New clinical trial practices specific to cancer include new risk assessment strategies, decentralized and remote trial coordination, data collection, and delegation of specific therapeutic activities.

Data from the phase III REACH2 study indicated that ruxolitinib therapy led to significant improvements in efficacy outcomes in patients with steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease.

The study found that pembrolizumab has activity in brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer that is similar to its systemic activity and can result in prolonged survival in a subset of patients.
As prospective clinical trials continue to accrue data, the researchers indicated that this data may help clinicians in decision-making regarding adjuvant systemic therapy for patients with small HR-positive, ERBB2-positive breast cancers.
In this study, researchers found data that suggested immune suppression and increased infection could occur during the precancerous period.
This study found a substantial difference in the number of agents available for use in the metastatic and adjuvant settings for non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and colon cancer.
Results from the trial showed a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival with olaparib versus enzalutamide or abiraterone in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer selected for BRCA1/2 or ATM gene mutations.