
This video reviews the use of endoscopic therapy for the management of Barrett esophagus and early esophageal cancer.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


This video reviews the use of endoscopic therapy for the management of Barrett esophagus and early esophageal cancer.

Nurse practitioners play a central role in helping patients with esophageal cancer understand and manage their disease and treatment complications.

A novel calculator can more easily identify which esophageal adenocarcinoma patients derive an overall survival benefit from neoadjuvant chemoradiation to help guide treatment choices.

Overweight individuals in early adulthood who gained additional weight to become obese later in life are at an increased risk for esophageal and gastric cardia adenocarcinomas.

Ahead of the 2017 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancer Symposium in San Francisco, we spoke with Dr. Geoffrey Ku on the advances in systemic therapy for esophageal and gastric cancer.

Using PET scans during induction chemotherapy for esophageal cancer, researchers were able to assess patient response to treatment and adjust their therapy, leading to an improved rate of pathologic complete response prior to surgery.

Lymph node status after undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy and resection of esophagogastric cancer was the only independent predictor of survival.
Results of a new Swedish study have shown that a surgeon needed to perform at least 15 esophagectomies in cancer patients in order to achieve stable survival results in the first months after the operation.

The addition of lapatinib to capecitabine/oxaliplatin did not prolong overall survival among patients with previously untreated HER2-amplified gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma.

This comprehensive guide for oncologists covers the diagnosis, staging, treatment, and management of esophageal cancer.

Long-term results of the CROSS study have confirmed that neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy added to surgery should be the standard of care in esophageal or esophagogastric junction carcinoma.
A retrospective analysis found that high expression levels of two angiogenic factors were associated with poor prognosis in esophageal cancer.

The FDA approved ramucirumab (Cyramza) in combination with paclitaxel for treating patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.

Measuring expression of several microRNAs were significantly predictive of complete pathologic response to treatment in patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma.
The stage of esophageal adenocarcinomas after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is predictive of outcomes, rather than the stage determined prior to therapy.
New research has identified specific gene mutations that occur in precancerous esophageal lesions, a finding which was then put into use with a simple non-endoscopic test.

Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy did not improve resection rates or survival outcomes in patients with early-stage, locally advanced esophageal cancer.
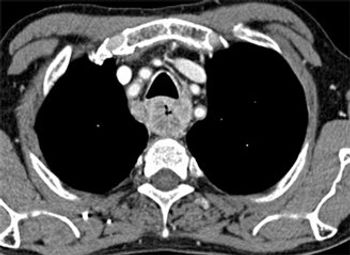
Preoperative staging of esophageal cancer with PET/MR is approximately as good as with endoscopic ultrasound, and may improve slightly over ultrasound and PET/CT scans, according to a new study.

Until anatomic staging and physiologic prediction models improve, induction therapy serves as a useful crutch that can mitigate the weaknesses in both of these important preoperative tasks.

Both esophageal cancer and stomach cancer are aggressive malignancies with contrasting risk factors, histologies, and molecular characteristics-yet for the most part comparable therapeutic approaches.

The purpose of this review is to update, present some of the new data on, and outline the controversies regarding neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy of esophagogastric junction and gastric adenocarcinoma.
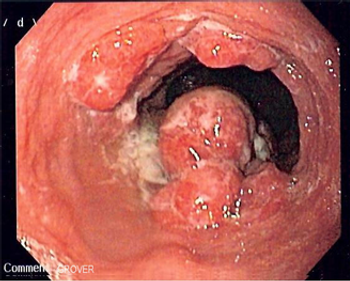
Adding ramucirumab to FOLFOX did not delay progression in patients with untreated advanced gastric or esophageal adenocarcinoma, according to trial results presented at the 2014 ASCO Annual Meeting.

Patients who exhibited certain clusters of symptoms after undergoing surgery for esophageal cancer were at an increased risk for mortality, according to the results of a prospective Swedish cohort study.
A meta-analysis by researchers in Australia shows that those infected with the human papillomavirus have a threefold higher risk of developing esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Adding the chemotherapy docetaxel to active symptom control in advanced esophagogastric adenocarcinoma improves survival of patients. These are the results of the phase III COUGAR-02 trial.