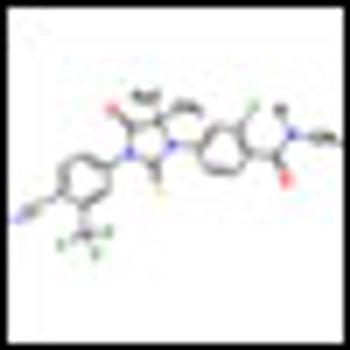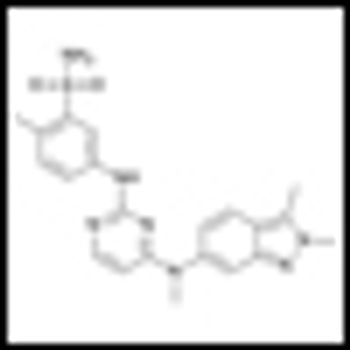
The antiangiogenic agent pazopanib demonstrated clinically meaningful activity in patients with refractory urothelial cancer in a phase II proof-of-concept study, identifying pazopanib as the first targeted compound to have clinically meaningful activity in patients with refractory urothelial cancer.