
FDA warns, however, about the possibility of TLS due to rapid tumor cell destruction.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


FDA warns, however, about the possibility of TLS due to rapid tumor cell destruction.

Until the superiority of novel agents is proven for all prognostically relevant subgroups of patients with CLL, we believe chemoimmunotherapy continues to have a role.

Elimination of chemotherapy from our combination regimens should be a shared goal among researchers that will move us a step closer to more patient-friendly and scientifically driven therapies for CLL.

In CAPTIVATE, first-line ibrutinib plus venetoclax yielded a high rate of undetectable residual disease, without new safety signals, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
This approach may lead to better understanding of risk-mitigation strategies, and perhaps better outcomes in patients with secondary AML.

Unconventional strategies and targeted therapeutics may be required to overcome the adverse risks associated with TP53-mutated AML.

T-ALL may be treatable by targeting signaling pathways affected by STIL-TAL1 fusion, according to a team from The Institute of Cancer Research, London, UK.

Achieving undetectable MRD after chemoimmunotherapy predicted longer progression-free and overall survival in CLL patients.

The combination of rituximab and the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax significantly lengthened PFS among CLL patients in the phase III MURANO trial.

In the DUO and DYNAMO trials, duvelisib improved clinical responses in patients with R/R CLL/SLL and FL, respectively.
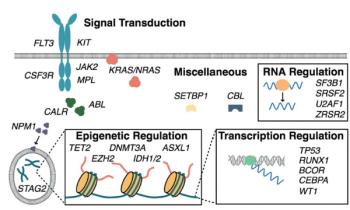
In this first part of our two-part review, we introduce mutation profiling as a relevant clinical tool for hematologists treating patients with myeloid malignancies.

A multicenter team of researchers reports that JAK3/STAT5 mutations are important in ALL and may be targetable.

Follicular large cleaved cell lymphoma is frequently misclassified, according to researchers.

At the NCCN Annual Conference, Dr. Bijal Shah of Tampa’s Moffitt Cancer Center highlighted ongoing challenges in administration of CAR T-cell therapy.

The US Food and Drug Administration has approved blinatumomab (Blincyto) for patients in remission from B-cell precursor ALL with MRD.

In a phase II study, voxtalisib, which targets all four class I PI3Ks, had efficacy in FL but limited clinical effect in MCL, DLBCL, and CLL/SLL.

The International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia has updated its 2008 consensus guidelines for design and conduct of CLL clinical trials.

Using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to remove CD7 from healthy T cells, researchers have found a way to use third party T cells for CAR-T therapy in T-cell hematologic malignancies.

Researchers have discovered that AML cells require high levels of cholesterol for survival, so the cholesterol pathway could represent a potential therapeutic option for the disease.

Umbralisib, a dual inhibitor of PI3Kδ and casein kinase-1Ɛ, was well tolerated and showed early signs of clinical activity in a phase I lymphoma study.

In this interview, Dr. Frederick Locke discusses the promise of CAR T-cell therapy for lymphomas, and how this gene therapy could offer hope for patients who don't respond to standard treatments.

CLL patients responded well to induction with the RCC regimen cladribine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab followed by maintenance rituximab.

Single-agent ibrutinib resulted in sustained efficacy and durable responses in treatment-naive or relapsed/refractory CLL or SLL, 5-year results show.

A single infusion of the anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy tisagenlecleucel produced durable remissions in pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic lymphoma.

Venetoclax had promising clinical activity in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia previously treated with idelalisib.