Expression of certain immune markers in tumor and surrounding cells can help predict probabilities of recurrence in patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma, according to new researcher.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Expression of certain immune markers in tumor and surrounding cells can help predict probabilities of recurrence in patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma, according to new researcher.

The clinical management of malignant mesothelioma may ultimately be transformed by the elucidation of novel biomarkers that can predict the evolution of disease and guide the development of targeted therapies. However, despite relevant advances, more basic research is urgently required to support the development of therapies applicable to the patients for whom surgical resection is not an option.

Significant advances have been made in our understanding of the factors affecting the prognosis of malignant mesothelioma, and a number of biomarkers appear promising. However, at present it may be more fruitful to better define and characterize clinical factors that are well recognized as significantly impacting patient survival.

Here we examine recent advances in the knowledge of this severe and heterogeneous malignancy, and we analyze the clinical significance of prognostic factors.

Initiating discussions about end-of-life care with patients with incurable cancers early in their disease was associated with a decrease in late-stage aggressive cancer treatments such as chemotherapy or acute care, and with an increase in the use of hospice care at the end of life.
In the first chemoprevention trial with a non-FDA-approved, oral, small-molecule-targeted agent, enzastaurin did not meet a primary endpoint but showed reasonable tolerability and some success in subgroup analyses.
Obese lung cancer patients undergoing lobectomy spend more time in the operating room than patients with lower body mass index, according to a new study. BMI was not associated with 30-day mortality or increased length of hospital stay.

Researchers have found a novel cellular mechanism that determines resistance to various targeted cancer therapies and several different cancers. The gene may be a key biomarker that could predict responses and provide better strategies to treat drug-resistant cancers.

Genotyping, sometimes referred to as molecular fingerprinting, must be distinguished from genetic testing. Genotyping is done to tumor samples and tests genes in the malignancy only.
This second article in our two-part series on targeted therapies in solid tumors covers the emergence of targeted therapies for the treatment of two common malignancies: lung cancer and breast cancer.
A phase II trial and a pooled analysis with another study found no benefit to adding carboplatin to pemetrexed versus pemetrexed alone in previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
A significant portion of patients with incurable lung cancer believe that palliative radiation therapy will cure the disease or at least help them live longer, according to a new study. Only about one-third of patients acknowledged that the treatment was not at all likely to cure their cancer.

The rarity and heterogeneity of these tumors limits research and obviates the possibility of large randomized clinical trials. Surgery remains the mainstay of treatment, but often radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy is required. The role of neoadjuvant therapy is evolving. In the not too distant future, new therapies tailored to the molecular profile of the tumor will be available.

Thymomas are uncommon neoplasms that have generated considerable controversy among pathologists. The following questions can be used to evaluate the evidence supporting current concepts about the pathology of thymomas and the clinical applicability of those concepts.
This review considers the status of the different histological classifications thus far presented for thymomas and offers an analysis of the association between histology and clinical behavior.

Stereotactic body radiation therapy is being compared to standard surgery in a phase III trial in high-risk operable patients with early-stage non–small-cell lung cancer.
A recent study profiling the genetic details of 178 lung squamous cell carcinomas yielded a clearer picture of the mutations that characterize the disease, and potentially revealed therapeutic targets.
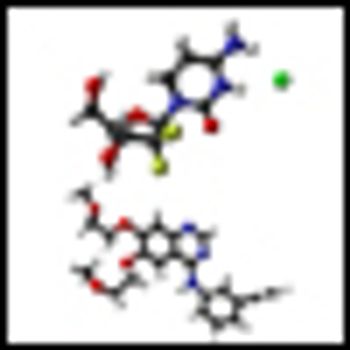
Maintenance therapy with both gemcitabine and erlotinib improved progression-free survival in patients with non–small-cell lung cancer who were initially treated with cisplatin-gemcitabine induction chemotherapy, according to a new phase III trial.
For the first time, two research groups have sequenced and analyzed the genomes of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and identified new gene mutatations that could drive the development of new therapies and the application of existing ones.
The presence of a mutation in the KRAS gene in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinomas was associated with significantly shorter overall survival than patients without the mutation, according to a new study.
A new phase III trial found that first-line erlotinib followed by chemotherapy at disease progression to be significantly inferior to the standard practice of first-line cisplatin-gemcitabine followed by erlotinib.

Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer death in the United States, with only 16% of patients living 5 years or more after they are diagnosed.
Chemotherapy is now employed in earlier-stage disease in neoadjuvant, adjuvant, and combined-modality treatments. The aim of this article is to review the current systemic treatments for NSCLC.

Lung cancer remains the number one cancer killer in both men and women, with more deaths attributable to lung cancer than breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers combined.[1]

In the pre–ALK-inhibitor era, patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC had significantly worse survival outcomes compared with ALK-wild type patients, according to a recent study.