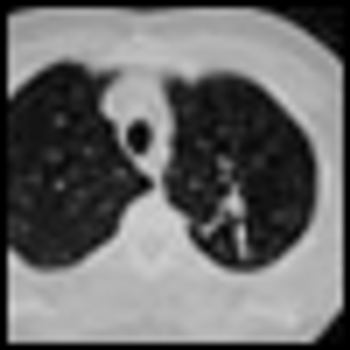
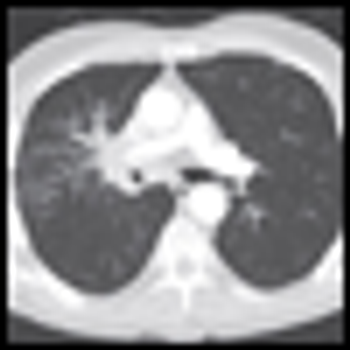
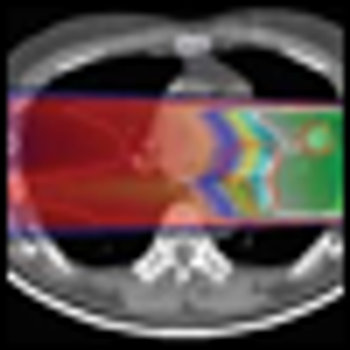
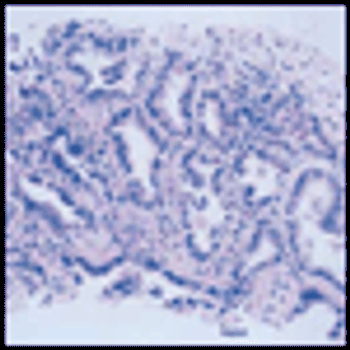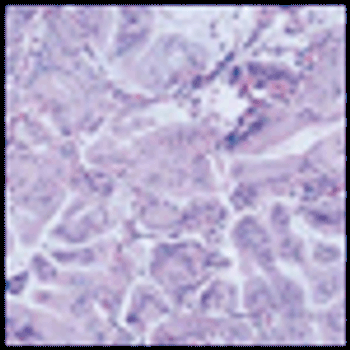
Calendar age and biological age do not always correspond. Pablo Picasso, source of the quote that begins the title of this commentary, lived a notoriously robust and active life through his later decades, dying in his nineties in the midst of a dinner party. In the oncology community, with the advent of targeted therapeutics and better supportive care, the disparity between the two is likely to be increasingly relevant to both research and practice. In this issue of ONCOLOGY, Chiappori et al review data supporting the idea that even in the context of standard cytotoxic chemotherapy, elderly patients with advanced NSCLC experience similar response rates and similar survival benefits to those seen in younger patients. They note that biases excluding elderly patients from clinical trials result in gaps in our knowledge of how to best treat older patients.