In patients with advanced NSCLC and without any mutation in the EGFR gene, docetaxel provides significantly improved progression-free survival compared to erlotinib, according to a phase III randomized trial.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


In patients with advanced NSCLC and without any mutation in the EGFR gene, docetaxel provides significantly improved progression-free survival compared to erlotinib, according to a phase III randomized trial.
Final results of the PARAMOUNT study in non-squamous non–small-cell lung cancer confirmed improved survival with continuation pemetrexed maintenance therapy.

The idea of adding the targeted EGFR inhibitor cetuximab to standard chemotherapy took a hit, as results from the SELECT phase III trial showed no improvement in efficacy when cetuximab was combined with pemetrexed in patients with recurrent or progressive non–small-cell lung cancer.
Patients with EGFR mutation-positive lung cancer had improved progression-free survival and better quality of life with new drug afatinib than with standard chemotherapy, according to results from a large phase III trial.
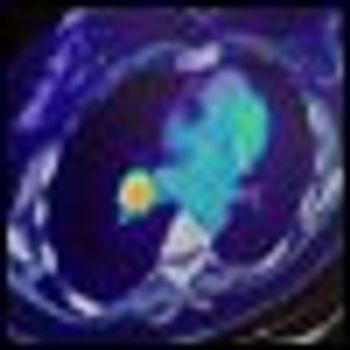
The use of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET), for diagnosing lung cancer may have to be rethought. According to an analysis of data from a national prospective trial, FDG-PET has substantially lower sensitivity and specificity than in previously published studies.

The debate over screening for lung cancer continues. While there have been many advances in treatment for late-stage disease, screening and prevention are likely the most cost effective and best approaches to preventing lung cancer deaths.

Treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that is anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive as detected by an FDA-approved test.

Maintenance therapy with bevacizumab following combination therapy with bevacizumab, pemetrexed, and carboplatin could be an effective treatment for patients with advanced, nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to a new study.
The American Lung Association recently released new guidelines for lung cancer screening, recommending low-dose computed tomography screening in high-risk smokers.

Body mass index appears to be inversely associated with the risk for lung cancer, even after smoking status is carefully taken into account. A new prospective study found this association was restricted to current and former smokers and was actually stronger after adjustments for smoking were made.
Scotland will soon begin a large prospective trial of early screening for lung cancer in high-risk patients using a simple blood test. The test, called EarlyCDT-Lung, has been in use and trials in the United States for more than two years.
Addition of a Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) inhibitor to therapies that target commonly altered oncogenes such as KRAS or EGFR could improve clinical outcomes for patients with non–small cell-lung cancer.

Using detailed patient data and mathematical modeling programs, a US–international team of investigators has concluded that in the US, public health efforts beginning in the 1950s prevented nearly 800,000 deaths from lung cancer between 1975 and 2000.

In this review, the authors discuss past attempts at lung cancer screening, the results of the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial, and innovative tests for lung cancer screening currently being evaluated.

Tanner et al provide a concise review of lung cancer screening, including discussion of past failed attempts, the success of the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST), and promising new avenues for improving on the NLST results.

Screening is always an issue that generates a great deal of emotion, as recently seen with the controversies surrounding mammography and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing.
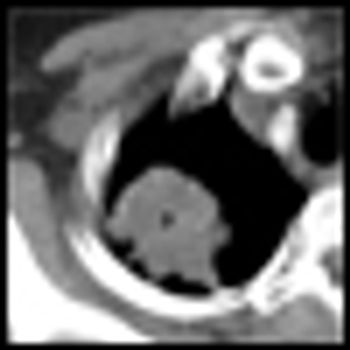
A new finding suggests that inhibiting the cytokine interleukin-17A, produced by inflammatory cells of the immune system, may be a novel approach in the treatment of lung tumors.
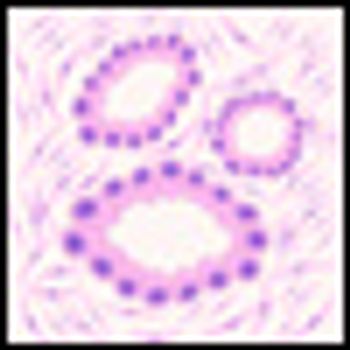
A study has identified a gene fusion from a never-smoker lung cancer patient that may act as a driver in a subset of lung cancer cases. The results suggest that the newly identified fusion is not that rare and that the mutation exists in primary lung adenocarcinomas.

The past year in oncology was highlighted by the continuation of breakthroughs in targeted therapies-with new treatments receiving US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), lymphoma, and melanoma.
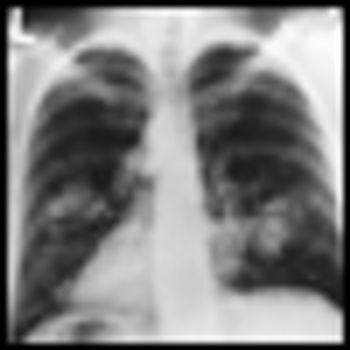
A trial of 154,901 participants between the ages of 55 and 74 sought to address whether chest radiographs as lung cancer screenings affect lung cancer incidence and mortality rates from lung cancer.

of a prospective biomarker analysis for the phase III SATURN trial in NSCLC patients taking erlotinib as maintenance therapy now show that those with activating EGFR mutations had extended progression-free survival compared to patients with KRAS mutations.
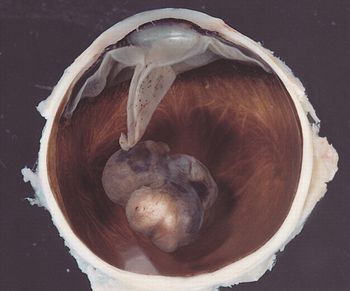
Researchers have discovered that individuals carrying a mutation in the BAP1 gene are at greater risk of developing mesothelioma and uveal melanoma.
Scientists at Jennerex, Inc. in San Francisco, and collaborators from University of Pennsylvania and the University of Ottawa in Canada have just engineered a poxvirus, JX-594, to selectively replicate in tumor cells that have an activated EGFR/ Ras pathway, but not in normal tissue.

The FDA has approved crizotinib (Xalkori) for the treatment of late-stage non–small-cell lung cancer patients who express the abnormal anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene.

Dr. Ramaswamy Govindan, Washington U at St. Louis, discusses patient screening, new research in targeted therapies, as well as the continued role of traditional chemotherapy in lung cancer.