
Thoracic radiotherapy along with prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) significantly prolonged progression-free and overall survival in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer, according to results of a new study presented at ASCO.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!


Thoracic radiotherapy along with prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) significantly prolonged progression-free and overall survival in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer, according to results of a new study presented at ASCO.

The addition of the MET-targeting antibody onartuzumab to erlotinib added no benefit, and may have been detrimental, to patients with MET-amplified stage IIIb/IV metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer, according to a new phase III trial.

As part of our coverage of the 2014 ASCO Annual Meeting, we discuss chemotherapy's curative role in treating lung cancer.

To ultimately find what we are actually looking for, the invasive malignant nodule in a haystack of benign lesions, new strategies and qualitative and quantitative tools are needed to propel noninvasive evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules into the 21st century.

The number of lesions detected with low-dose CT, only some of which are early cancers, is so great that algorithms are being developed for more efficient evaluation and management of solitary pulmonary nodules. This article will discuss current tools, approaches, and concerns regarding patient care in this setting.

The simple answer, according to some, is that lung cancer screening’s time has come. However, in my opinion, the answer is not that simple.

Implementation of a national lung cancer screening program using low-dose CT will identify almost 55,000 additional lung cancer cases over 5 years, but will add $9.3 billion to Medicare expenditures.
A novel agent known as AZD9291 showed promising results in a phase I dose escalation trial among non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients whose disease progresses after treatment with EGFR-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Modafinil, which is commonly prescribed to manage fatigue in cancer patients, had no effect on fatigue in a new study of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.

Earlier today the FDA granted accelerated approval to ceritinib (Zykadia) for the treatment of patients with metastatic ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

As part of our coverage of the AACR Annual Meeting, we discuss combination therapies and new research in the treatment of lung cancer.
New research has shown that a new assay for measuring circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) could detect essentially all stage II-IV non-small-cell lung cancers (NSCLC).

A combination of amrubicin and cisplatin was inferior to irinotecan and cisplatin in chemotherapy-naïve patients with extensive disease small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) in a phase III trial conducted in Japan.

GlaxoSmithKline has stopped a phase III trial of a novel lung cancer immunotherapeutic agent, after determining that it may not be possible to identify which genetic subgroups may benefit from the treatment.
The new ALK inhibitor certinib showed strong antitumor activity in a phase I expansion study of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

In a phase I trial, non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with tumors that expressed PD-L1 had significantly better outcomes with MK-3475 therapy compared with patients with PD-L1–negative tumors.

Surgery continues to advance with the availability of new technology, knowledge and skills gained through experience, and collaboration between specialties. Some tumors that were unresectable in years past are now resectable. Other tumors that we currently consider beyond our ability to remove may be conquered in the near future.

In summary, central lung cancers, when appropriately staged, are optimally treated by surgical resection. Initial evaluation is best done by a multidisciplinary team, involving a trained thoracic surgeon.

We now have more tools than ever in the fight against tobacco-related death and disability, but unfortunately, there is not equal access to resources for smoking cessation, early lung cancer diagnosis, and treatment.
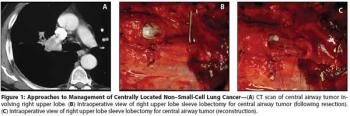
Treatment optimization for centrally located lung cancers requires special considerations for determining resectability and patient selection.

In this interview we discuss the oncogenes driving the development of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, a type of non-small-cell lung cancer.

A breath test that looks for carbonyl volatile organic compounds could help distinguish between benign and malignant nodules, and be used as an adjunct to CT scans in lung cancer diagnosis.

A study in mice showed that antioxidant supplementation increases tumor progression and reduced survival in Braf- and Kras-induced lung cancer.

The use of a microRNA signature classifier assay was found to have high predictive, diagnostic, and prognostic value in a lung cancer screening trial in Italy. Adding the plasma microRNA test to low-dose CT screening reduced false positive rates.

In this interview we discuss lung cancer prevention, the recent low-dose CT screening recommendations from the USPSTF, hurdles in preventing the disease, and more.