
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer that has become resistant to docetaxel chemotherapy represents one of the greatest clinical challenges in the management of this disease.

Your AI-Trained Oncology Knowledge Connection!



Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer that has become resistant to docetaxel chemotherapy represents one of the greatest clinical challenges in the management of this disease.

Immediate treatment with androgen-deprivation therapy for men with asymptomatic non-curable prostate cancer did not have major effects on quality of life compared with delayed use, according to a phase III trial.

Two different doses of cabazitaxel failed to show superiority with regard to overall survival over docetaxel as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
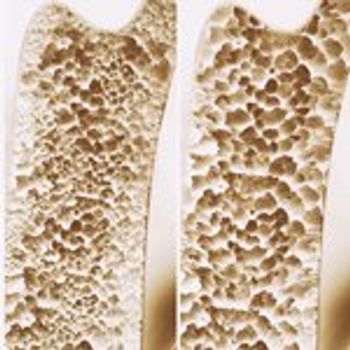
Men with non-metastatic prostate cancer who receive androgen deprivation therapy risk loss of bone mineral density and fractures, but both bisphosphonates and denosumab can improve their bone health.

In this interview we discuss the ASCO provisional clinical opinion on second-line hormonal therapy for chemotherapy-naive castration-resistant prostate cancer.

Taller men are at increased risk for high-grade prostate cancer and prostate cancer death, according to a large registry study. Greater adiposity is also associated with higher-grade tumors and mortality.

Long-term follow-up found no significant differences in all-cause or disease-related mortality in men with early prostate cancer randomized to either radical prostatectomy or to observation. Surgery led to more adverse events, but less treatment for disease progression.
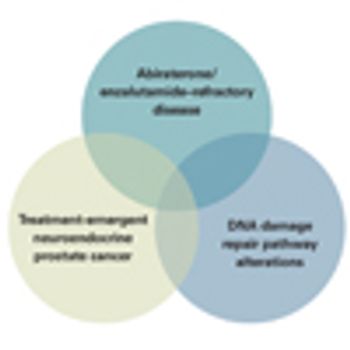
In this article, we look at both metastatic hormone-sensitive and metastatic castration-resistant disease, and we highlight several of the emerging categories of advanced prostate cancer that have direct implications for patient management.

Germline genetic testing guidelines and Gleason scores do not predict which patients with prostate cancer will test positive for pathogenic gene variants.

A new study found that patients with mCRPC had higher PSA response with enzalutamide vs abiraterone, but no difference in time to progression, and reported worse outcomes in those with quantifiable ctDNA.

Androgen deprivation therapy can be safely reduced from 36 months to 18 months in high-risk prostate cancer, according to results of a phase III trial.

Continued enzalutamide with abiraterone failed to improve PFS in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer who progressed on enzalutamide alone.

Tumor expression of the oncogene ERG might predict patient benefit from adding docetaxel to androgen deprivation therapy, according to analyses of two phase III clinical trials.

A molecular signature for aggressive-variant prostate carcinoma can predict which men with castration-resistant prostate cancer will benefit from cabazitaxel with or without carboplatin.

Abiraterone at the start of ADT for men with metastatic prostate cancer significantly improved overall survival and failure-free survival, with manageable toxicity.

Combined therapy with abiraterone acetate/prednisone plus ADT significantly improved overall survival and radiographic progression-free survival among men with metastatic hormone-naive prostate cancer.

In this interview ahead of ASCO 2017 we discuss the physical and cognitive effects of androgen deprivation therapy in older men treated for prostate cancer.

Molecular subtyping of prostate cancer into three categories-luminal A, luminal B, and basal-identifies differences in prognosis and response to treatment.
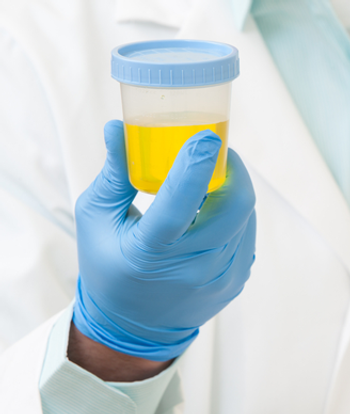
Urinary testing for PCA3 and TMPRSS2:ERG (T2:ERG) RNA can help avoid unnecessary biopsies while maintaining ability to detect aggressive prostate cancer.

A prospective phase III validation study found that AZGP1 has significant prognostic utility as a biomarker in localized prostate cancer.

A study may be able to identify which men with aggressive prostate cancer will benefit from androgen deprivation therapy.
In this review of active surveillance for favorable-risk prostate cancer, we will discuss the rationality of this approach, the biological evidence for employing active surveillance in Gleason pattern 3 and 4 prostate cancer, patient selection for active surveillance, clinical trial data on active surveillance, and the role of prostate cancer biomarkers and imaging studies for clinical decision making in patients with low-risk disease.

Two new studies presented at the Annual Scientific Meeting of the American Urological Association offer an improved understanding of some genetic underpinnings of prostate cancer.

Active surveillance can yield excellent results in carefully selected younger men with prostate cancer, according to a new study presented at the AUA Annual Meeting.

In this interview we discuss a study that looked at the effect of an 8-week exercise intervention on treatment side effects for patients with prostate cancer.